Abstract
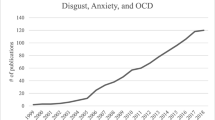
Over the previous two to three decades there has been accumulating evidence that the disease-avoidance emotion of disgust is closely associated with and regularly experienced in a number of different psychopathologies and mental health problems. Some of the symptoms of these mental health problems have obvious links to disgust and the kinds of events and stimuli that elicit the emotion (e.g., contamination fears in obsessive compulsive disorder [OCD]). Some other conditions appear to have an indirect link with disgust through perceived harbingers of disease, such as small animal phobias. While still other psychopathologies have characteristics similar to the avoidance responses typical of disgust, such as fear of oral incorporation.
The growing list of disgust-related psychopathologies raises a number of theoretical questions about how the disgust emotion has become associated with these conditions, and what role, if any, disgust plays in the development and maintenance of these psychopathologies. Such questions are not just of theoretical interest, they may also provide vital information about the kinds of effective interventions we might develop to alleviate these psychopathologies.
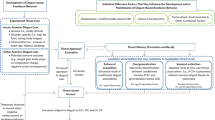
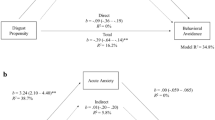
In this chapter, I will describe a number of putative mechanisms through which the emotion of disgust might influence the symptoms of mental health problems and examine how these putative mechanisms might fit the existing evidence on disgust-relevant psychopathologies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Hamid, S., Denman, C., & Dudas, R. B. (2014). Self-relevant disgust and self-harm urges in patients with borderline personality disorder and depression: a pilot study with a newly designed psychological challenge. PLoS One, 9(6), e99696.
Al-Shawaf, Lewis, & Buss (2017) Sex differences in disgust: Why are women more easily disgusted than men? Emotion Review, 10, 149-160.
Armstrong, T., McClenahan, L., Kittle, J., & Olatunji, B. O. (2014). Don’t look now! Oculomotor avoidance as a conditioned disgust response. Emotion, 14(1), 95–104.
Blacker, K.-A., & LoBue, V. (2016). Behavioral avoidance of contagion in childhood. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 143, 162–170.
Bradley, M. M., Costa, V. D., & Lang, P. J. (2015). Selective looking at natural scenes: Hedonic content and gender. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 98, 54–58.
Britton, G. I., & Davey, G. C. L. (2014). Interrelationships between negative mood and clinical constructs: A motivational systems approach. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 393.
Brown, S. D., & Harris, G. (2012). Disliked food acting as a contaminant during infancy. A disgust based motivation for rejection. Appetite, 58(2), 535–538.
Cisler, J. M., Olatunji B. O., & Lohr, J. M. (2009a). Disgust sensitivity and emotion regulation potentiate the effect of disgust propensity on spider fear, blood-injection-injury fear, and contamination fear. Journal of Behaviour Therapy & Experimental Psychiatry, 40, 219-229.
Cisler, J. M., Olatunji, B. O., Lohr, J. M., & Williams, N. L. (2009b). Attentional bias differences between fear and disgust: implications for the role of disgust in disgust-related anxiety disorders. Cognition and Emotion, 23(4), 675–687.
Clarke, A., Simpson, J., & Varese, F. (2018). A systematic review of the clinical utility of the concept of self-disgust. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 26, 110-134.
Curtis, V., & de Barra, M. (2018). The structure and function of pathogen disgust. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences, 373, 20170208.
Davey, G. C. L. (1994a). Self-reported fears to common indigenous animals in a UK population: the role of disgust sensitivity. British Journal of Psychology, 85, 541-554.
Davey, G. C. L. (1994b). Disgust. In V.S. Ramachandran (Ed.), Encyclopedia of human behavior. San Diego Press.
Davey, G. C. L. (2011). Disgust: the disease-avoidance emotion and its dysfunctions. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 366(1583), 3453-3465.
Davey, G. C. L. (2018). The anxiety epidemic. Little Brown Books.
Davey, G. C. L., & Bond, N. (2006). Using controlled comparisons in disgust psychopathology research: The case of disgust, hypochondriasis and health anxiety. Journal of Behavior Therapy & Experimental Psychiatry, 37, 4-15.
Davey, G. C. L., Buckland, G., Tantow, B., & Dallos, R. (1998). Disgust and eating disorders. European Eating Disorders Review, 6, 201-211.
Davey, G. C. L., Bickerstaffe, S., & MacDonald, B.A. (2006). Experienced disgust causes a negative interpretation bias: A causal role for disgust in anxiety psychopathology. Behaviour Research & Therapy, 44, 1375-1384.
Davey, G. C. L., MacDonald, B., & Brierley, L. (2008). The effect of disgust on anxiety ratings to fear-relevant, disgust-relevant and fear-irrelevant stimuli. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 22, 1347-1354.
Davey, G. C. L., Dash, S., & Meeten, F. (2014). Obsessive compulsive disorder. Palgrave.
De Houwer, J., Thomas, S., & Baeyens, F. (2001). Associative learning of likes and dislikes: A review of 25 years of research on human evaluative conditioning. Psychological Bulletin, 127, 853-869.
de Jong, P.J., & Merckelbach, H. (1998). Blood-injection-injury phobia and fear of spiders. Domain specific individual differences in disgust sensitivity. Personality & Individual Differences, 24, 153-158.
DeJesus, J. M., Shutts, K., & Kinzler, K. D. (2015). Eww she sneezed! Contamination context affects children’s food preferences and consumption. Appetite, 87, 303–309.
Everaert, J., Tierens, M., Uzieblo, K., & Koster, E. H. W. (2013). The indirect effect of attention bias on memory via interpretation bias: evidence for the combined cognitive bias hypothesis in subclinical depression. Cognition & Emotion, 27, 1450–1459.
Feder, Y. (2015). Contamination appraisals, pollution beliefs, and the role of cultural inheritance in shaping disease avoidance behavior. Cognitive Science, 40(6), 1561–1585.
Field, A. F., & Davey, G. C. L. (1997). Conceptual conditioning: Evidence for an artifactual account of evaluative learning. Learning & Motivation, 28, 446-464.
Field, A. F., & Davey, G. C. L. (1998). Evaluative conditioning: Arti-fact or -fiction?—A reply to Baeyens, De Houwer, Vansteenwegen, and Eelen (1998) Learning & Motivation, 29, 475-491.
Fleischman, D.S., Hamilton, L.D., Fessler, D.M.T., & Meston, C.M. (2015). Disgust versus lust: Exploring the interactions of disgust and fear with sexual arousal in women. PLoS ONE, 10, e0118151.
Gilbert, P., Clarke, M., Hempel, S., Miles, J. N. V., & Irons, C. (2004). Criticizing and reassuring oneself: An exploration of forms, styles and reasons in female students. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 43(1), 31–50.
Giner-Sorolla, R., Kupfer, T., & Sabo, J. (2018). What makes moral disgust special? An integrative functional review. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 57, 223-289.
Graham, J., & Haidt, J. (2010). Beyond beliefs: Religions bind individuals into moral communities. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 14(1), 140-150.
Haidt, J. (2012). The righteous mind: Why good people are divided by politics and religion. Pantheon/Random House.
Haidt, J., McCauley, C., & Rozin, P. (1994). Individual differences in sensitivity to disgust: A scale sampling seven domains of disgust elicitors. Personality & Individual Differences, 16, 701-713.
Harris, A. A., Romer, A. L., Hanna, E. K., Keeling, L. A., LaBar, K. S. Sinnott-Armstrong, W., Strauman, T. J., Wagner, H. R., Marcus, M. D., & Zucker, N. L. (2019). The central role of disgust in disorders of food avoidance. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 52, 543-553.
Harvey, T., Troop, N. A., Treasure, J. L., & Murphy, T. (2002). Fear, disgust, and abnormal eating attitudes: A preliminary study. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 32, 213-218.
Herz, R. S., & Hinds, A. (2013). Stealing is not gross: Language distinguishes visceral disgust from moral violations. The American Journal of Psychology, 126, 275–286.
Hirsch, C. R., Clark, D. M., & Mathews, A. (2006). Imagery and interpretations in social phobia: Support for the combined cognitive biases hypothesis. Behavior Therapy, 37, 223–236.
Horberg, E. J., Oveis, C., Keltner, D., & Cohen, A. B. (2009). Disgust and the moralization of purity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 97(6), 963-976.
Huppert J. D., Siev J., & Kushner E. S. (2007) When religion and obsessive-compulsive disorder collide: Treating scrupulosity in Ultra-Orthodox Jews. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 63, 925-941.
Ille, R., Schöggl, H., Kapfhammer, H.P., Arendasy, M., Sommer, M., & Schienle, A. (2014). Self-disgust in mental disorders—symptom-related or disorder specific. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55, 938-943.
Inozu, M., Ulukut, F.O., Ergun, G., & Alcolado, G.M. (2014). The mediating role of disgust sensitivity and thought-action fusion between religiosity and obsessive compulsive symptoms. International Journal of Psychology, 49, 334-341.
Izard, C. E. (1993). Four systems for emotion activation: Cognitive and noncognitive processes. Psychological Review, 100, 68-90.
Izard, C. E. (2007). Basic emotions, natural kinds, emotion schemas, and a new paradigm. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 2, 260-269.
Knowles, K. A., Jessup, S. C., & Olatunji, B. O. (2018). Disgust in anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorders: Recent findings and future directions. Current Psychiatry Reports, 20, 68.
Knowles, K. A., Cox, R. C., Armstrong, T., & Olatunji, B.O. (2019). Cognitive mechanisms of disgust in the development and maintenance of psychopathology: A qualitative review and synthesis. Clinical Psychology Review, 69, 30-50.
Kollareth, D., & Russell, J. A. (2019). Disgust and the sacred: Do people react to violations of the sacred with the same emotion they react to something putrid. Emotion, 19, 37-52.
Leathers-Smith, E., & Davey, G. C. L. (2011). The disgust threat interpretation bias is not moderated by anxiety and disgust sensitivity. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology, 2, 63-76.
Lieberman, D., Tooby, J., & Cosmides, L. (2003). Does morality have a biological basis? An empirical test of factors governing moral statements relating to incest. Proc. R. Soc. Lond., B270, 819–826.
Mancini, F., Grannani, A., & D’Olimpio, F. (2001). The connection between disgust and obsessions and compulsions in a non-clinical sample. Personality & Individual Differences, 31, 1173-1180.
Marzillier, S. L. & Davey, G. C. L. (2004). The emotional profiling of disgust-eliciting stimuli: Evidence for primary and complex disgusts. Cognition & Emotion, 18, 313-336.
Marzillier, S. L. & Davey, G. C. L. (2005). Anxiety and disgust: Evidence for a unidirectional relationship. Cognition & Emotion, 19, 729-750.
Mason, E. C., & Richardson, R. (2010). Looking beyond fear: The extinction of other emotions implicated in anxiety disorders. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 24, 63-70.
Matchett, G., & Davey, G. C. L. (1991). A test of a disease-avoidance model of animal phobias. Behaviour, Research and Therapy, 29, 91-94.
Mathews, A., & Mackintosh, B. (2000). Induced emotional interpretation bias and anxiety. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109, 602-615.
Mayer, B., Muris, P., Busser, K., & Bergamin, J. (2009). A disgust mood state causes a negative interpretation bias, but not in the specific domain of body-related concerns. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 47(10), 876–881.
Melli, G., Poli, A., Chiorri, C., & Olatunji, B.O. (2019). Is heightened disgust propensity truly a risk factor for contamination-related obsessive-compulsive disorder? Behavior Therapy, 50, 621-629.
Mulkens, S.A., de Jong, P.J., & Merckelbach, H. (1996). Disgust and spider phobia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 105, 464-468.
Muris, P., Merckelbach, H., Schmidt, H., & Tierny, S. (1999). Disgust sensitivity, trait anxiety and anxiety disorders symptoms in normal children. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 37, 953-961.
Muris, P., Merckelbach, H., Nederkoorn, S., Rassin, E., Candel, I., & Horselenberg, R. (2000). Disgust and psychopathological symptoms in a nonclinical sample. Personality & Individual Differences, 29, 1163-1167.
Neuberg, S. L., Kenrick, D. T., & Schaller, M. (2011). Human threat management systems: self-protection and disease-avoidance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 35, 1042-1051.
Ólafsson, R. P., Friðriksdóttir, A. E., Sveinsdóttir, S. þ., & Kristjánsson, A. (2019). Evidence for an attention bias toward disgust in contamination fear. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology. https://doi.org/10.1177/2043808719870043.
Olatunji, B. O. (2010). Changes in disgust correspond with changes in symptoms of contamination-based OCD: A prospective examination of specificity. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 24(3), 313-317.
Olatunji, B.O., & Armstrong, T. (2009). Contamination fear and effects of disgust on distress in a public restroom. Emotion, 9, 592-597.
Olatunji B. O., Sawchuk C. N., Lohr J. M. & de Jong P. J. (2004). Disgust domains in the prediction of contamination fear. Behaviour Research & Therapy, 42, 93-104.
Olatunji, B. O., Tolin, D. F., Huppert, J. D., & Lohr, J. M. (2005). The relation between fearfulness, disgust sensitivity and religious obsessions in a non-clinical sample. Personality and Individual Differences, 38, 891–902.
Olatunji, B. O., Lohr, J. M., Sawchuk, C. N., & Tolin, D. F. (2007a). Multimodal assessment of disgust in contamination-related obsessive-compulsive disorder. Behaviour Research & Therapy, 45, 263-276.
Olatunji, B. O., Smits, J. A. J., Connolly, K., Willems, J., & Lohr, J. M. (2007b). Examination of the decline in fear and disgust during exposure to threat-relevant stimuli in blood-injection-injury phobia. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 21, 445-455.
Olatunji, B. O., Wolitzky-Taylor, K. B., Willems, J., Lohr, J. M., & Armstrong, T. (2009). Differential habituation of fear and disgust during exposure to threat-relevant stimuli in contamination-based OCD: an analogue study. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 23, 118–123.
Olatunji, B. O., Cisler, J., McKay, D., & Phillips, M. L. (2010). Is disgust associated with psychopathology? Emerging research in the anxiety disorders. Psychiatry Research, 175, 1-10.
Ouimet, A. J., Gawronski, B., & Dozois, D. J. A. (2009). Cognitive vulnerability to anxiety: A review and integrative model. Clinical Psychology Review, 29, 459-470.
Overton, P. G., Markland, F. E., Taggart, H. S., Bagshaw, G. L., & Simpson, J. (2008). Self-disgust mediates the relationship between dysfunctional cognitions and depressive symptomatology. Emotion, 8(3), 379.
Phillips, M. L., Senior, C., Fahy, T., & David, A. S. (1998). Disgust—the forgotten emotion of psychiatry. British Journal of Psychiatry, 172, 373-375.
Plakias, A. (2018). The response model of moral disgust. Synthese, 195, 5453-5472.
Poli, A., Melli, G., & Radomsky, A. S. (2019). Different disgust domains specifically relate to mental and contact contamination fear in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Evidence from a path analytic model in an Italian clinical sample. Behavior Therapy, 50, 380-394.
Powell, P. A., Simpson, J., & Overton, P. G. (2013). When disgust leads to dysphoria: A three-wave longitudinal study assessing the temporal relationship between self-disgust and depressive symptoms. Cognition and Emotion, 27(5), 900–913.
Powell, P. A., Simpson, J., & Overton, P. G. (2015a). An introduction to the revolting self: Self-disgust as an emotion schema. In P. A. Powell, P. G. Overton, & J. Simpson (Eds.), The revolting self: Perspectives on the psychological, social, and clinical implications of self-directed disgust (pp. 1–24). Karnac.
Powell, P. A., Simpson, J., & Overton, P. G. (2015b). Self-affirming trait kindness regulates disgust toward one’s physical appearance. Body Image, 12, 98-107.
Ritter, R. S., & Preston, J. L. (2011). Gross gods and icky atheism: Disgust responses to rejected religious beliefs. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 47, 1225–1230.
Rottman, J., DeJesus, J., & Greenebaum, H. (2019). Developing disgust: Theory, measurement, and application. In V. LoBue et al. (Eds.) Handbook of emotional development (pp. 283-309). Springer.
Royzman, E., & Kurzban, R. (2011). Minding the metaphor: The elusive character of moral disgust. Emotion Review, 3, 269–271.
Royzman, E. B., Atanasov, P., Landy, J. F., Parks, A., & Gepty, A. (2014). CAD or MAD? Anger (not disgust) as the predominant response to pathogen-free violations of the divinity code. Emotion, 14, 892–907.
Rozin, P., & Fallon, A. E. (1987). A perspective on disgust. Psychological Review, 94, 23-41.
Rozin, P., Haidt, J., & McCauley, C. R. (2009). Disgust: The body and soul emotion in the 21st century. In B. O. Olatunji & D. McKay (Eds.), Disgust and its disorders: Theory, assessment, and treatment implications (pp. 9–29). American Psychological Association.
Rozin, P., Haidt, J., & McCauley, C. R. (2016). Disgust. In L. F. Barrett, M. Lewis, & J. M. Haviland-Jones (Eds.), Handbook of emotions (4th ed., pp. 815–834). Guilford Press.
Russell, P. A. (1979). Fear-evoking stimuli. In W. Sluckin (Ed.), Fear in Animals and Man. Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Salemink, E., van den Hout, M., & Kindt, M. (2007). Trained interpretive bias: Validity and effects on anxiety. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 38, 212-224.
Salter-Pedneault, K., Tull, M. T., & Roemer, L. (2004). The role of avoidance of emotional material in the anxiety disorders. Applied & Preventive Psychology, 11, 95-114.
Schienle, A., Schafer, A., Stark, R., Walter, B., Franz, M., & Vaitl, D. (2003). Disgust sensitivity in psychiatric disorders: A questionnaire study. Journal of Nervous & Mental Disease, 191, 831-834.
Schienle, A., Ille, R., Sommer, M., & Arendasy, M. (2014). Diagnosis of self-disgust in the context of depression. Verhaltenstherapie, 24(1), 15–20.
Sica, C., Novara, C., & Sanavio, E. (2002). Religiousness and obsessive–compulsive cognitions and symptoms in an Italian population. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 40(7), 813-823.
Simpson, J., Hillman, R., Crawford, T., & Overton, P. G. (2010). Self-esteem and self-disgust both mediate the relationship between dysfunctional cognitions and depressive symptoms. Motivation and Emotion, 34(4), 399–406.
Smith, N. B., Steele, A. M., Weitzman, M. L., Trueba, A. F., & Meuret, A. E. (2015). Investigating the role of self-disgust in nonsuicidal self-injury. Archives of Suicide Research, 19(1), 60–74.
Sparks, A. M., Fessler, D. M. T., Chan, K. Q., Ashokkumar, A., & Holbrook, C. (2018). Disgust as a mechanism for decision making under risk: Illuminating sex differences and individual risk-taking correlates of disgust propensity. Emotion, 18, 942-958.
Stevenson, R. J., Oaten, M. J., Case, T. I., Repacholi, B. M., & Wagland, P. (2010). Children’s response to adult disgust elicitors: Development and acquisition. Developmental Psychology, 46(1), 165–177.
Stevenson, R. J., Oaten, M. J., Case, T. I., & Repacholi, B. (2014). Is disgust prepared? A preliminary examination in young children. The Journal of General Psychology, 141(4), 326–347.
Stevenson, R. J., Case, T. I., Oaten, M. J., Stafford, L., & Saluja, S. (2019). A proximal perspective on disgust. Emotion Review, 11(3), 209-225.
Summerfeldt, L., Antony, M. M., Downie, F., Richter, M. A., & Swinson, R. P. (1998). Prevalence of particular obsessions and compulsions in a clinic sample. Unpublished manuscript.
Terrizzi, Jr., J. A., Shook, N. J., & Ventis, L. (2012). Religious conservatism: An evolutionary evoked disease-avoidance strategy. Religions, Brains, & Behavior, 2, 105-120
Thorpe, S. J. and Salkovskis, P. M. (1998). Studies on the role of disgust in the acquisition and maintenance of specific phobias. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 36, 877-893.
Tybur, J. M., Lieberman, D., Kurzban, R., & DeScioli, P. (2013). Disgust: Evolved function and structure. Psychological Review, 120, 65-84.
Vogt, J., Lozo, L., Koster, E. H. W., & de Houwer, J. (2011). On the role of goal relevance in emotional attention: disgust evokes early attention to cleanliness. Cognition and Emotion, 25(3), 466–478.
Ware J., Jain K., Burgess I. & Davey G. C. L. (1994). Disease-avoidance model: Factor analysis of common animal fears. Behaviour Research & Therapy, 32, 57-63.
Webb, K., & Davey, G. C. L. (1993). Disgust sensitivity and fear of animals: Effect of exposure to violent or revulsive material. Anxiety, Stress and Coping, 5, 329-335.
Wheatley, T., & Haidt, J. (2005). Hypnotic disgust makes moral judgments more severe. Psychological Science, 16, 780-784.
Woody, S. R., & Teachman, B. A. (2000). Intersection of disgust and fear: Normative and pathological views. Clinical Psychology: Science & Practice, 7, 291-311.
Zanjani, Z., Yaghubi, H., Shaeiri, M. R., & Fata, L. (2018). Relationship between disgust propensity and contamination obsessive-compulsive symptoms: The mediating role of information processing bias. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal, 20, e67133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Davey, G.C.L. (2021). Mechanisms of Disgust in Psychopathology. In: Powell, P.A., Consedine, N.S. (eds) The Handbook of Disgust Research. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84486-8_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84486-8_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-84485-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-84486-8
eBook Packages: Behavioral Science and PsychologyBehavioral Science and Psychology (R0)