Abstract
Twitter is one of the most popular social media platforms. Due to its simplicity of use and the services provided by twitter API, it is extensively used around the world, including Morocco. It provides huge volume of information and is considered as a large source of data for opinion mining.
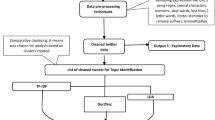
The aim of this paper is to analyze Moroccan tweets, in order to generate some useful statistics, identify different sentiments, and extract then visualize predominant topics. In our research work, we collected 25 146 tweets using Twitter API and python language, and stored them into MongoDB database. Stored tweets were preprocessed by applying natural language processing techniques (NLP) using NLTK library. Then, we performed sentiment analysis which classifies the polarity of twitter comments into negative, positive, and neutral categories. Finally, we applied topic modeling over the tweets to obtain meaningful data from Twitter, comparing and analyzing topics detected by two popular topic modeling algorithms; Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA). The observed results show that LDA outperforms NMF in terms of their topic coherence.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
«Twitter Usage Statistics - Internet Live Stats». https://www.internetlivestats.com/twitter-statistics/. (consultéle févr. 19, 2020)
«DataReportal – Global Digital Insights». [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://datareportal.com. [Consulté le: le mars 25, 2020]
Tripathi, P., Vishwakarma, S., Lala, A.: Sentiment analysis of English tweets using rapid miner. In : 2015 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Jabalpur, India, pp. 668–672 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CICN.2015.137
Al-Thubaity, A., Alqahtani, Q., Aljandal, A.: Sentiment lexicon for sentiment analysis of Saudi dialect tweets. Proc. Comput. Sci. 142, 301–307 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.494
Wang, X., Yu, Y., Lin, L.: Tweeting the United Nations climate change conference in Paris (COP21): an analysis of a social network and factors determining the network influence. Online Soc. Netw. Med. 15, 100059 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.osnem.2019.100059
Cvetojevic, S., Hochmair, H.H.: Analyzing the spread of tweets in response to Paris attacks. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 71, 14–26 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2018.03.010
Ray, S.K., Ahmad, A., Kumar, C.A.: Review and implementation of topic modeling in Hindi. Appl. Artif. Intell. 33(11), 979–1007 (2019).https://doi.org/10.1080/08839514.2019.1661576
Greene, D., Cross, J.P.: Exploring the Political Agenda of the European Parliament Using a Dynamic Topic Modeling Approach. ArXiv160703055 Cs, juill. 2016, Consulté le: mai 30, 2020. [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.03055
Pasquali, A.R.: Automatic coherence evaluation applied to Topic Models (2016)
Ilyas, S.H.W., Soomro, Z.T., Anwar, A., Shahzad, H., Yaqub, U.: «Analyzing Brexit’s impact using sentiment analysis and topic modeling on Twitter discussion», p. 7 (2020)
Dahal, B., Kumar, S.A.P., Li, Z.: Topic modeling and sentiment analysis of global climate change tweets. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 9(1), 24 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-019-0568-8
«Tweepy». [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://www.tweepy.org/. [Consulté le: 25-nov-2019]
«The most popular database for modern apps», MongoDB. [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://www.mongodb.com. [Consulté le: 25-nov-2019]
Siddharth, S., Darsini, R., Sujithra, D.M.: Sentiment Analysis On Twitter Data Using Machine Learning Algorithms in Python, p. 15
«seaborn: statistical data visualization—seaborn 0.10.0 documentation». [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://seaborn.pydata.org/. [Consulté le: 12-févr-2020]
«Matplotlib: Python plotting—Matplotlib 3.1.3 documentation». [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://matplotlib.org/. [Consulté le: 12-févr-2020]
Blei, D.M. : Latent Dirichlet Allocation, p. 30
Chen, Y., et al.: Experimental explorations on short text topic mining between LDA and NMF based schemes. Knowl.-Based Syst. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.08.011
Mclachlan, G.J., Krishnan, T.: The EM Algorithm and Extensions. John Wiley (2007)
Nugraha, P., Rifky Yusdiansyah, M., Murfi, H.: Fuzzy C-means in lower dimensional space for topics detection on Indonesian online news. In: Tan, Y., Shi, Y. (eds.) Data Mining and Big Data, vol. 1071, pp. 269–276. Springer, Singapore (2019)
«Natural Language Toolkit—NLTK 3.4.5 documentation». [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://www.nltk.org/. [Consulté le: 17-févr-2020]
Loria, S.: textblob Documentation, pp. 1–73 (2018)
Rehurek, R.: «gensim: Python framework for fast Vector Space Modelling». [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://pypi.org/project/gensim/. [Consulté le: 26-févr-2020]
«scikit-learn: machine learning in Python—scikit-learn 0.23.1 documentation». https://scikit-learn.org/stable/ (consulté le juin 06, 2020)
McCallum, A.: Mallet: A Machine Learning for Language Toolkit (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Habbat, N., Anoun, H., Hassouni, L. (2021). Topic Modeling and Sentiment Analysis with LDA and NMF on Moroccan Tweets. In: Ben Ahmed, M., Rakıp Karaș, İ., Santos, D., Sergeyeva, O., Boudhir, A.A. (eds) Innovations in Smart Cities Applications Volume 4. SCA 2020. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 183. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66840-2_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66840-2_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-66839-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-66840-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)