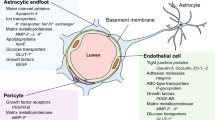
Abstract
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is important to maintain brain homeostasis, which is crucial for the functionality of neuronal networks. BBB dysfunction is observed in several neurological diseases, including epilepsy. Prolonged BBB dysfunction and subsequent perivascular inflammation as well as alterations in the extracellular matrix (ECM) play an important role in epileptogenesis. In this chapter we aim to give an overview of the processes involved in BBB dysfunction and epileptogenesis and provide evidence from animal as well as from human studies. We will focus on modulators of BBB function including specific cell types, inflammatory mediators as well as ECM molecules. Furthermore, we will discuss new therapeutic targets and the results of intervention studies that are important for the development of novel therapeutic approaches in epilepsy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daneman R. The blood-brain barrier in health and disease. Ann Neurol. 2012;72(5):648–72.
Baeten KM, Akassoglou K. Extracellular matrix and matrix receptors in blood-brain barrier formation and stroke. Dev Neurobiol. 2011;71(11):1018–39.
van Vliet EA, Aronica E, Vezzani A, Ravizza T. Review: neuroinflammatory pathways as treatment targets and biomarker candidates in epilepsy: emerging evidence from preclinical and clinical studies. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2018;44(1):91–111.
Aronica E, Bauer S, Bozzi Y, Caleo M, Dingledine R, Gorter JA, Henshall DC, Kaufer D, Koh S, Loscher W, Louboutin JP, Mishto M, Norwood BA, Palma E, Poulter MO, Terrone G, Vezzani A, Kaminski RM. Neuroinflammatory targets and treatments for epilepsy validated in experimental models. Epilepsia. 2017;58(Suppl 3):27–38.
Smyth LCD, Rustenhoven J, Park TI, Schweder P, Jansson D, Heppner PA, O’Carroll SJ, Mee EW, Faull RLM, Curtis M, Dragunow M. Unique and shared inflammatory profiles of human brain endothelia and pericytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):138.
Duan L, Zhang XD, Miao WY, Sun YJ, Xiong G, Wu Q, Li G, Yang P, Yu H, Li H, Wang Y, Zhang M, Hu LY, Tong X, Zhou WH, Yu X. PDGFRbeta cells rapidly relay inflammatory signal from the circulatory system to neurons via chemokine CCL2. Neuron. 2018;100(1):183–200. e8
Tomkins O, Feintuch A, Benifla M, Cohen A, Friedman A, Shelef I. Blood-brain barrier breakdown following traumatic brain injury: a possible role in posttraumatic epilepsy. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol. 2011;2011:765923.
van Vliet EA, da Costa Araújo S, Redeker S, Aronica E, Gorter JA. Blood-brain barrier leakage may lead to progression of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 2):521–34.
van Vliet EA, Aronica E, Gorter JA. Role of blood-brain barrier in temporal lobe epilepsy and pharmacoresistance. Neuroscience. 2014;277:455–73.
Klement W, Garbelli R, Zub E, Rossini L, Tassi L, Girard B, Blaquiere M, Bertaso F, Perroy J, de Bock F, Marchi N. Seizure progression and inflammatory mediators promote pericytosis and pericyte-microglia clustering at the cerebrovasculature. Neurobiol Dis. 2018;113:70–81.
Milesi S, Boussadia B, Plaud C, Catteau M, Rousset MC, De Bock F, Schaeffer M, Lerner-Natoli M, Rigau V, Marchi N. Redistribution of PDGFRbeta cells and NG2DsRed pericytes at the cerebrovasculature after status epilepticus. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;71:151–8.
Kyyriainen J, Ekolle Ndode-Ekane X, Pitkanen A. Dynamics of PDGFRbeta expression in different cell types after brain injury. Glia. 2017;65(2):322–41.
Broekaart DW, Bertran A, Jia S, Korotkov A, Senkov O, Bongaarts A, Mills JD, Anink JJ, Seco-Moral J, Baaijen J, Idema S, Chabrol E, Becker A, Wadman W, Tarrago T, Gorter JA, Aronica E, Prades R, Dityatev A, van Vliet EA. The matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor IPR-179 has antiseizure and antiepileptogenic effects. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(1):e138332
Gorter JA, Van Vliet EA, Rauwerda H, Breit T, Stad R, van Schaik L, Vreugdenhil E, Redeker S, Hendriksen E, Aronica E, Lopes da Silva FH, Wadman WJ. Dynamic changes of proteases and protease inhibitors revealed by microarray analysis in CA3 and entorhinal cortex during epileptogenesis in the rat. Epilepsia. 2007;48(Suppl 5):53–64.
Korotkov A, Broekaart DWM, van Scheppingen J, Anink JJ, Baayen JC, Idema S, Gorter JA, Aronica E, van Vliet EA. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase 3 can be attenuated by inhibition of microRNA-155 in cultured human astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):211.
Zhang JW, Deb S, Gottschall PE. Regional and differential expression of gelatinases in rat brain after systemic kainic acid or bicuculline administration. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10(11):3358–68.
Zhang JW, Deb S, Gottschall PE. Regional and age-related expression of gelatinases in the brains of young and old rats after treatment with kainic acid. Neurosci Lett. 2000;295(1–2):9–12.
Hunsberger JG, Bennett AH, Selvanayagam E, Duman RS, Newton SS. Gene profiling the response to kainic acid induced seizures. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005;141(1):95–112.
Dubey D, McRae PA, Rankin-Gee EK, Baranov E, Wandrey L, Rogers S, Porter BE. Increased metalloproteinase activity in the hippocampus following status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res. 2017;132:50–8.
Penkowa M, Florit S, Giralt M, Quintana A, Molinero A, Carrasco J, Hidalgo J. Metallothionein reduces central nervous system inflammation, neurodegeneration, and cell death following kainic acid-induced epileptic seizures. J Neurosci Res. 2005;79(4):522–34.
Lee J, Lim E, Kim Y, Li E, Park S. Ghrelin attenuates kainic acid-induced neuronal cell death in the mouse hippocampus. J Endocrinol. 2010;205(3):263–70.
Jourquin J, Tremblay E, Decanis N, Charton G, Hanessian S, Chollet AM, Le Diguardher T, Khrestchatisky M, Rivera S. Neuronal activity-dependent increase of net matrix metalloproteinase activity is associated with MMP-9 neurotoxicity after kainate. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18(6):1507–17.
Kim GW, Kim HJ, Cho KJ, Kim HW, Cho YJ, Lee BI. The role of MMP-9 in integrin-mediated hippocampal cell death after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;36(1):169–80.
Pijet B, Stefaniuk M, Kostrzewska-Ksiezyk A, Tsilibary PE, Tzinia A, Kaczmarek L. Elevation of MMP-9 levels promotes epileptogenesis after traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55:9294–306.
Motti D, Le Duigou C, Eugene E, Chemaly N, Wittner L, Lazarevic D, Krmac H, Marstrand T, Valen E, Sanges R, Stupka E, Sandelin A, Cherubini E, Gustincich S, Miles R. Gene expression analysis of the emergence of epileptiform activity after focal injection of kainic acid into mouse hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;32(8):1364–79.
Arisi GM, Foresti ML, Katki K, Shapiro LA. Increased CCL2, CCL3, CCL5, and IL-1beta cytokine concentration in piriform cortex, hippocampus, and neocortex after pilocarpine-induced seizures. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:129.
De Simoni MG, Perego C, Ravizza T, Moneta D, Conti M, Marchesi F, De Luigi A, Garattini S, Vezzani A. Inflammatory cytokines and related genes are induced in the rat hippocampus by limbic status epilepticus. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12(7):2623–33.
Gorter JA, Van Vliet EA, Aronica E, Breit T, Rauwerda H, Lopes da Silva FH, Wadman WJ. Potential new anti-epileptogenic targets indicated by microarray analysis in a rat model for temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci. 2006;26(43):11083–110.
Dhote F, Peinnequin A, Carpentier P, Baille V, Delacour C, Foquin A, Lallement G, Dorandeu F. Prolonged inflammatory gene response following soman-induced seizures in mice. Toxicology. 2007;238(2–3):166–76.
Dube CM, Ravizza T, Hamamura M, Zha Q, Keebaugh A, Fok K, Andres AL, Nalcioglu O, Obenaus A, Vezzani A, Baram TZ. Epileptogenesis provoked by prolonged experimental febrile seizures: mechanisms and biomarkers. J Neurosci. 2010;30(22):7484–94.
Ravizza T, Noe F, Zardoni D, Vaghi V, Sifringer M, Vezzani A. Interleukin converting enzyme inhibition impairs kindling epileptogenesis in rats by blocking astrocytic IL-1beta production. Neurobiol Dis. 2008;31(3):327–33.
Voutsinos-Porche B, Koning E, Kaplan H, Ferrandon A, Guenounou M, Nehlig A, Motte J. Temporal patterns of the cerebral inflammatory response in the rat lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 2004;17(3):385–402.
Plata-Salaman CR, Ilyin SE, Turrin NP, Gayle D, Flynn MC, Romanovitch AE, Kelly ME, Bureau Y, Anisman H, McIntyre DC. Kindling modulates the IL-1beta system, TNF-alpha, TGF-beta1, and neuropeptide mRNAs in specific brain regions. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000;75(2):248–58.
Riazi K, Galic MA, Pittman QJ. Contributions of peripheral inflammation to seizure susceptibility: cytokines and brain excitability. Epilepsy Res. 2010;89(1):34–42.
Shandra AA, Godlevsky LS, Vastyanov RS, Oleinik AA, Konovalenko VL, Rapoport EN, Korobka NN. The role of TNF-alpha in amygdala kindled rats. Neurosci Res. 2002;42(2):147–53.
Kim JE, Ryu HJ, Choi SY, Kang TC. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated threonine 435 phosphorylation of p65 nuclear factor-kappaB subunit in endothelial cells induces vasogenic edema and neutrophil infiltration in the rat piriform cortex following status epilepticus. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:6.
Ashhab MU, Omran A, Kong H, Gan N, He F, Peng J, Yin F. Expressions of tumor necrosis factor alpha and microRNA-155 in immature rat model of status epilepticus and children with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci. 2013;51(3):950–8.
Ravizza T, Rizzi M, Perego C, Richichi C, Veliskova J, Moshe SL, De Simoni MG, Vezzani A. Inflammatory response and glia activation in developing rat hippocampus after status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2005;46(Suppl 5):113–7.
Vezzani A, Moneta D, Richichi C, Aliprandi M, Burrows SJ, Ravizza T, Perego C, De Simoni MG. Functional role of inflammatory cytokines and antiinflammatory molecules in seizures and epileptogenesis. Epilepsia. 2002;43(Suppl 5):30–5.
Lehtimaki KA, Peltola J, Koskikallio E, Keranen T, Honkaniemi J. Expression of cytokines and cytokine receptors in the rat brain after kainic acid-induced seizures. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003;110(2):253–60.
Aronica E, van Vliet EA, Mayboroda O, Troost D, da Silva FHL, Gorter JA. Upregulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR3 and mGluR5 in reactive astrocytes in a rat model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12(7):2333–45.
Xu JH, Long L, Tang YC, Zhang JT, Hut HT, Tang FR. CCR3, CCR2A and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1a, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) in the mouse hippocampus during and after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus (PISE). Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2009;35(5):496–514.
Tian DS, Peng J, Murugan M, Feng LJ, Liu JL, Eyo UB, Zhou LJ, Mogilevsky R, Wang W, Wu LJ. Chemokine CCL2-CCR2 signaling induces neuronal cell death via STAT3 activation and IL-1beta production after status epilepticus. J Neurosci. 2017;37(33):7878–92.
Broekaart DWM, Anink JJ, Baayen JC, Idema S, de Vries HE, Aronica E, Gorter JA, van Vliet EA. Activation of the innate immune system is evident throughout epileptogenesis and is associated with blood-brain barrier dysfunction and seizure progression. Epilepsia. 2018;59(10):1931–44.
Foresti ML, Arisi GM, Katki K, Montanez A, Sanchez RM, Shapiro LA. Chemokine CCL2 and its receptor CCR2 are increased in the hippocampus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J Neuroinflammation. 2009;6:40.
Hung YW, Lai MT, Tseng YJ, Chou CC, Lin YY. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 affects migration of hippocampal neural progenitors following status epilepticus in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2013;10:11.
Manley NC, Bertrand AA, Kinney KS, Hing TC, Sapolsky RM. Characterization of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression following a kainate model of status epilepticus. Brain Res. 2007;1182:138–43.
Kalehua AN, Nagel JE, Whelchel LM, Gides JJ, Pyle RS, Smith RJ, Kusiak JW, Taub DD. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 are involved in both excitotoxin-induced neurodegeneration and regeneration. Exp Cell Res. 2004;297(1):197–211.
Aronica E, Fluiter K, Iyer A, Zurolo E, Vreijling J, van Vliet EA, Baayen JC, Gorter JA. Expression pattern of miR-146a, an inflammation-associated microRNA, in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;31(6):1100–7.
Huang LG, Zou J, Lu QC. Silencing rno-miR-155-5p in rat temporal lobe epilepsy model reduces pathophysiological features and cell apoptosis by activating Sestrin-3. Brain Res. 2018;1689:109–22.
Cai Z, Li S, Li S, Song F, Zhang Z, Qi G, Li T, Qiu J, Wan J, Sui H, Guo H. Antagonist targeting microRNA-155 protects against lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in C57BL/6 mice by activating brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:129.
Liwnicz BH, Leach JL, Yeh HS, Privitera M. Pericyte degeneration and thickening of basement membranes of cerebral microvessels in complex partial seizures: electron microscopic study of surgically removed tissue. Neurosurgery. 1990;26(3):409–20.
Garbelli R, de Bock F, Medici V, Rousset MC, Villani F, Boussadia B, Arango-Lievano M, Jeanneteau F, Daneman R, Bartolomei F, Marchi N. PDGFRbeta(+) cells in human and experimental neuro-vascular dysplasia and seizures. Neuroscience. 2015;306:18–27.
Li S, Yu S, Zhang C, Shu H, Liu S, An N, Yang M, Yin Q, Yang H. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in cortical lesions from patients with focal cortical dysplasia type IIb and tuberous sclerosis complex. Brain Res. 2012;1453:46–55.
Quirico-Santos T, Nascimento Mello A, Casimiro Gomes A, de Carvalho LP, de Souza JM, Alves-Leon S. Increased metalloprotease activity in the epileptogenic lesion–lobectomy reduces metalloprotease activity and urokinase-type uPAR circulating levels. Brain Res. 2013;1538:172–81.
Acar G, Tanriover G, Acar F, Demir R. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Turk Neurosurg. 2015;25(5):749–56.
Konopka A, Grajkowska W, Ziemianska K, Roszkowski M, Daszkiewicz P, Rysz A, Marchel A, Koperski L, Wilczynski GM, Dzwonek J. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in human intractable epilepsy caused by focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsy Res. 2013;104(1–2):45–58.
Broekaart DWM, van Scheppingen J, Anink JJ, Wierts L, van Het Hof B, Jansen FE, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Kamphuis WW, de Vries HE, Aronica E, van Vliet EA. Increased matrix metalloproteinases expression in tuberous sclerosis complex: modulation by microRNA 146a and 147b in vitro. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020;46(2):142–59.
Bongaarts A, de Jong JM, Broekaart DWM, van Scheppingen J, Anink JJ, Mijnsbergen C, Jansen FE, Spliet WGM, den Dunnen WFA, Gruber VE, Scholl T, Hainfellner JA, Feucht M, Borkowska J, Kotulska K, Jozwiak S, Grajkowska W, Buccoliero AM, Caporalini C, Giordano F, Genitori L, Scicluna BP, Schouten-van Meeteren AYN, van Vliet EA, Muhlebner A, Mills JD, Aronica E. Dysregulation of the MMP/TIMP proteolytic system in subependymal giant cell Astrocytomas in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex: modulation of MMP by MicroRNA-320d in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020;79(7):777–90.
Ravizza T, Gagliardi B, Noe F, Boer K, Aronica E, Vezzani A. Innate and adaptive immunity during epileptogenesis and spontaneous seizures: evidence from experimental models and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 2008;29(1):142–60.
Lachos J, Zattoni M, Wieser HG, Fritschy JM, Langmann T, Schmitz G, Errede M, Virgintino D, Yonekawa Y, Frei K. Characterization of the gene expression profile of human hippocampus in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsy Res Treat. 2011;2011:758407.
Iyer A, Zurolo E, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Baayen JC, Gorter JA, Aronica E. Evaluation of the innate and adaptive immunity in type I and type II focal cortical dysplasias. Epilepsia. 2010;51(9):1763–73.
Ravizza T, Boer K, Redeker S, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Troost D, Vezzani A, Aronica E. The IL-1beta system in epilepsy-associated malformations of cortical development. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;24(1):128–43.
Boer K, Jansen F, Nellist M, Redeker S, van den Ouweland AM, Spliet WG, van Nieuwenhuizen O, Troost D, Crino PB, Aronica E. Inflammatory processes in cortical tubers and subependymal giant cell tumors of tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsy Res. 2008;78(1):7–21.
Balosso S, Ravizza T, Aronica E, Vezzani A. The dual role of TNF-alpha and its receptors in seizures. Exp Neurol. 2013;247:267–71.
Mittelman A, Puccio C, Gafney E, Coombe N, Singh B, Wood D, Nadler P, Ahmed T, Arlin Z. A phase I pharmacokinetic study of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor administered by a 5-day continuous infusion. Investig New Drugs. 1992;10(3):183–90.
Maldonado M, Baybis M, Newman D, Kolson DL, Chen W, McKhann G 2nd, Gutmann DH, Crino PB. Expression of ICAM-1, TNF-alpha, NF kappa B, and MAP kinase in tubers of the tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurobiol Dis. 2003;14(2):279–90.
Das A, Wallace GCt, Holmes C, McDowell ML, Smith JA, Marshall JD, Bonilha L, Edwards JC, Glazier SS, Ray SK, Banik NL. Hippocampal tissue of patients with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with astrocyte activation, inflammation, and altered expression of channels and receptors. Neuroscience. 2012;220:237–46.
Feng ZH, Hao J, Ye L, Dayao C, Yan N, Yan Y, Chu L, Shi FD. Overexpression of mu-calpain in the anterior temporal neocortex of patients with intractable epilepsy correlates with clinicopathological characteristics. Seizure. 2011;20(5):395–401.
Kim SK, Wang KC, Hong SJ, Chung CK, Lim SY, Kim YY, Chi JG, Kim CJ, Chung YN, Kim HJ, Cho BK. Gene expression profile analyses of cortical dysplasia by cDNA arrays. Epilepsy Res. 2003;56(2–3):175–83.
Kim SY, Senatorov VV Jr, Morrissey CS, Lippmann K, Vazquez O, Milikovsky DZ, Gu F, Parada I, Prince DA, Becker AJ, Heinemann U, Friedman A, Kaufer D. TGFbeta signaling is associated with changes in inflammatory gene expression and perineuronal net degradation around inhibitory neurons following various neurological insults. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7711.
Wu Y, Wang X, Mo X, Xi Z, Xiao F, Li J, Zhu X, Luan G, Wang Y, Li Y, Zhang J. Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in brain tissue of patients with intractable epilepsy. Clin Neuropathol. 2008;27(2):55–63.
Choi J, Nordli DR Jr, Alden TD, DiPatri A Jr, Laux L, Kelley K, Rosenow J, Schuele SU, Rajaram V, Koh S. Cellular injury and neuroinflammation in children with chronic intractable epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation. 2009;6:38.
van Scheppingen J, Iyer AM, Prabowo AS, Muhlebner A, Anink JJ, Scholl T, Feucht M, Jansen FE, Spliet WG, Krsek P, Zamecnik J, Buccoliero AM, Giordano F, Genitori L, Kotulska K, Jozwiak S, Jaworski J, Liszewska E, van Vliet EA, Aronica E. Expression of microRNAs miR21, miR146a, and miR155 in tuberous sclerosis complex cortical tubers and their regulation in human astrocytes and SEGA-derived cell cultures. Glia. 2016;64(6):1066–82.
van Scheppingen J, Mills JD, Zimmer TS, Broekaart DWM, Iori V, Bongaarts A, Anink JJ, Iyer AM, Korotkov A, Jansen FE, van Hecke W, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Baayen JC, Vezzani A, van Vliet EA, Aronica E. miR147b: a novel key regulator of interleukin 1 beta-mediated inflammation in human astrocytes. Glia. 2018;66(5):1082–97.
Roncon P, Soukupova M, Binaschi A, Falcicchia C, Zucchini S, Ferracin M, Langley SR, Petretto E, Johnson MR, Marucci G, Michelucci R, Rubboli G, Simonato M. MicroRNA profiles in hippocampal granule cells and plasma of rats with pilocarpine-induced epilepsy--comparison with human epileptic samples. Sci Rep. 2015;5:14143.
Fabene PF, Navarro Mora G, Martinello M, Rossi B, Merigo F, Ottoboni L, Bach S, Angiari S, Benati D, Chakir A, Zanetti L, Schio F, Osculati A, Marzola P, Nicolato E, Homeister JW, Xia L, Lowe JB, McEver RP, Osculati F, Sbarbati A, Butcher EC, Constantin G. A role for leukocyte-endothelial adhesion mechanisms in epilepsy. Nat Med. 2008;14(12):1377–83.
Marchi N, Granata T, Freri E, Ciusani E, Ragona F, Puvenna V, Teng Q, Alexopolous A, Janigro D. Efficacy of anti-inflammatory therapy in a model of acute seizures and in a population of pediatric drug resistant epileptics. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e18200.
Ravizza T, Lucas SM, Balosso S, Bernardino L, Ku G, Noe F, Malva J, Randle JC, Allan S, Vezzani A. Inactivation of caspase-1 in rodent brain: a novel anticonvulsive strategy. Epilepsia. 2006;47(7):1160–8.
Maroso M, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Iori V, Wright CI, French J, Vezzani A. Interleukin-1beta biosynthesis inhibition reduces acute seizures and drug resistant chronic epileptic activity in mice. Neurotherapeutics. 2011;8(2):304–15.
Akin D, Ravizza T, Maroso M, Carcak N, Eryigit T, Vanzulli I, Aker RG, Vezzani A, Onat FY. IL-1beta is induced in reactive astrocytes in the somatosensory cortex of rats with genetic absence epilepsy at the onset of spike-and-wave discharges, and contributes to their occurrence. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;44(3):259–69.
Noe FM, Polascheck N, Frigerio F, Bankstahl M, Ravizza T, Marchini S, Beltrame L, Bandero CR, Loscher W, Vezzani A. Pharmacological blockade of IL-1beta/IL-1 receptor type 1 axis during epileptogenesis provides neuroprotection in two rat models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;59:183–93.
Iori V, Iyer AM, Ravizza T, Beltrame L, Paracchini L, Marchini S, Cerovic M, Hill C, Ferrari M, Zucchetti M, Molteni M, Rossetti C, Brambilla R, Steve White H, D’Incalci M, Aronica E, Vezzani A. Blockade of the IL-1R1/TLR4 pathway mediates disease-modification therapeutic effects in a model of acquired epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;99:12–23.
Maroso M, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Liu J, Aronica E, Iyer AM, Rossetti C, Molteni M, Casalgrandi M, Manfredi AA, Bianchi ME, Vezzani A. Toll-like receptor 4 and high-mobility group box-1 are involved in ictogenesis and can be targeted to reduce seizures. Nat Med. 2010;16(4):413–9.
Vezzani A, Conti M, De Luigi A, Ravizza T, Moneta D, Marchesi F, De Simoni MG. Interleukin-1beta immunoreactivity and microglia are enhanced in the rat hippocampus by focal kainate application: functional evidence for enhancement of electrographic seizures. J Neurosci. 1999;19(12):5054–65.
Vezzani A, Moneta D, Conti M, Richichi C, Ravizza T, De Luigi A, De Simoni MG, Sperk G, Andell-Jonsson S, Lundkvist J, Iverfeldt K, Bartfai T. Powerful anticonvulsant action of IL-1 receptor antagonist on intracerebral injection and astrocytic overexpression in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(21):11534–9.
Librizzi L, Noe F, Vezzani A, de Curtis M, Ravizza T. Seizure-induced brain-borne inflammation sustains seizure recurrence and blood-brain barrier damage. Ann Neurol. 2012;72(1):82–90.
Shinoda S, Skradski SL, Araki T, Schindler CK, Meller R, Lan JQ, Taki W, Simon RP, Henshall DC. Formation of a tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 molecular scaffolding complex and activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 during seizure-induced neuronal death. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17(10):2065–76.
Cacheaux LP, Ivens S, David Y, Lakhter AJ, Bar-Klein G, Shapira M, Heinemann U, Friedman A, Kaufer D. Transcriptome profiling reveals TGF-beta signaling involvement in epileptogenesis. J Neurosci. 2009;29(28):8927–35.
Ivens S, Kaufer D, Flores LP, Bechmann I, Zumsteg D, Tomkins O, Seiffert E, Heinemann U, Friedman A. TGF-beta receptor-mediated albumin uptake into astrocytes is involved in neocortical epileptogenesis. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 2):535–47.
Bar-Klein G, Cacheaux LP, Kamintsky L, Prager O, Weissberg I, Schoknecht K, Cheng P, Kim SY, Wood L, Heinemann U, Kaufer D, Friedman A. Losartan prevents acquired epilepsy via TGF-beta signaling suppression. Ann Neurol. 2014;75(6):864–75.
Weissberg I, Wood L, Kamintsky L, Vazquez O, Milikovsky DZ, Alexander A, Oppenheim H, Ardizzone C, Becker A, Frigerio F, Vezzani A, Buckwalter MS, Huguenard JR, Friedman A, Kaufer D. Albumin induces excitatory synaptogenesis through astrocytic TGF-beta/ALK5 signaling in a model of acquired epilepsy following blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Neurobiol Dis. 2015;78:115–25.
Cerri C, Caleo M, Bozzi Y. Chemokines as new inflammatory players in the pathogenesis of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2017;136:77–83.
Wilczynski GM, Konopacki FA, Wilczek E, Lasiecka Z, Gorlewicz A, Michaluk P, Wawrzyniak M, Malinowska M, Okulski P, Kolodziej LR, Konopka W, Duniec K, Mioduszewska B, Nikolaev E, Walczak A, Owczarek D, Gorecki DC, Zuschratter W, Ottersen OP, Kaczmarek L. Important role of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in epileptogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2008;180(5):1021–35.
Mizoguchi H, Nakade J, Tachibana M, Ibi D, Someya E, Koike H, Kamei H, Nabeshima T, Itohara S, Takuma K, Sawada M, Sato J, Yamada K. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to kindled seizure development in pentylenetetrazole-treated mice by converting pro-BDNF to mature BDNF in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2011;31(36):12963–71.
Asahi M, Wang X, Mori T, Sumii T, Jung JC, Moskowitz MA, Fini ME, Lo EH. Effects of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene knock-out on the proteolysis of blood-brain barrier and white matter components after cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 2001;21(19):7724–32.
Yeghiazaryan M, Rutkowska-Wlodarczyk I, Konopka A, Wilczynski GM, Melikyan A, Korkotian E, Kaczmarek L, Figiel I. DP-b99 modulates matrix metalloproteinase activity and neuronal plasticity. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e99789.
Gurney KJ, Estrada EY, Rosenberg GA. Blood-brain barrier disruption by stromelysin-1 facilitates neutrophil infiltration in neuroinflammation. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;23(1):87–96.
Tao H, Zhao J, Liu T, Cai Y, Zhou X, Xing H, Wang Y, Yin M, Zhong W, Liu Z, Li K, Zhao B, Zhou H, Cui L. Intranasal delivery of miR-146a mimics delayed seizure onset in the lithium-Pilocarpine mouse model. Mediat Inflamm. 2017;2017:6512620.
Chen J, Cai F, Jiang L, Hu Y, Feng C. A prospective study of dexamethasone therapy in refractory epileptic encephalopathy with continuous spike-and-wave during sleep. Epilepsy Behav. 2016;55:1–5.
Verhelst H, Boon P, Buyse G, Ceulemans B, D’Hooghe M, Meirleir LD, Hasaerts D, Jansen A, Lagae L, Meurs A, Coster RV, Vonck K. Steroids in intractable childhood epilepsy: clinical experience and review of the literature. Seizure. 2005;14(6):412–21.
Bialer M, Johannessen SI, Levy RH, Perucca E, Tomson T, White HS. Progress report on new antiepileptic drugs: a summary of the eleventh EILAT conference (EILAT XI). Epilepsy Res. 2013;103(1):2–30.
Kenney-Jung DL, Vezzani A, Kahoud RJ, LaFrance-Corey RG, Ho ML, Muskardin TW, Wirrell EC, Howe CL, Payne ET. Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome treated with anakinra. Ann Neurol. 2016;80(6):939–45.
Westbrook C, Subramaniam T, Seagren RM, Tarula E, Co D, Furstenberg-Knauff M, Wallace A, Hsu D, Payne E. Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome treated successfully with Anakinra in a 21-year-old woman. WMJ. 2019;118(3):135–9.
Jyonouchi H, Geng L. Intractable epilepsy (IE) and responses to Anakinra, a human recombinant IL-1 receptor agonist (IL-1ra): case reports. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2016;7(5):456.
Sa M, Singh R, Pujar S, D’Arco F, Desai N, Eltze C, Hughes E, Al Obaidi M, Eleftheriou D, Tisdall M, Selway R, Cross JH, Kaliakatsos M, Valentin A. Centromedian thalamic nuclei deep brain stimulation and Anakinra treatment for FIRES – two different outcomes. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2019;23(5):749–54.
Dilena R, Mauri E, Aronica E, Bernasconi P, Bana C, Cappelletti C, Carrabba G, Ferrero S, Giorda R, Guez S, Scalia Catenacci S, Triulzi F, Barbieri S, Calderini E, Vezzani A. Therapeutic effect of Anakinra in the relapsing chronic phase of febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome. Epilepsia Open. 2019;4(2):344–50.
Lagarde S, Villeneuve N, Trebuchon A, Kaphan E, Lepine A, McGonigal A, Roubertie A, Barthez MA, Trommsdorff V, Lefranc J, Wehbi S, des Portes V, Laguitton V, Quartier P, Scavarda D, Giusiano B, Milh M, Bulteau C, Bartolomei F. Anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy (adalimumab) in Rasmussen’s encephalitis: An open pilot study. Epilepsia. 2016;57(6):956–66.
Coomber BL, Stewart PA. Morphometric analysis of CNS microvascular endothelium. Microvasc Res. 1985;30(1):99–115.
Dejana E, Orsenigo F. Endothelial adherens junctions at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 12):2545–9.
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:403–29.
Van Itallie CM, Holmes J, Bridges A, Gookin JL, Coccaro MR, Proctor W, Colegio OR, Anderson JM. The density of small tight junction pores varies among cell types and is increased by expression of claudin-2. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 3):298–305.
Neuhaus J. Orthogonal arrays of particles in astroglial cells: quantitative analysis of their density, size, and correlation with intramembranous particles. Glia. 1990;3(4):241–51.
Attwell D, Buchan AM, Charpak S, Lauritzen M, Macvicar BA, Newman EA. Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature. 2010;468(7321):232–43.
Gordon GR, Howarth C, MacVicar BA. Bidirectional control of arteriole diameter by astrocytes. Exp Physiol. 2011;96(4):393–9.
Verhoog QP, Holtman L, Aronica E, Van Vliet EA. Astrocytes as guardians of neuronal excitability: mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis. Front Neurol. 2020;11:591690.
Obermeier B, Daneman R, Ransohoff RM. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med. 2013;19(12):1584–96.
Ozen I, Deierborg T, Miharada K, Padel T, Englund E, Genove G, Paul G. Brain pericytes acquire a microglial phenotype after stroke. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;128(3):381–96.
Balabanov R, Washington R, Wagnerova J, Dore-Duffy P. CNS microvascular pericytes express macrophage-like function, cell surface integrin alpha M, and macrophage marker ED-2. Microvasc Res. 1996;52(2):127–42.
Roth M, Gaceb A, Enstrom A, Padel T, Genove G, Ozen I, Paul G. Regulator of G-protein signaling 5 regulates the shift from perivascular to parenchymal pericytes in the chronic phase after stroke. FASEB J. 2019;33(8):8990–8.
Daneman R, Prat A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(1):a020412.
Del Zoppo GJ, Milner R, Mabuchi T, Hung S, Wang X, Koziol JA. Vascular matrix adhesion and the blood-brain barrier. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34(Pt 6):1261–6.
Sorokin L. The impact of the extracellular matrix on inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(10):712–23.
Wu C, Ivars F, Anderson P, Hallmann R, Vestweber D, Nilsson P, Robenek H, Tryggvason K, Song J, Korpos E, Loser K, Beissert S, Georges-Labouesse E, Sorokin LM. Endothelial basement membrane laminin alpha5 selectively inhibits T lymphocyte extravasation into the brain. Nat Med. 2009;15(5):519–27.
Poschl E, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U, Brachvogel B, Saito K, Ninomiya Y, Mayer U. Collagen IV is essential for basement membrane stability but dispensable for initiation of its assembly during early development. Development. 2004;131(7):1619–28.
Dong L, Chen Y, Lewis M, Hsieh JC, Reing J, Chaillet JR, Howell CY, Melhem M, Inoue S, Kuszak JR, DeGeest K, Chung AE. Neurologic defects and selective disruption of basement membranes in mice lacking entactin-1/nidogen-1. Lab Investig. 2002;82(12):1617–30.
Lau LW, Cua R, Keough MB, Haylock-Jacobs S, Yong VW. Pathophysiology of the brain extracellular matrix: a new target for remyelination. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14(10):722–9.
Dityatev A. Remodeling of extracellular matrix and epileptogenesis. Epilepsia. 2010;51(Suppl 3):61–5.
Hardingham TE, Fosang AJ. Proteoglycans: many forms and many functions. FASEB J. 1992;6(3):861–70.
Knudson CB, Knudson W. Hyaluronan-binding proteins in development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. FASEB J. 1993;7(13):1233–41.
Bonnans C, Chou J, Werb Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):786–801.
Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinases and their multiple roles in neurodegenerative diseases. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(2):205–16.
Haas TL, Madri JA. Extracellular matrix-driven matrix metalloproteinase production in endothelial cells: implications for angiogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999;9(3–4):70–7.
Rempe RG, Hartz AM, Bauer B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood-brain barrier: versatile breakers and makers. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(9):1481–507.
Mun-Bryce S, Rosenberg GA. Gelatinase B modulates selective opening of the blood-brain barrier during inflammation. Am J Phys. 1998;274(5):R1203–11.
Korotkov A, Broekaart DWM, Banchaewa L, Pustjens B, van Scheppingen J, Anink JJ, Baayen JC, Idema S, Gorter JA, van Vliet EA, Aronica E. microRNA-132 is overexpressed in glia in temporal lobe epilepsy and reduces the expression of pro-epileptogenic factors in human cultured astrocytes. Glia. 2020;68(1):60–75.
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Tepper D, Leonard A. Matrix metalloproteinases and blood-brain barrier disruption in acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. 2013;4:32.
Gidday JM, Gasche YG, Copin JC, Shah AR, Perez RS, Shapiro SD, Chan PH, Park TS. Leukocyte-derived matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates blood-brain barrier breakdown and is proinflammatory after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289(2):H558–68.
Rosell A, Cuadrado E, Ortega-Aznar A, Hernandez-Guillamon M, Lo EH, Montaner J. MMP-9-positive neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2008;39(4):1121–6.
Higashida T, Kreipke CW, Rafols JA, Peng C, Schafer S, Schafer P, Ding JY, Dornbos D 3rd, Li X, Guthikonda M, Rossi NF, Ding Y. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, aquaporin-4, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in blood-brain barrier disruption and brain edema after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2011;114(1):92–101.
Yang Y, Estrada EY, Thompson JF, Liu W, Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27(4):697–709.
Lischper M, Beuck S, Thanabalasundaram G, Pieper C, Galla HJ. Metalloproteinase mediated occludin cleavage in the cerebral microcapillary endothelium under pathological conditions. Brain Res. 2010;1326:114–27.
Rempe RG, Hartz AMS, Soldner ELB, Sokola BS. Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated blood-brain barrier dysfunction in epilepsy. J Neurosci. 2018;38(18):4301–15.
Vandenbroucke RE, Libert C. Is there new hope for therapeutic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(12):904–27.
Lees KR, Bornstein N, Diener HC, Gorelick PB, Rosenberg G, Shuaib A, Investigators M. Results of membrane-activated Chelator stroke intervention randomized trial of DP-b99 in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2013;44(3):580–4.
Chaturvedi M, Molino Y, Sreedhar B, Khrestchatisky M, Kaczmarek L. Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1 loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for delivery across the blood-brain barrier. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:575–88.
Zhao BQ, Wang S, Kim HY, Storrie H, Rosen BR, Mooney DJ, Wang X, Lo EH. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in delayed cortical responses after stroke. Nat Med. 2006;12(4):441–5.
Rosell A, Lo EH. Multiphasic roles for matrix metalloproteinases after stroke. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008;8(1):82–9.
Sood R, Yang Y, Taheri S, Candelario-Jalil E, Estrada EY, Walker EJ, Thompson J, Rosenberg GA. Increased apparent diffusion coefficients on MRI linked with matrix metalloproteinases and edema in white matter after bilateral carotid artery occlusion in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(2):308–16.
Henninger DD, Panes J, Eppihimer M, Russell J, Gerritsen M, Anderson DC, Granger DN. Cytokine-induced VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in different organs of the mouse. J Immunol. 1997;158(4):1825–32.
Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 2007;100(2):158–73.
Daneman R, Zhou L, Agalliu D, Cahoy JD, Kaushal A, Barres BA. The mouse blood-brain barrier transcriptome: a new resource for understanding the development and function of brain endothelial cells. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e13741.
Marchi N, Johnson AJ, Puvenna V, Johnson HL, Tierney W, Ghosh C, Cucullo L, Fabene PF, Janigro D. Modulation of peripheral cytotoxic cells and ictogenesis in a model of seizures. Epilepsia. 2011;52(9):1627–34.
Dinkel K, MacPherson A, Sapolsky RM. Novel glucocorticoid effects on acute inflammation in the CNS. J Neurochem. 2003;84(4):705–16.
Turrin NP, Rivest S. Innate immune reaction in response to seizures: implications for the neuropathology associated with epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 2004;16(2):321–34.
Kan AA, van Erp S, Derijck AA, de Wit M, Hessel EV, O’Duibhir E, de Jager W, Van Rijen PC, Gosselaar PH, de Graan PN, Pasterkamp RJ. Genome-wide microRNA profiling of human temporal lobe epilepsy identifies modulators of the immune response. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(18):3127–45.
Marchi N, Teng Q, Ghosh C, Fan Q, Nguyen MT, Desai NK, Bawa H, Rasmussen P, Masaryk TK, Janigro D. Blood-brain barrier damage, but not parenchymal white blood cells, is a hallmark of seizure activity. Brain Res. 2010;1353:176–86.
Vezzani A, Granata T. Brain inflammation in epilepsy: experimental and clinical evidence. Epilepsia. 2005;46(11):1724–43.
Xu D, Robinson AP, Ishii T, Duncan DS, Alden TD, Goings GE, Ifergan I, Podojil JR, Penaloza-MacMaster P, Kearney JA, Swanson GT, Miller SD, Koh S. Peripherally derived T regulatory and gammadelta T cells have opposing roles in the pathogenesis of intractable pediatric epilepsy. J Exp Med. 2018;215(4):1169–86.
Zattoni M, Mura ML, Deprez F, Schwendener RA, Engelhardt B, Frei K, Fritschy JM. Brain infiltration of leukocytes contributes to the pathophysiology of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci. 2011;31(11):4037–50.
Rock KL, Latz E, Ontiveros F, Kono H. The sterile inflammatory response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010;28:321–42.
Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997;8(4):253–65.
Vezzani A, Maroso M, Balosso S, Sanchez MA, Bartfai T. IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling in infection, inflammation, stress and neurodegeneration couples hyperexcitability and seizures. Brain Behav Immun. 2011;25(7):1281–9.
Tsai SJ. Effects of interleukin-1beta polymorphisms on brain function and behavior in healthy and psychiatric disease conditions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;37:89–97.
Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ. Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(8):629–40.
Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1(2):135–45.
Li G, Bauer S, Nowak M, Norwood B, Tackenberg B, Rosenow F, Knake S, Oertel WH, Hamer HM. Cytokines and epilepsy. Seizure. 2011;20(3):249–56.
Virta M, Hurme M, Helminen M. Increased frequency of interleukin-1beta (-511) allele 2 in febrile seizures. Pediatr Neurol. 2002;26(3):192–5.
Kanemoto K, Kawasaki J, Yuasa S, Kumaki T, Tomohiro O, Kaji R, Nishimura M. Increased frequency of interleukin-1beta-511T allele in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy, hippocampal sclerosis, and prolonged febrile convulsion. Epilepsia. 2003;44(6):796–9.
Haspolat S, Mihci E, Coskun M, Gumuslu S, Ozben T, Yegin O. Interleukin-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and nitrite levels in febrile seizures. J Child Neurol. 2002;17(10):749–51.
Shaftel SS, Carlson TJ, Olschowka JA, Kyrkanides S, Matousek SB, O’Banion MK. Chronic interleukin-1beta expression in mouse brain leads to leukocyte infiltration and neutrophil-independent blood brain barrier permeability without overt neurodegeneration. J Neurosci. 2007;27(35):9301–9.
Marchi N, Fan Q, Ghosh C, Fazio V, Bertolini F, Betto G, Batra A, Carlton E, Najm I, Granata T, Janigro D. Antagonism of peripheral inflammation reduces the severity of status epilepticus. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;33(2):171–81.
Proescholdt MG, Chakravarty S, Foster JA, Foti SB, Briley EM, Herkenham M. Intracerebroventricular but not intravenous interleukin-1beta induces widespread vascular-mediated leukocyte infiltration and immune signal mRNA expression followed by brain-wide glial activation. Neuroscience. 2002;112(3):731–49.
Bernardes-Silva M, Anthony DC, Issekutz AC, Perry VH. Recruitment of neutrophils across the blood-brain barrier: the role of E- and P-selectins. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21(9):1115–24.
John GR, Lee SC, Song X, Rivieccio M, Brosnan CF. IL-1-regulated responses in astrocytes: relevance to injury and recovery. Glia. 2005;49(2):161–76.
Devinsky O, Vezzani A, Najjar S, De Lanerolle NC, Rogawski MA. Glia and epilepsy: excitability and inflammation. Trends Neurosci. 2013;36(3):174–84.
Viviani B, Bartesaghi S, Gardoni F, Vezzani A, Behrens MM, Bartfai T, Binaglia M, Corsini E, Di Luca M, Galli CL, Marinovich M. Interleukin-1beta enhances NMDA receptor-mediated intracellular calcium increase through activation of the Src family of kinases. J Neurosci. 2003;23(25):8692–700.
Wang S, Cheng Q, Malik S, Yang J. Interleukin-1beta inhibits gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A)) receptor current in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;292(2):497–504.
Roseti C, van Vliet EA, Cifelli P, Ruffolo G, Baayen JC, Di Castro MA, Bertollini C, Limatola C, Aronica E, Vezzani A, Palma E. GABAA currents are decreased by IL-1beta in epileptogenic tissue of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: implications for ictogenesis. Neurobiol Dis. 2015;82:311–20.
Dey A, Kang X, Qiu J, Du Y, Jiang J. Anti-inflammatory small molecules to treat seizures and epilepsy: from bench to bedside. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016;37(6):463–84.
Ferrarese C, Mascarucci P, Zoia C, Cavarretta R, Frigo M, Begni B, Sarinella F, Frattola L, De Simoni MG. Increased cytokine release from peripheral blood cells after acute stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19(9):1004–9.
Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, di Sciacca R, Pinto A, Licata G. Inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(33):3574–89.
Sriram K, O’Callaghan JP. Divergent roles for tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2007;2(2):140–53.
Griffin WS, Barger SW. Neuroinflammatory cytokines-the common thread in Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. US Neurol. 2010;6(2):19–27.
Balosso S, Ravizza T, Perego C, Peschon J, Campbell IL, De Simoni MG, Vezzani A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits seizures in mice via p75 receptors. Ann Neurol. 2005;57(6):804–12.
Akassoglou K, Probert L, Kontogeorgos G, Kollias G. Astrocyte-specific but not neuron-specific transmembrane TNF triggers inflammation and degeneration in the central nervous system of transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1997;158(1):438–45.
Vezzani A, Balosso S, Ravizza T. The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Brain Behav Immun. 2008;22(6):797–803.
MacEwan DJ. TNF ligands and receptors – a matter of life and death. Br J Pharmacol. 2002;135(4):855–75.
Balosso S, Ravizza T, Pierucci M, Calcagno E, Invernizzi R, Di Giovanni G, Esposito E, Vezzani A. Molecular and functional interactions between tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptors and the glutamatergic system in the mouse hippocampus: implications for seizure susceptibility. Neuroscience. 2009;161(1):293–300.
Weinberg MS, Blake BL, McCown TJ. Opposing actions of hippocampus TNFalpha receptors on limbic seizure susceptibility. Exp Neurol. 2013;247:429–37.
Mark KS, Miller DW. Increased permeability of primary cultured brain microvessel endothelial cell monolayers following TNF-alpha exposure. Life Sci. 1999;64(21):1941–53.
Nishioku T, Matsumoto J, Dohgu S, Sumi N, Miyao K, Takata F, Shuto H, Yamauchi A, Kataoka Y. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates the blood-brain barrier dysfunction induced by activated microglia in mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;112(2):251–4.
Fiala M, Looney DJ, Stins M, Way DD, Zhang L, Gan X, Chiappelli F, Schweitzer ES, Shapshak P, Weinand M, Graves MC, Witte M, Kim KS. TNF-alpha opens a paracellular route for HIV-1 invasion across the blood-brain barrier. Mol Med. 1997;3(8):553–64.
Lopez-Ramirez MA, Fischer R, Torres-Badillo CC, Davies HA, Logan K, Pfizenmaier K, Male DK, Sharrack B, Romero IA. Role of caspases in cytokine-induced barrier breakdown in human brain endothelial cells. J Immunol. 2012;189(6):3130–9.
Forster C, Burek M, Romero IA, Weksler B, Couraud PO, Drenckhahn D. Differential effects of hydrocortisone and TNFalpha on tight junction proteins in an in vitro model of the human blood-brain barrier. J Physiol. 2008;586(7):1937–49.
Aslam M, Ahmad N, Srivastava R, Hemmer B. TNF-alpha induced NFkappaB signaling and p65 (RelA) overexpression repress Cldn5 promoter in mouse brain endothelial cells. Cytokine. 2012;57(2):269–75.
Lutgendorf MA, Ippolito DL, Mesngon MT, Tinnemore D, Dehart MJ, Dolinsky BM, Napolitano PG. Effect of dexamethasone administered with magnesium sulfate on inflammation-mediated degradation of the blood-brain barrier using an in vitro model. Reprod Sci. 2014;21(4):483–91.
Abdullah Z, Bayraktutan U. NADPH oxidase mediates TNF-alpha-evoked in vitro brain barrier dysfunction: roles of apoptosis and time. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014;61:72–84.
Wilson CM, Gaber MW, Sabek OM, Zawaski JA, Merchant TE. Radiation-induced astrogliosis and blood-brain barrier damage can be abrogated using anti-TNF treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74(3):934–41.
Lv S, Song HL, Zhou Y, Li LX, Cui W, Wang W, Liu P. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha affects blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction-associated occludin in acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2010;30(8):1198–210.
Kim JE, Ryu HJ, Kang TC. Status epilepticus induces vasogenic edema via tumor necrosis factor-alpha/ endothelin-1-mediated two different pathways. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74458.
Vezzani A, Viviani B. Neuromodulatory properties of inflammatory cytokines and their impact on neuronal excitability. Neuropharmacology. 2015;96(Pt A):70–82.
Iori V, Frigerio F, Vezzani A. Modulation of neuronal excitability by immune mediators in epilepsy. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016;26:118–23.
Beattie EC, Stellwagen D, Morishita W, Bresnahan JC, Ha BK, Von Zastrow M, Beattie MS, Malenka RC. Control of synaptic strength by glial TNFalpha. Science. 2002;295(5563):2282–5.
Stellwagen D, Beattie EC, Seo JY, Malenka RC. Differential regulation of AMPA receptor and GABA receptor trafficking by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Neurosci. 2005;25(12):3219–28.
Wheeler D, Knapp E, Bandaru VV, Wang Y, Knorr D, Poirier C, Mattson MP, Geiger JD, Haughey NJ. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced neutral sphingomyelinase-2 modulates synaptic plasticity by controlling the membrane insertion of NMDA receptors. J Neurochem. 2009;109(5):1237–49.
Takeuchi H, Jin S, Wang J, Zhang G, Kawanokuchi J, Kuno R, Sonobe Y, Mizuno T, Suzumura A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces neurotoxicity via glutamate release from hemichannels of activated microglia in an autocrine manner. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(30):21362–8.
Bezzi P, Domercq M, Brambilla L, Galli R, Schols D, De Clercq E, Vescovi A, Bagetta G, Kollias G, Meldolesi J, Volterra A. CXCR4-activated astrocyte glutamate release via TNFalpha: amplification by microglia triggers neurotoxicity. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4(7):702–10.
Abdullah Z, Rakkar K, Bath PM, Bayraktutan U. Inhibition of TNF-alpha protects in vitro brain barrier from ischaemic damage. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015;69:65–79.
Massague J. TGFbeta signalling in context. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(10):616–30.
Ralay Ranaivo H, Wainwright MS. Albumin activates astrocytes and microglia through mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Brain Res. 2010;1313:222–31.
Ralay Ranaivo H, Patel F, Wainwright MS. Albumin activates the canonical TGF receptor-smad signaling pathway but this is not required for activation of astrocytes. Exp Neurol. 2010;226(2):310–9.
Friedman A, Bar-Klein G, Serlin Y, Parmet Y, Heinemann U, Kaufer D. Should losartan be administered following brain injury? Expert Rev Neurother. 2014;14(12):1365–75.
Kim SY, Buckwalter M, Soreq H, Vezzani A, Kaufer D. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction-induced inflammatory signaling in brain pathology and epileptogenesis. Epilepsia. 2012;53(Suppl 6):37–44.
Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Kunkel SL, Andjelkovic AV. Potential role of MCP-1 in endothelial cell tight junction ‘opening’: signaling via Rho and Rho kinase. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 22):4615–28.
Song L, Pachter JS. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 alters expression of tight junction-associated proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 2004;67(1):78–89.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97.
Henshall DC. MicroRNA and epilepsy: profiling, functions and potential clinical applications. Curr Opin Neurol. 2014;27(2):199–205.
Korotkov A, Mills JD, Gorter JA, van Vliet EA, Aronica E. Systematic review and meta-analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):11592.
Quinn SR, O’Neill LA. A trio of microRNAs that control toll-like receptor signalling. Int Immunol. 2011;23(7):421–5.
Tiwari D, Peariso K, Gross C. MicroRNA-induced silencing in epilepsy: opportunities and challenges for clinical application. Dev Dyn. 2018;247(1):94–110.
Iyer A, Zurolo E, Prabowo A, Fluiter K, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Gorter JA, Aronica E. MicroRNA-146a: a key regulator of astrocyte-mediated inflammatory response. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44789.
Caballero-Garrido E, Pena-Philippides JC, Lordkipanidze T, Bragin D, Yang Y, Erhardt EB, Roitbak T. In vivo inhibition of miR-155 promotes recovery after experimental mouse stroke. J Neurosci. 2015;35(36):12446–64.
Lopez-Ramirez MA, Wu D, Pryce G, Simpson JE, Reijerkerk A, King-Robson J, Kay O, de Vries HE, Hirst MC, Sharrack B, Baker D, Male DK, Michael GJ, Romero IA. MicroRNA-155 negatively affects blood-brain barrier function during neuroinflammation. FASEB J. 2014;28(6):2551–65.
Jimenez-Mateos EM, Engel T, Merino-Serrais P, McKiernan RC, Tanaka K, Mouri G, Sano T, O’Tuathaigh C, Waddington JL, Prenter S, Delanty N, Farrell MA, O’Brien DF, Conroy RM, Stallings RL, DeFelipe J, Henshall DC. Silencing microRNA-134 produces neuroprotective and prolonged seizure-suppressive effects. Nat Med. 2012;18(7):1087–94.
Henshall DC. Manipulating microRNAs in murine models: targeting the multi-targeting in epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr. 2017;17(1):43–7.
Chakraborty C, Sharma AR, Sharma G, Doss CGP, Lee SS. Therapeutic miRNA and siRNA: moving from bench to clinic as next generation medicine. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;8:132–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Broekaart, D.W.M., Korotkov, A., Gorter, J.A., van Vliet, E.A. (2021). Perivascular Inflammation and Extracellular Matrix Alterations in Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction and Epilepsy. In: Janigro, D., Nehlig, A., Marchi, N. (eds) Inflammation and Epilepsy: New Vistas. Progress in Inflammation Research, vol 88. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67403-8_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67403-8_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-67402-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-67403-8
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)