Abstract
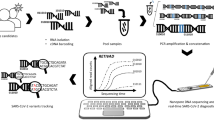
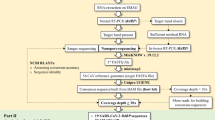
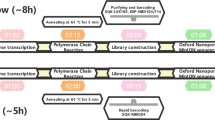
The sequencing of the genome of new virus, such as the coronavirus type 2 of the acute severe respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2), is essential and of great importance to mitigate new zoonotic outbreaks, which are caused by mutations present in structural and non-structural proteins that make up the viruses. Sequencing allows tracking the behavior of the virus locally and globally, knowing the route of transmission and spread of the virus, and determine the virulence rate. Current studies have been carried out, using first, second or third generation sequencing techniques, which have allowed reading and analyzing the nucleotides that make up the virus genome. Thus, the benefits of effective technologies to know its genetic composition in the shortest possible time become evident. New technologies are able to monitor an epidemic in real time, monitor the evolution and efficacy of a drug, the development of a vaccine as well as epidemiological advances. This work addresses the Oxford Nanopore sequencing, which is considered the most efficient and applied method for sequencing viruses that cause epidemics. Some of the advantages of using this sequencing are highlighted in this work, such as the ability to perform long readings and be able to obtain sample responses in short time. It’s also able to discover as much information as possible about the pathogen, being an important feature to deal with public health emergencies, such is the case of the COVID-19.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang C, Liu Z, Chen Z et al (2020) The establishment of reference sequence for SARS-CoV-2 and variation analysis. J Med Virol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25762
Fehr AR, Perlman S (2015) Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol Biol 1282:1–23
Yin C (2020) Genotyping coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.04.016
Ji W, Wang W, Zhao X, Zai J, Li X (2020) Cross-species transmission of the newly identified coronavirus 2019-nCoV. J Med Virol 92:433–440
GISAID at https://www.gisaid.org/
Chen Y et al (2020) Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication and pathogenesis. J Med Virol 92:418–423
Dawood AA (2020) Mutated CoVID-19 may foretell a great risk for making the future. New Microbes New Infect 35:1000673
Phan T (2020) Genetic diversity and evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Infect Genet Evol 81:104260
Zhamg J et al (2020) The continuous evolutions and disseminations of 2019 novel human coronavirus. J Infect 80:671–693
Sanjuán R, Domingo-Calap P (2016) Mechanisms of viral mutation. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:4433–4448
Rye C et al (2017) Biology. OpenStax, Houston
Schadt EE, Turner S, Kasarskis A (2010) A window into third-generation sequencing. Hum Mol Genet 19:R227–R240
Lu H et al (2016) Oxford nanopore MinION sequencing and genome assembly. Genomics Proteomicis Bioinform 14:265–279
Kraft F, Kurth I (2019) Long-read sequencing in human genetics. medizinische genetik 31:198–204
Kchouk M, Jean-François Gibrat Elloumi M (2017) Generations of sequencing technologies: from first to next generation. Biol Med 9:395
Pillai S et al (2017) Review of sequencing platforms and their applications in phaeochromocytoma and paragangliomas. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol 116:58–67
Laver T, Harrison J, O’Neill PA, Moore K, Farbos A, Paszkiewicz K et al (2015) Assessing the performance of the Oxford nanopore technologies MinION. Biomol Detect Quantif 1(3):1–8
Huang J, Liang X, Xuan Y, Geng C, Li Y, Lu H et al (2017) Real-time DNA barcoding in a rainforest using nanopore sequencing: opportunities for rapid biodiversity assessments and local capacity building. Gigascience 6(5):1 [cited 2020 Jul 30]
Li Y, He X, Li M et al (2020) Comparison of third-generation sequencing approaches to identify viral pathogens under public health emergency conditions. Virus Genes 56(3):228–297
Roach NP et al (2020) The full-length transcriptome of C. elegans using direct RNA sequencing. Genome Res 30(2):299–312
Venkatesan B (2011) Nanopore sensors for nucleic acid analysis. Nat Nanotechnol 6:615–624
Greninger AL, Naccache SN, Federman S et al (2015) Rapid metagenomic identification of viral pathogens in clinical samples by real-time nanopore sequencing analysis. Genome Med 7:99
Quick J, Grubaugh N, Pullan S et al (2017) Multiplex PCR method for MinION and Illumina sequencing of Zika and other virus genomes directly from clinical samples. Nat Protoc 112:1261–1276
Li Y, Han R, Bi C, Li M, Wang S, Gao X (2018) DeepSimulator: a deep simulator for nanopore sequencing. Bioinformatics 34(17):2899–2908
Jesus J (2020) Importation and early local transmission of COVID-19 on Brazil, 2020. J São Paulo Inst Trop Med 62:e30
Loit K, Adamson K, Bahram M, Puusepp R, Anslan S, Kiiker R et al (2019) Relative performance of MinION (Oxford Nanopore Technologies) versus Sequel (Pacific Biosciences) thirdgeneration sequencing instruments in identification of agricultural and forest fungal pathogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 85(21)
NANOCORR at https://github.com/jgurtowski/nanocorr
NANOOK at https://documentation.tgac.ac.uk/display/NANOOK/NanoOK
NANOCORRECT at https://github.com/jts/nanocorrect/
Lu H, Giordano F, Ning Z (2016) Oxford nanopore MinION sequencing and genome assembly. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf 14:265–279
MINKNOW at https://www.protocols.io/view/starting-a-minion-sequencing-run-using-minknow-7q6hmze
Acknowledgements
The authors thank CAPES and CNPq for their scholarships.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Corredor-Vargas, A.M., Torezani, R., Paneto, G., Bastos-Filho, T.F. (2022). Importance of Sequencing the SARS-CoV-2 Genome Using the Nanopore Technique to Understand Its Origin, Evolution and Development of Possible Cures. In: Bastos-Filho, T.F., de Oliveira Caldeira, E.M., Frizera-Neto, A. (eds) XXVII Brazilian Congress on Biomedical Engineering. CBEB 2020. IFMBE Proceedings, vol 83. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70601-2_199
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70601-2_199
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-70600-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-70601-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)