Abstract
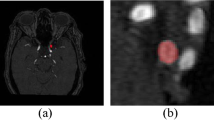
Early detection and accurate segmentation of cerebral aneurysm is important for clinical diagnosis and prevention of rupture, which would be life threatening. 3D images can provide abundant information for characterizing the aneurysm. But the traditional manual segmentation of aneurysms takes lots of time and effort. Therefore, accurate and rapid automatic algorithm for 3D segmentation of aneurysm is needed. U-Net is a widely used deep learning network in medical image segmentation, but its performance is limited by the amount of data. In this challenge of aneurysm segmentation, we proposed to add attention gate and Models Genesis pretraining mechanisms to the classical U-Net model to improve the results. The dice of 3D U-net, 3D Attention U-Net, pretrained 3D U-Net and pretrained 3D Attention U-Net are 0.881, 0.884, 0.890 and 0.907, respectively. The experimental results show that the use of attention gate and Models Genesis can significantly improve the performance of U-Net model in segmenting aneurysms. This work achieved rank one in CADA 2020- Aneurysm Segmentation Challenge.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anker‐Møller, T., Hvas, A.M., Sunde, N., et al.: Proteins of the Lectin Pathway of complement activation at the site of injury in subarachnoid hemorrhage compared with peripheral blood. Brain Behav. 10(8), e01728(2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1728
Duan, Z., Montes, D., Huang, Y., et al.: Deep Learning Based Detection and Localization of Cerebal Aneurysms in Computed Tomography Angiography. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.11098 (2020)
Jin, H., Geng, J., Yin, Y., et al.: Fully automated intracranial aneurysm detection and segmentation from digital subtraction angiography series using an end-to-end spatiotemporal deep neural network. J. NeuroInterv. Surgery 12, 1023–1027 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-015824
Mohammadi, S., Mohammadi, M., Dehlaghi, V., Ahmadi, A.: Automatic segmentation, detection, and diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) using convolutional neural networks and hough circles algorithm. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 10(3), 490–499 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-019-00421-6
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Ibtehaz, N., Rahman, M.S.: MultiResUNet: rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 121, 74–87 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2019.08.025
Isensee, F., Jaeger, P.F., Kohl, S.A.A., et al.: nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nature Methods, 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-01008-z
Zhou, T., Ruan, S., Canu, S.: A review: deep learning for medical image segmentation using multi-modality fusion. Array 3, 100004 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.array.2019.100004
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L.L., et al.: Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999 (2018)
Morid, M.A., Borjali, A., Del Fiol, G.: A scoping review of transfer learning research on medical image analysis using ImageNet. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.13175 (2020)
Zhou, Z., et al.: Models genesis: generic autodidactic models for 3D medical image analysis. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11767, pp. 384–393. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32251-9_42
Zhou, S., et al.: Statistical intensity- and shape-modeling to automate cerebrovascular segmentation from TOF-MRA data. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11765, pp. 164–172. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32245-8_19
Pedrosa, J., et al.: LNDb: a lung nodule database on computed tomography. arXiv:1911.08434
Li, H., Lin, Z., Shen, X., Brandt, J., Hua, G.: A convolutional neural network cascade for face detection. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recogn. IEEE (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Su, Z. et al. (2021). 3D Attention U-Net with Pretraining: A Solution to CADA-Aneurysm Segmentation Challenge. In: Hennemuth, A., Goubergrits, L., Ivantsits, M., Kuhnigk, JM. (eds) Cerebral Aneurysm Detection and Analysis. CADA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12643. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72862-5_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72862-5_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-72861-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-72862-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)