Abstract
Binary “YES-NO” notions of process compliance are not very helpful to managers for assessing the operational performance of their company because a large number of cases fall in the grey area of partial compliance. Hence, it is necessary to have ways to quantify partial compliance in terms of metrics and be able to classify actual cases by assigning a numeric value of compliance to them. In this paper, we formulate an evaluation framework to quantify the level of compliance of business processes across different levels of abstraction (such as task, trace and process level) and across multiple dimensions of each task (such as temporal, monetary, role-, data-, and quality-related) to provide managers more useful information about their operations and to help them improve their decision making processes. Our approach can also add social value by making social services provided by local, state and federal governments more flexible and improving the lives of citizens.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
From now on, we will use
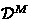 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  to denote the monetary, time, role, data, and quality dimensions of a task, respectively.
to denote the monetary, time, role, data, and quality dimensions of a task, respectively. - 2.
ProM Tools: http://www.promtools.org/doku.php.
References
Bistarelli, S.: Semirings for Soft Constraint Solving and Programming. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-25925-1
Gerber, A.S., Green, D.P.: Field Experiments: Design, Analysis, and Interpretation. W. W. Norton & Company (2012)
Governatori, G.: Business Process Compliance: An Abstract Normative Framework. IT Inf. Technol. 55(6), 231–238 (2013)
Hashmi, M.: A methodology for extracting legal norms from regulatory documents. In: 2015 IEEE 19th International Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Workshop, Adelaide, SA, Australia, pp. 41–50. EDOCW 2015, IEEE, September 2015
Hashmi, M., Governatori, G., Wynn, M.T.: Normative requirements for regulatory compliance: an abstract formal framework. Inf. Syst. Front. 18(3), 429–455 (2016)
Huchard, M., Hacene, M.R., Roume, C., Valtchev, P.: Relational concept discovery in structured datasets. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 49(1), 39–76 (2007)
Jin, H., Rubin, D.B.: Principal stratification for causal inference with extended partial compliance. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 103(481), 101–111 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1198/016214507000000347
Kumar, A., Barton, R.R.: Controlled violation of temporal process constraints - models, algorithms and results. Inf. Syst. 64, 410–424 (2017)
Lu, R., Sadiq, S., Governatori, G.: Measurement of compliance distance in business processes. Inf. Syst. Manage. 25(4), 344–355 (2008)
Ly, L.T., Rinderle-Ma, S., Göser, K., Dadam, P.: On enabling integrated process compliance with semantic constraints in process management systems. Inf. Syst. Front. 14(2), 195–219 (2012)
Maggi, F.M., Montali, M., Westergaard, M., van der Aalst, W.M.P.: Monitoring business constraints with linear temporal logic: an approach based on colored automata. In: Rinderle-Ma, S., Toumani, F., Wolf, K. (eds.) BPM 2011. LNCS, vol. 6896, pp. 132–147. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23059-2_13
Morrison, E., Ghose, A., Koliadis, G.: Dealing with imprecise compliance requirements. In: Proceedings of the 13th Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Conference Workshops, Auckland, New Zealand, pp. 6–14. IEEE, September 2009
Sadiq, S., Governatori, G., Namiri, K.: Modeling control objectives for business process compliance. In: Alonso, G., Dadam, P., Rosemann, M. (eds.) BPM 2007. LNCS, vol. 4714, pp. 149–164. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75183-0_12
Schumm, D., Turetken, O., Kokash, N., Elgammal, A., Leymann, F., van den Heuvel, W.-J.: Business process compliance through reusable units of compliant processes. In: Daniel, F., Facca, F.M. (eds.) ICWE 2010. LNCS, vol. 6385, pp. 325–337. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16985-4_29
Shamsaei, A.: Indicator-based policy compliance of business processes. In: Boldyreff, C., Islam, S., Leonard, M., Thalheim, B. (eds.) Proceedings of the CAiSE Doctoral Consortium 2011, London, UK, pp. 3–14, June 2011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lam, HP., Hashmi, M., Kumar, A. (2021). Towards a Formal Framework for Partial Compliance of Business Processes. In: Rodríguez-Doncel, V., Palmirani, M., Araszkiewicz, M., Casanovas, P., Pagallo, U., Sartor, G. (eds) AI Approaches to the Complexity of Legal Systems XI-XII. AICOL AICOL XAILA 2020 2018 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13048. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89811-3_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89811-3_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-89810-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-89811-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)





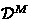 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  to denote the monetary, time, role, data, and quality dimensions of a task, respectively.
to denote the monetary, time, role, data, and quality dimensions of a task, respectively.