Abstract
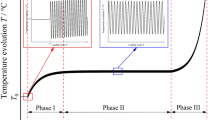
Fatigue damage is associated with heat release leading to material self-heating. The present study deals with the measurement of mechanical dissipation from temperature measurements by infrared (IR) thermography during a fatigue test with varying stress amplitude. The experiment was performed in two steps on an additively manufactured steel specimen. First, specific acquisition conditions of the thermal response were used to remove the cyclic fluctuation due to thermoelastic coupling. Second, heat source reconstruction was applied to evaluate the calorific origin of the self-heating during the test. A simplified version of the heat diffusion equation was used assuming a uniform distribution of mechanical dissipation within the specimen. The relationship between stress amplitude and mechanical dissipation was identified without the need for a steady thermal regime at constant load amplitude.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stromeyer, C.E.: The determination of fatigue limits under alternating stress conditions. Proc Royal Soc London. 90, 411–425 (1914)
Luong, M.P.: Infrared thermographic scanning of fatigue in metals. Nucl. Eng. Des. 158, 363–376 (1995)
Luong, M.P.: Fatigue limit evaluation of metals using an infrared thermographic technique. Mech. Mater. 28, 155–163 (1998)
Geraci A.L., La Rosa G., Risitano A., Grech M.: Determination of the fatigue limit of an austempered ductile iron using thermal infrared imagery, In: Fedosov E.A. (ed.) Proceedings of SPIE. Digital Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing '95, Moscow, Russia, June 25–30, 1995, Vol. 2646, pp. 306–317 (1995)
La Rosa, G., Risitano, A.: Thermographic methodology for rapid determination of the fatigue limit of materials and mechanical components. Int. J. Fatigue. 22, 65–73 (2000)
Huang, J., Pastor, M.L., Garnier, C., Gong, X.: Rapid evaluation of fatigue limit on thermographic data analysis. Int. J. Fatigue. 104, 293–301 (2017)
de Finis, R., Palumbo, D., da Silva, M.M., Galietti, U.: Is the temperature plateau of a self-heating test a robust parameter to investigate the fatigue limit of steels with thermography? Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 41, 917–934 (2018)
Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Hild, F., Cugy, P., Galtier, A.: Identification of the scatter in high cycle fatigue from temperature measurements. Comptes Rendus Mécanique. 332, 795–801 (2004)
Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Cugy, P., Galtier, A., Hild, F.: A probabilistic two-scale model for high cycle fatigue life predictions. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 28, 279–288 (2005)
Munier, R., Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Weber, B.: Determination of high cycle fatigue properties of a wide range of steel sheet grades from self-heating measurements. Int. J. Fatigue. 63, 46–61 (2014)
Munier, R., Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Weber, B.: Identification of the micro-plasticity mechanisms at the origin of self-heating under cyclic loading with low stress amplitude. Int. J. Fatigue. 103, 122–135 (2017)
De Finis, R., Palumbo, D., Ancona, F., Galietti, U.: Fatigue limit evaluation of various martensitic stainless steels with new robust thermographic data analysis. Int. J. Fatigue. 74, 88–96 (2015)
Cao, Y.F., Moumni, Z., Zhu, J.H., Zhang, Y.H., You, Y.J., Zhang, W.H.: Comparative investigation of the fatigue limit of additive-manufactured and rolled 316 steel based on self-heating approach. Eng. Fract. Mech. 223, 106746 (2020)
Shiozawa, D., Inagawa, T., Washio, T., Sakagami, T.: Fatigue limit estimation of stainless steels with new dissipated energy data analysis. Procedia Struct Integr. 2, 2091–2096 (2016)
Stankovicova, Z., Dekys, V., Uhricik, M., Novak, P., Strnadel, B.: Fatigue limit estimation using IR camera. In: Vasko, M., et al. (eds.) XXII Slovak-Polish Scientific Conference on Machine Modelling and Simulations 2017 (MMS 2017), p. 05021. EDP Sciences, Les Ulis (2018). https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201815705021
Guo, S.F., Liu, X.S., Zhang, H.X., Yan, Z.F., Zhang, Z.D., Fang, H.Y.: Thermographic study of AZ31B magnesium alloy under cyclic loading: temperature evolution analysis and fatigue limit estimation. Materials. 13, 5209 (2020)
Guo, S.F., Liu, X.S., Zhang, H.X., Yan, Z.F., Fang, H.Y.: Fatigue limit evaluation of AZ31B magnesium alloy based on temperature distribution analysis. Metals. 10, 1331 (2020)
Akai A., Shiozawa D., Sakagami T., Fatigue limit estimation of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V with infrared thermography, In: Bison P., Burleigh D. (eds) Proceedings of SPIE. Thermosense: Thermal Infrared Applications XXXIX, Anaheim, CA, April 10–13, 2017, Vol. 10214, 102141J (2017)
De Finis, R., Palumbo, D., Galietti, U.: Fatigue damage analysis of composite materials using thermography-based techniques. Procedia Struct Integr. 18, 781–791 (2019)
Palumbo, D., De Finis, R., Demelio, P.G., Galietti, U.: A new rapid thermographic method to assess the fatigue limit in GFRP composites. Compos Part B-Eng. 103, 60–67 (2016)
Douellou, C., Balandraud, X., Duc, E., Verquin, B., Lefebvre, F., Sar, F.: Rapid characterization of the fatigue limit of additive-manufactured maraging steels using infrared measurements. Addit. Manuf. 35, 101310 (2020)
Douellou, C., Balandraud, X., Duc, E.: Fatigue characterization of 3D-printed maraging steel by infrared thermography. In: Kramer, S., et al. (eds.) Mechanics of Additive and Advanced Manufacturing, Vol 8. Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series, pp. 5–9. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95083-9_2
Douellou, C., Balandraud, X., Duc, E., Verquin, B., Lefebvre, F., Sar, F.: Fast fatigue characterization by infrared thermography for additive manufacturing. Procedia Struct Integr. 19, 90–100 (2019)
Chrysochoos, A., Peyroux, R.: Experimental analysis and numerical simulation of thermomechanical couplings in solid materials. Revue Générale de Thermique. 37, 582–606 (1998)
Boulanger, T., Chrysochoos, A., Mabru, C., Galtier, A.: Calorimetric analysis of dissipative and thermoelastic effects associated with the fatigue behavior of steels. Int. J. Fatigue. 26, 221–229 (2004)
Chrysochoos, A., Louche, H.: An infrared image processing to analyse the calorific effects accompanying strain localization. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 38, 1759–1788 (2000)
Jongchansitto, P., Douellou, C., Preechawuttipong, I., Balandraud, X.: Comparison between 0D and 1D approaches for mechanical dissipation measurement during fatigue tests. Strain. 55, e12307 (2019)
Delpueyo, D., Balandraud, X., Grediac, M., Stanciu, S., Cimpoesu, N.: A specific device for enhanced measurement of mechanical dissipation in specimens subjected to long-term tensile tests in fatigue. Strain. 54, e12252 (2018)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Région Auvergne-Rhônes-Alpes for the support in this study (Project: IRICE Fabrication additive, number: 18 009727 01-59941, operation: P088O005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Society for Experimental Mechanics, Inc.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Douellou, C., Gravier, A., Balandraud, X., Duc, E. (2022). Heat Source Reconstruction Applied to Fatigue Characterization Under Varying Stress Amplitude. In: Kramer, S.L., Tighe, R., Lin, MT., Furlong, C., Hwang, CH. (eds) Thermomechanics & Infrared Imaging, Inverse Problem Methodologies, Mechanics of Additive & Advanced Manufactured Materials, and Advancements in Optical Methods & Digital Image Correlation, Volume 4. Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86745-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86745-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-86744-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-86745-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)