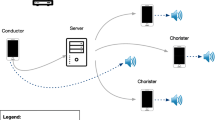
Abstract
The slow but steady shift away from printed text into digital media has not yet modified the working habits of chamber music practitioners. If most instrumentalists still heavily rely on printed scores, audiences increasingly access notated music online, with printed scores synced to an audio recording on youtube for instance. This paper proposes to guide the listener and/or the performer with a cursor scrolling on the page with INScore, in order to examine the consequences of representing time in this way as opposed to traditional bars and beats notation. In addition to its score following interest for pedagogy and analysis, the networking possibilities of today’s ubiquitous technologies reveal interesting potentials for works in which the presence of a conductor is required for synchronization between performers and/or with fixed media (film or tape). A Raspberry Pi-embedded prototype for animated/distributed notation is presented here as a score player (such as the Decibel ScorePlayer, or SmartVox), in order to send and synchronize mp4 scores to any browser capable device connected to the same WIFI network. The corpus will concern pieces edited at BabelScores, an online library for contemporary classical music. The BabelScores pdf works, composed in standard engraving softwares, will be animated using INScore and video editors, in order to find strategies for animation or dynamic display of the unfolding of time, originally represented statically on the page.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The term screen-scores is attributed to Lindsey Vickery and Cat Hope [17].
- 2.
Tablature, as opposed to common music notation, can be conceived as prescriptive notation, in the sense defined by Mieko Kanno: ‘Prescriptive notation specifies the means of execution rather than the resultant configurations of pitch and rhythm’ (Kanno, 2007, p.1). The distinction between prescriptive and descriptive notation (or common music) was already discussed in the fifties, as can attest the following statement by Charles Seeger: ‘Prescriptive and descriptive uses of music writing, which is to say, between a blue-print of how a specific piece of music shall be made to sound and a report of how a specific performance of it actually did sound (...)’ (Seeger, 1958, p. 1).
- 3.
- 4.
Babelscores (https://www.babelscores.com/) is an online score database for classical contemporary music, currently actively supporting the SmartVox project: http://1uh2.mj.am/nl2/1uh2/lgi4u.html.
- 5.
Those three pieces are respectively available at: https://youtu.be/SyFdR2HiF00, https://youtu.be/hQtyu1dcCaI, and https://youtu.be/ET_OBgFWx04.
- 6.
SoundWorks was initiated by the CoSiMa research project funded by the French National Research Agency (ANR) and coordinated by Ircam.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
Babelscores (https://www.babelscores.com/) currently supports actively supporting the SmartVox project: http://1uh2.mj.am/nl2/1uh2/lgi4u.html. The first piece performed in Caen with the Babelbox is available at the following address: https://youtu.be/wUyw0KQa5Wo.
- 11.
A recording is available here.
- 12.
See for instance The Dying Pillow by Cat Hope.
- 13.
The corresponding tools are available at the following address: https://github.com/grame-cncm/inscore/tree/dev/scripts/Tools/drawmap.
- 14.
See Figols - Fullscore for demonstration, together with the corresponding separate part here).
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
A video of the performance is available here.
- 18.
BabelScores now has partnerships with the world’s most prestigious universities, see: https://www.babelscores.com/partners.
- 19.
Rather than a static address (such as http://37.59.101.205:8000/), a bootstrap or a web-application may be more appropriate here.
- 20.
Via Max-for-Live, see https://youtu.be/rLy8DW_p2JE for demonstration.
References
Agostini, A., Ghisi, D.: BACH: an environment for computer-aided composition in Max. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Computer Music Conference (ICMC), Ljubljana, Slovenia (2012)
Bean, J.: DENM (dynamic environmental notation for music): introducing a performance-centric musical interface. In: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation (TENOR), Ann Paris, France (2015)
Bell, T. C., Church, A., McPherson, J., Bainbridge, D.: Page turning and image size in a digital music stand. In: Proceedings of the International Computer Music Conference, Barcelona, Spain (2005)
Bell, J. Audio-scores, a resource for composition and computer-aided performance, Ph.D. dissertation, Guildhall School of Music and Drama (2016). http://openaccess.city.ac.uk/17285/
Bell, J., Matuszewski, B.: SmartVox. a web-based distributed media player as notation tool for choral practices. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation (TENOR). Universidade da Coruña, Coruña, Spain (2017)
Bell, J.: Audiovisual scores and parts synchronized over the web. In: TENOR 2018, Montreal, France (2018). https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01779806
Bell, J., Wyatt, A.: Common ground, music and movement directed by a Raspberry PI. In: TENOR 2020, Montreal, France, 2018. Tenor, Hambourg (2020). https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02774082/document
Bresson, J., Agon, C., Assayag, G.: OpenMusic - visual programming environment for music composition, analysis and research. In: ACM MultiMedia (MM 2011), Scottsdale, United States (2011). https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01182394
Fober, D., Orlarey, Y., Letz, S.: INScore - an environment for the design of live music scores. In: Proceedings of the Linux Audio Conference - LAC 2012, pp. 47–54 (2012). INScore-ID12-2.pdf
Fober, D., Gouilloux, G., Orlarey, Y., Letz, S.: Distributing music scores to mobile platforms and to the internet using INScore. In: Proceedings of the Sound and Music Computing conference – SMC 2015, pp. 229–233 (2015). inscore-web-SMC15.pdf
Fober, D., Orlarey, Y., Letz, S.: Towards dynamic and animated music notation using inscore. In: Ciciliato, V., Orlarey, Y., Pottier, L. (eds.) Proceedings of the Linux Audio Conference – LAC 2017, pp. 43–51, Saint-Etienne. CIEREC (2017)
Fober, D., Orlarey, Y., Letz, S.: Inscore time model. In: Proceedings of the International Computer Music Conference, pp. 64–68 (2017)
Giavitto, J.L., Agostini, A. Bell, J.: A textual language for the bach library. In: ICMC 2019 - International Computer Music Conference, New York, United States (2019). https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02348176
Gottfried, R., Bresson, J.: Symbolist: an open authoring environment for user-defined symbolic notation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation - TENOR 2018, Bhagwati, S., Bresson, J. (eds.) Concordia University, Montreal, Canada, pp. 111–118 (2018)
Hajdu, G., Didkovsky, N.: MaxScore: recent developments. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation - TENOR 2018, Bhagwati, S., Bresson, J. (eds.) Concordia University, Montreal, Canada, pp. 138–146 (2018)
Hope, C., Vickery, L., Wyatt, A., James, S.: The DECIBEL Scoreplayer - a digital tool for reading graphic notation. In: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation - TENOR 2015, Battier, M., Bresson, J., et al. (eds.) Paris, France, pp. 58–69 (2015)
Hope, C.: Electronic scores for music: the possibilities of animated notation. Comput. Music J. 41(3), 21–35 (2017)
Hope, C. Wyatt, A., Thorpe, D.: Scoring an animated notation opera - the decibel score player and the role of the digital copyist in ‘Speechless’. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation - TENOR 2018, Bhagwati, S., Bresson, J. (eds.) Concordia University, Montreal, Canada, pp. 193–200 (2018)
Kocher, P.: Polytempo network: a system for technology-assisted conducting. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Sound and Music Computing (SMC), Athens, Greece (2014)
Louzeiro, P.: Improving sight-reading skills through dynamic notation - the case of comprovisador. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation - TENOR 2018, Bhagwati, S., Bresson, J. (eds.) Concordia University, Montreal, Canada, pp. 55–61 (2018)
McPherson, J.: Turning-score automation for musicians. Honours report, University of Canterbury, New Zealand (1999)
Nathan Magnus, D.G.: Musician assistance and score distribution (MASD). In: Proceedings of The International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression - NIME 2012. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (2012)
Rottondi, C., Chafe, C., Allocchio, C., Sarti, A.: An overview on networked music performance technologies. IEEE Access 4, 8823–8843 (2016)
Schnell, N., Robaszkiewicz, S.: Soundworks - a playground for artists and developers to create collaborative mobile web performances. In: Proceedings of the first Web Audio Conference (WAC), Paris, France (2015)
Vickery, L.: Hybrid real/mimetic sound works. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation - TENOR 2016, Hoadley, R., Nash, C., Fober, D. (eds.) Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge, UK, pp. 19–24 (2016)
Zagorac, S., Alessandrini, P.: ZScore: a distributed system for integrated mixed music composition and performance. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation - TENOR 2018, Bhagwati, S., Bresson, J. (eds.) Concordia University, Montreal, Canada, pp. 62–70 (2018)
Vickery, L.: Some approaches to representing sound with colour and shape. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Music Notation and Representation - TENOR 2018, Bhagwati, S., Bresson, J. (eds.) Concordia University, Montreal, Canada, pp. 165–173 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (mp4 815 KB)
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bell, J., Fober, D., Fígols-Cuevas, D., Garcia-Velasquez, P. (2021). The BabelBox: An Embedded System for Score Distribution on Raspberry Pi with INScore, SmartVox and BabelScores. In: Kronland-Martinet, R., Ystad, S., Aramaki, M. (eds) Perception, Representations, Image, Sound, Music. CMMR 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12631. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70210-6_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70210-6_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-70209-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-70210-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)