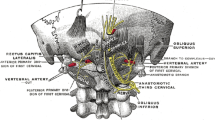
Abstract
Occipital neuralgia is a condition that is caused by irritation or pressure on the occipital nerves. The pain can be sharp, jabbing, or shock like and is felt in the back of the head and neck. There are various treatments including occipital nerve blocks. This chapter will provide a brief overview of the condition, treatment options, as well as a description of the occipital nerve block technique.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/all-disorders/occipital-neuralgia-information-page.
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia. 2013;33(9):629–808.
Palamar D, Uluduz D, Saip S, Erden G, Unalan H, Akarirmak U. Ultrasound-guided greater occipital nerve block: an efficient technique in chronic refractory migraine without aura? Pain Physician. 2015;18(2):153–62.
Pingree MJ, Sole JS, O’Brien TG, Eldrige JS, Moeschler SM. Clinical efficacy of an ultrasound-guided greater occipital nerve block at the level of C2. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2017;42(1):99–104.
Further Reading
Choi I, Jeon SR. Neuralgias of the head: occipital neuralgia. J Korean Med Sci. 2016;31(4):479–88.
Greengrass RA, Narouze S, Bendtsen TF, Hadzic A. Cervical plexus and greater occipital nerve blocks: controversies and technique update. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019;44(6):623–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/rapm-2018-100261.
Greher M, Moriggl B, Curatolo M, Kirchmair L, Eichenberger U. Sonographic visualization and ultrasound-guided blockade of the greater occipital nerve: a comparison of two selective techniques confirmed by anatomical dissection. Br J Anaesth. 2010;104(5):637–42.
Inan LE, Inan N, Unal-Artık HA, Atac C, Babaoglu G. Greater occipital nerve block in migraine prophylaxis: narrative review. Cephalalgia. 2019;39(7):908–20. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102418821669. Epub 2019 Jan 6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Habibi, B.A., Kim, C. (2022). Craniofacial Pain: Occipital Neuralgia and Nerve Block. In: Banik, R.K. (eds) Anesthesiology In-Training Exam Review. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87266-3_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87266-3_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87265-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87266-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)