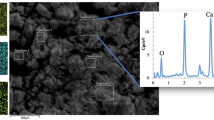
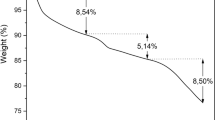
Abstract
In this study, the elimination of phenol compounds from phenolic solutions by adsorption method in column was studied. The adsorbent is a polymer’s bead which is synthesized from an apatite by a method based on cross-linking process. Studies showed that the synthesized adsorbent (Pap) can retain phenol with a high adsorption capacity (about 244 mg/g of apatite) and a slow reaction kinetics (about 4 h), which can be described by an equation corresponding to a pseudo second order. The exploitation of the adsorption isotherm indicates that the best fit is obtained with the Freundlik model. Results of regeneration of phenol show that adsorbed phenol remains almost unstable and can be desorbed using only distilled water.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Achak, N. Ouazzani, L. Mandi, Treatment of modern olive mill effluent by infiltration-percolation on a sand filter. J. Water Sci. Technol. 22, 421–433 (2009)
S. El Asri, A. Laghzizil, A. Saoiabi, A. Alaoui, K. El Abassi, R. M’hamdi, T. Coradin, A novel process for the fabrication of nanoporousapatites from Moroccan phosphate rock. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 350, 73–78 (2009)
F. Aziz, M. El Achaby, A. Lissaneddine, K.H. Aziz, N. Ouazzani, R. Mamouni, L. Mandi, Composites with alginate beads: a novel design of nano-adsorbents impregnation for large-scale continuous flow wastewater treatment pilots. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.11.019
R. Benaddi, K. El Harfi, F.Aziz, F. Berrekhis, N. Ouazzani, Removal of phenolic compounds from synthetic solution and oil mill waste water by adsorption onto nanoparticles synthesized from phosphate rock. J. Surface Sci. Technol. 36(1–2), 01–05 (2020). https://doi.org/10.18311/jsst/2020/23780
L.G. Cordova Villegas, N. Mashhadi, M. Chen, D. Mukherjee, K.E. Taylor, N. Biswas, A short review of techniques for phenol removal from wastewater. Water Pollut.https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-016-0035-3
M. El-Naas, M.A. Alhaija, S. Al-Zuhair, Evaluation of an activated carbon packed bed for the adsorption of phenols from petroleum refinery wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8469-8
C.H. Giles, T.H. Macewan, S.N. Nakhwa, D. Smith, A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids 786, 3973–3993 (1960)
L. Jakobek, Interactions of polyphenols with carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Food Chem. 175, 556–567 (2015)
L.C. Margarita, S.R. Eduardo, B. Refugio, R. García, C.C. Felipe de Jesús, C.G. María Teresa, A.R. MónicaMaría, D.G. Nancy Elizabeth, Adsorption and desorption of phenol onto barley husk-activated carbon in an airlift reactor. J. Desalination Water Treat. 1, 1–16 (2014)
G. Mihoc, R. Ianoş, C. Păcurariu, Adsorption of phenol and p-chlorophenol from aqueous solutions by magnetic nanopowder. Water Sci. Technol. 69, 385–391 (2014)
D.M. Nuhu, J. Nabeel, Z. Mukarram, A. Omar, Removal of phenolic compounds from water using sewage sludge-based activated carbon adsorption: a review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 14(10), 1094 (2017)
A. Oumani, L. Mandi, F. Berrekhis, N. Ouazzani, Removal of Cr3+ from tanning effluents by adsorption onto phosphate minewaste: key parameters and mechanisms. J. Hazardous Mater. 378, 120718 (2019)
O. Sacco, V. Vaiano, C. Daniel, W. Navarra, V. Vincenzo Venditto, Removal of phenol in aqueous media by N-doped TiO2 based photocatalytic Aerogels. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 80, 104–110 (2018)
S. Saoiabi, A. Gouza, H. Bouyarmane, A. Laghzizil, A. Saoiabi, Organophosphonate-modified Hydroxyapatites for Zn(II) and Pb(II) adsorption in relation of their structure and surface properties. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 428–433 (2016)
B.M. Villar da Gama, G.L. Elisandra do Nascimento, D.C. Silva Sales, J.M. Rodríguez-Díaz, C.M. Bezerra De Menezes Barbosa, M.M. Menezes Bezerra Duarte, Mono and binary component adsorption of phenol and cadmium using adsorbent derived from peanut shells. J. Clean. Prod. 201, 219–228 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Benaddi, R., Aziz, F., harfi, K.E., Ouazzani, N. (2022). Column Adsorption Studies of Phenolic Compounds on Nanoparticles Synthesized from Moroccan Phosphate Rock. In: Heggy, E., Bermudez, V., Vermeersch, M. (eds) Sustainable Energy-Water-Environment Nexus in Deserts. Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-76081-6_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-76081-6_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-76080-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-76081-6
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)