Abstract
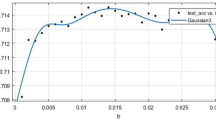
GCN based on time and space is an essential part of smart city construction because it can capture the spatiotemporal dynamics and effectively analyze the traffic data to get the best prediction results. In the specific operation of the model, the adjustment and optimal selection of super parameters can make the model provide the best results, thus saving time, cost and computing power. When it comes to the prediction scenarios with low computational power and urgent demand, the existing super parameter search methods and optimization models lack efficiency and accuracy. Therefore, this paper proposes a super parameter search and optimization method based on cross validation, which can efficiently and accurately optimize the parameters, and select the best parameters by using the similarity between the learning and training errors corresponding to each super parameter To improve the prediction ability of the model. Through the verification of the actual data set, the model runs well, and can provide the best prediction results for the traffic flow and other scenarios dominated by spatiotemporal state.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, K., Chen, L., An, Y., et al.: A QoE test system for vehicular voice cloud services. Mob. Netw. Appl. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01415-3
Wang, F., Jiang, D., Qi, S.: An adaptive routing algorithm for integrated information networks. China Commun. 7(1), 196–207 (2019)
Huo, L., Jiang, D., Lv, Z., et al.: An intelligent optimization-based traffic information acquirement approach to software-defined networking. Comput. Intell. 1–21 (2019)
Chen, L., Jiang, D., Bao, R., Xiong, J., Liu, F., Bei, L.: MIMO Scheduling effectiveness analysis for bursty data service from view of QoE. Chin. J. Electron. 26(5), 1079–1085 (2017)
Jiang, D., Wang, Y., Lv, Z., et al.: Big data analysis-based network behavior insight of cellular networks for industry 4.0 applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 16(2), 1310–1320 (2020)
Jiang, D., Huo, L., Song, H.: Rethinking behaviors and activities of base stations in mobile cellular networks based on big data analysis. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 1(1), 1–12 (2018)
Chen, L., et al.: A lightweight end-side user experience data collection system for quality evaluation of multimedia communications. IEEE Access 6(1), 15408–15419 (2018)
Chen, L., Zhang, L.: Spectral efficiency analysis for massive MIMO system under QoS constraint: an effective capacity perspective. Mob. Netw. Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01414-4
Wang, F., Jiang, D., Qi, S., et al.: A dynamic resource scheduling scheme in edge computing satellite networks. Mob. Netw. Appl. 1–12 (2019)
Jiang, D., Huo, L., Lv, Z., et al.: A joint multi-criteria utility-based network selection approach for vehicle-to-infrastructure networking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 19(10), 3305–3319 (2018)
Jiang, D., Zhang, P., Lv, Z., et al.: Energy-efficient multi-constraint routing algorithm with load balancing for smart city applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 3(6), 1437–1447 (2016)
Jiang, D., Li, W., Lv, H.: An energy-efficient cooperative multicast routing in multi-hop wireless networks for smart medical applications. Neurocomputing 220, 160–169 (2017)
Jiang, D., Wang, Y., Lv, Z., et al.: Intelligent optimization-based reliable energy-efficient networking in cloud services for IIoT networks. IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun. 1–6 (2019)
Jiang, D., Wang, W., Shi, L., et al.: A compressive sensing-based approach to end-to-end network traffic reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 5(3), 1–12 (2018)
Jiang, D., Huo, L., Li, Y.: Fine-granularity inference and estimations to network traffic for SDN. PLoS ONE 13(5), 1–23 (2018)
Wang, Y., Jiang, D., Huo, L., et al.: A new traffic prediction algorithm to software defined networking. Mob. Netw. Appl. 1–10 (2019)
Qi, S., Jiang, D., Huo, L.: A prediction approach to end-to-end traffic in space information networks. Mob. Netw. Appl. 1–10 (2019)
Huo, L., Jiang, D., Qi, S., et al.: An AI-based adaptive cognitive modeling and measurement method of network traffic for EIS. Mob. Netw. Appl. 1–11 (2019)
Huo, L., Jiang, D., Zhu, X., et al.: An SDN-based fine-grained measurement and modeling approach to vehicular communication network traffic. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 1–12, (2019)
Silver, D., et al.: Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 529(7587), 484–489 (2016)
Silver, D., et al.: Mastering the game of go without human knowledge. Nature 550(7676), 354–359 (2017)
Moravˇcik, M., et al.: DeepStack: Expert-level artifificial intelligence in heads-up no-limit poker. Science 356(6337), 508–513 (2017)
Park, D., Rilett, L.R.: Forecasting freeway link travel times with a multilayer feedforward neural network. Comput.-Aided Civil Infrastruct. Eng. 14(5), 357–367 (1999)
Huang, W., Song, G., Hong, H., Xie, K.: Deep architecture for traffific flow prediction: Deep belief networks with multitask learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 15(5), 2191–2201 (2014)
Fu, R., Zhang, Z., Li, L.: Using LSTM and GRU neural network methods for traffific flow prediction. In: 31st Youth Academic Annual Conference China Association Automation (YAC), Wuhan, China, pp. 324–328 (2016)
Van Lint, J.W.C., Hoogendoorn, S.P., van Zuylen, H.J.: Freeway travel time prediction with state-space neural networks: modeling statespace dynamics with recurrent neural networks. Transp. Res. Rec. 1811(1), 30–39 (2002)
Zhao, L., Song, Y., Zhang, C., et al.: T-GCN: a temporal graph convolutional network for traffic prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 21(9), 3848–3858 (2018)
Ding, L., Huang, Z., Chen, G.: An FPGA implementation of GCN with sparse adjacency matrix. In: 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON) (2019)
Zheng, J., Li, D.: GCN-TC: combining trace graph with statistical features for network traffic classification. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (2019)
Li, Z., Xiong, G., Chen, Y.: A hybrid deep learning approach with GCN and LSTM for traffic flow prediction. In: 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC) (2019)
Reddi, S.J., Kale, S., Kumar, S.: On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond (2019)
Keskar, N.S., Socher, R.: Improving Generalization Performance by Switching from Adam to SGD (2017)
Hoffer, E., Hubara, I., Soudrym D.: Train longer, generalize better: closing the generalization gap in large batch training of neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1731–1741 (2017)
Goyal, P., Dollar, P., Girshick, R.B., et al.: Accurate, Large Minibatch SGD: Training ImageNet in 1 Hour. arXiv: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Keskar, N.S., Socher, R.: Improving generalization performance by switching from adam to sgd. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.07628 (2017)
Reddi, S.J., Kale, S., Kumar, S.: On the convergence of adam and beyond (2018)
Smith, L.N.: Cyclical learning rates for training neural networks. In: 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 464–472, IEEE (2017)
Smith, S.L., Kindermans, P.J., Ying, C., et al.: Don’t decay the learning rate, increase the batch size. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.00489 (2017)
Cardona-Escobar, A.F., Giraldo-Forero, A.F., Castro-Ospina, A.E., Jaramillo-Garzón, F.A.: Efficient hyperparameter optimization in convolutional neural networks by learning curves prediction. In: Mendoza, M., Velastín, S. (eds.) CIARP 2017. LNCS, vol. 10657, pp. 143–151. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75193-1_18
Defferrard, M., Bresson, X., Vandergheynst, P.: Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral fifiltering. Proc. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 3844–3852 (2016)
Kipf, T.N., Welling, M.: Semi-supervised classifification with graph convolutional networks (2016). https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.02907
Bruna, J., Zaremba, W., Szlam, A., Lecun, Y.: Spectral networks and locally connected networks on graphs. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6203 (2013)
Ma, Y., et al: High performance graph convolutional networks with applications in testability Analysis. In: ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), Las Vegas, NV, pp. 18:1–18:6 (2019)
Forecasting road traffic speeds by considering area-wide spatio temporal dependencies based on a graph convolutional neural network (GCN). In: 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC) (2019)
Wu, C., Chai, L., Yang, J., Sheng, Y.: Facial expression recognition using convolutional neural network on graphs. In: The 38th China Control Conference, pp. 90–94 (2019)
Cho, K., van Merrienboer, B., Bahdanau, D., Bengio, Y.: On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1259 (2014)
Chung, J., Gulcehre, C., Cho, K.H., Bengio, Y.: Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work is partly supported by Jiangsu technology project of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (No. 2018ZD265, No. 2019ZD039, No. 2019ZD040, No. 2019ZD041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Huang, J., Chen, L., An, Y., Zhang, K., Cui, P. (2021). Hyperparameter Analysis of Temporal Graph Convolutional Network Model Applied to Traffic Prediction. In: Song, H., Jiang, D. (eds) Simulation Tools and Techniques. SIMUtools 2020. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 369. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72792-5_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72792-5_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-72791-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-72792-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)