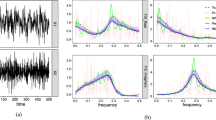
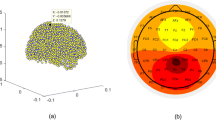
Abstract
Model estimation is an important issue in signal processing since it enables to characterize the signal and to obtain some parameters providing information about its shape. An example of a model widely used in various fields of science is the sum of exponentially damped sinusoids. In this work, a new method for parameters estimation of such a model is proposed. This method uses nonlinear least squares together with Fourier transform to estimate parameters of the sum of damped sinusoids. For model order selection, a bootstrap method is utilized. First, the presented method is verified on simulated signals. The efficacy of model order selection is assessed for signals with a different set value of signal-to-noise (SNR) ratio. It is shown that for the models with orders from 2 to 7, the order was estimated correctly in all trials for SNR greater than 20 dB. If a proper model order is selected, the set values of signal parameters are included in the confidence intervals for parameters values, determined by the nonlinear least squares method. Afterward, the described method is used for modeling the event-related potential in magnetoencephalography (MEG) signal. The method gives good fitting results with \(\text {R}^{2}\) values greater than 0.9, showing its potential in MEG signals modeling and the assessment of brain activity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duda, K., Magalas, L.B., Majewski, M., Zieliński, T.P.: DFT-based estimation of damped oscillation parameters in low-frequency mechanical spectroscopy. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 60, 3608–3618 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2011.2113124
Umesh, S., Tufts, D.W.: Estimation of parameters of exponentially damped sinusoids using fast maximum likelihood estimation with application to NMR spectroscopy data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44, 2245–2259 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.536681
Demiralp, T., Ademoglu, A., Istefanopulos, Y., Gülçür, H.Ö.: Analysis of event-related potentials (ERP) by damped sinusoids. Biol. Cybern. 78, 487–493 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004220050452
Franaszczuk, P.J., Blinowska, K.J.: Linear model of brain electrical activity-EEG as a superposition of damped oscillatory modes. Biol. Cybern. 53, 19–25 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00355687
Lovisolo, L., da Silva, E.A.B., Rodrigues, M.A.M., Diniz, P.S.R.: Efficient coherent adaptive representations of monitored electric signals in power systems using damped sinusoids. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53, 3831–3846 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2005.855400
Hermus, K., Verhelst, W., Lemmerling, P., et al.: Perceptual audio modeling with exponentially damped sinusoids. Signal Process. 85, 163–176 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2004.09.010
Nieuwenhuijse, J., Heusens, R., Deprettere, E.F.: Robust exponential modeling of audio signals. In: ICASSP, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing - Proceedings, pp. 3581–3584. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. (1998)
Gillard, J.W., Kvasov, D.E.: Lipschitz optimization methods for fitting a sum of damped sinusoids to a series of observations. Stat Interface 10, 59–70 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4310/SII.2017.v10.n1.a6
Kumaresan, R., Tufts, D.W.: Estimating the parameters of exponentially damped sinusoids and pole-zero modeling in noise. IEEE Trans. Acoust. 30, 833–840 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1109/TASSP.1982.1163974
Parthasarathy, S., Tufts, D.W.: Maximum-likelihood estimation of parameters of exponentially damped sinusoids. Proc. IEEE 73, 1528–1530 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1985.13328
Gopalakrishnan, R., Machado, A.G., Burgess, R.C., Mosher, J.C.: The use of contact heat evoked potential stimulator (CHEPS) in magnetoencephalography for pain research. J. Neurosci. Methods 220, 55–63 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.08.015
Savers, B., Beagley, H.A., Henshall, W.R.: The mechanism of auditory evoked EEG responses. Nature 247, 481–483 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/247481a0
Basar, E.: Toward a physical approach to integrative physiology. I. Brain dynamics and physical causality. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 245, R513–R533 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1983.245.4.r510
Quinn, B.G.: On fitting exponentially damped sinusoids. In: IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing Proceedings, pp. 201–204 (2014)
Zoubir, A.M., Iskander, D.R.: Bootstrap Techniques for Signal Processing. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Sieluzycki, C., König, R., Matysiak, A., et al.: Single-trial evoked brain responses modeled by multivariate matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56, 74–82 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2008.2002151
Papadopoulos, C.K., Nikias, C.L.: Parameter estimation of exponentially damped sinusoids using higher order statistics. IEEE Trans. Acoust. 38, 1424–1436 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1109/29.57577
Chan, F.K.W., So, H.C., Sun, W.: Subspace approach for two-dimensional parameter estimation of multiple damped sinusoids. Signal Process. 92, 2172–2179 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.02.003
Acknowledgement
The author thanks D. Robert Iskander for his support and supervision at all stages of this work, and Cezary Sieluzycki for his help with MEG signals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Niemczyk, M. (2022). Bootstrap Model Selection for Estimating the Sum of Exponentially Damped Sinusoids. In: Piaseczna, N., Gorczowska, M., Łach, A. (eds) Innovations and Developments of Technologies in Medicine, Biology and Healthcare. EMBS ICS 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1360. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88976-0_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88976-0_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-88975-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-88976-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)