Abstract
An important component of a NLP system with the neural network architecture is an encoder that represents word features as dense vector representations, i.e. feature embeddings. According to the concept of feature embeddings, features sharing common linguistic information should have similar vectors and thus feature similarities can be captured. In this paper we investigate which features should be used in estimating NLP models of the fusional languages – tokens or lemmata. Furthermore, we research the methodological question whether the results of the intrinsic evaluation of feature embeddings are informative for downstream applications, or feature embedding models should be evaluated extrinsically. The presented evaluation experiments are conducted on Polish – a fusional Slavic language with a relatively free word order. However, the evaluation results can be approximately generalised to other Slavic languages, because the studied problems are common to them.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
Not only words but also texts, e.g. sentences or documents, or even images, can be represented as feature embeddings. However, the research presented in this article is limited to word features.
- 2.
According to Aikhenvald (2007:4), in “fusional – sometimes misleadingly called (in)flectional languages – there is no clear boundary between morphemes, and thus semantically distinct features are usually merged in a single bound form or in closely united bound forms”. For example, the suffixes
 in Russian
in Russian
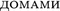 (‘house’.inst.pl) and -ami in Polish domami (‘house’.inst.pl) fuse the case and number information.
(‘house’.inst.pl) and -ami in Polish domami (‘house’.inst.pl) fuse the case and number information. - 3.
- 4.
Tokens are automatically lemmatised, in order to enable the comparison with the test sets.
- 5.
Throughout this paper, we use the following terms: lemma for a word’s base form (e.g. kot ‘cat’); token for a string of characters in running text (e.g. kota ‘cat’); inflectional form/inflection for a token assigned a morphosyntactic interpretation (e.g. kota.subst:acc:sg:m2, kota.subst:gen:sg:m2).
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
Cosine similarity is a measure of similarity between two words that measures the cosine of the angle between embeddings of these words.
- 14.
The \(\mathcal {L}\) models are not considered here since correct lemmata for tokens are typically not yet determined at the MD stage of text processing for Polish.
- 15.
We provide both the micro- and marco-average scores.
- 16.
- 17.
References
Andor, D., et al.: Globally normalized transition-based neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 2442–2452. Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin (2016). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P16-1231
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate (2014). http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0473
Bojanowski, P., Grave, E., Joulin, A., Mikolov, T.: Enriching word vectors with subword information. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 5, 135–146 (2017). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/Q17-1010
Chen, D., Manning, C.: A fast and accurate dependency parser using neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 740–750. Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha (2014). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/D14-1082
Chiu, B., Korhonen, A., Pyysalo, S.: Intrinsic evaluation of word vectors fails to predict extrinsic performance. In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Evaluating Vector-Space Representations for NLP, pp. 1–6. Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin (2016). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/W16-2501
Cho, K., et al.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 1724–1734. Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha (2014). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/D14-1179
Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pp. 4171–4186. Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis (2019). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N19-1423
Dozat, T., Qi, P., Manning, C.D.: Stanford’s graph-based neural dependency parser at the CoNLL 2017 shared task. In: Proceedings of the CoNLL 2017 Shared Task: Multilingual Parsing from Raw Text to Universal Dependencies, pp. 20–30. Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver (2017). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/K17-3002
Drozd, A., Gladkova, A., Matsuoka, S.: Word embeddings, analogies, and machine learning: beyond king\(-\)man\(+\)woman\(=\)queen. In: Proceedings of COLING 2016, the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers, pp. 3519–3530. The COLING 2016 Organizing Committee, Osaka (2016). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/C16-1332
Faruqui, M., Tsvetkov, Y., Rastogi, P., Dyer, C.: Problems with evaluation of word embeddings using word similarity tasks. In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Evaluating Vector-Space Representations for NLP, pp. 30–35. Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin (2016). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/W16-2506
Finkelstein, L., et al.: Placing search in context: the concept revisited. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 20(1), 116–131 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1145/503104.503110
Grave, E., Bojanowski, P., Gupta, P., Joulin, A., Mikolov, T.: Learning word vectors for 157 languages. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018). European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Miyazaki (2018). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/L18-1550
Hill, F., Reichart, R., Korhonen, A.: SimLex-999: evaluating semantic models with (genuine) similarity estimation. Computat. Linguist. 41(4), 665–695 (2015). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/J15-4004
Iyyer, M., Manjunatha, V., Boyd-Graber, J., Daumé III, H.: Deep unordered composition rivals syntactic methods for text classification. In: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 1681–1691. Association for Computational Linguistics, Beijing (2015). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P15-1162
Kiperwasser, E., Goldberg, Y.: Simple and accurate dependency parsing using bidirectional lstm feature representations. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 4, 313–327 (2016). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/Q16-1023
Kobyliński, Ł., Kieraś, W.: Part of speech tagging for polish: state of the art and future perspectives. In: Proceedings of Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing, pp. 307–319 (2016)
Kobyliński, Ł., Ogrodniczuk, M.: Results of the PolEval 2017 competition: part-of-speech tagging shared task. In: Vetulani, Z., Paroubek, P. (eds.) Proceedings of the 8th Language & Technology Conference: Human Language Technologies as a Challenge for Computer Science and Linguistics, pp. 362–366. Fundacja Uniwersytetu im. Adama Mickiewicza w Poznaniu, Poznań (2017)
Krasnowska-Kieraś, K.: Morphosyntactic disambiguation for Polish with bi-LSTM neural networks. In: Vetulani, Z., Paroubek, P. (eds.) Proceedings of the 8th Language & Technology Conference: Human Language Technologies as a Challenge for Computer Science and Linguistics, pp. 367–371. Fundacja Uniwersytetu im. Adama Mickiewicza w Poznaniu, Poznań (2017). http://ltc.amu.edu.pl/book2017/papers/PolEval1-2.pdf
Leviant, I., Reichart, R.: Separated by an un-common language: towards judgment language informed vector space modeling. CoRR abs/1508.00106 (2015). http://arxiv.org/abs/1508.00106
Linzen, T.: Issues in evaluating semantic spaces using word analogies. In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Evaluating Vector-Space Representations for NLP, pp. 13–18. Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin (2016). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/W16-2503
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S., Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Burges, C.J.C., Bottou, L., Welling, M., Ghahramani, Z., Weinberger, K.Q. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 26, pp. 3111–3119. Curran Associates, Inc. (2013). http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5021-distributed-representations-of-words-and-phrases-and-their-compositionality.pdf
Mikolov, T., Yih, W.t., Zweig, G.: Linguistic regularities in continuous space word representations. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 746–751. Association for Computational Linguistics, Atlanta (2013). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N13-1090
Mykowiecka, A., Marciniak, M., Rychlik, P.: Testing word embeddings for Polish. Cogn. Stud./Études Cogn. 17, 1–19 (2017). https://ispan.waw.pl/journals/index.php/cs-ec/article/view/cs.1468
Nivre, J., Hall, J., Nilsson, J.: MaltParser: a data-driven parser-generator for dependency parsing. In: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2006), pp. 2216–2219. European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Genoa (2006). http://www.lrec-conf.org/proceedings/lrec2006/pdf/162_pdf.pdf
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.: GloVe: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp. 1532–1543. Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha (2014). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/D14-1162
Przepiórkowski, A., Bańko, M., Górski, R.L., Lewandowska-Tomaszczyk, B. (eds.): Narodowy Korpus Języka Polskiego. Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN, Warsaw (2012)
Řehůřek, R., Sojka, P.: Software framework for topic modelling with large corpora. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on New Challenges for NLP Frameworks, pp. 45–50 (2010)
Rybak, P., Wróblewska, A.: Semi-supervised neural system for tagging, parsing and lematization. In: Proceedings of the CoNLL 2018 Shared Task: Multilingual Parsing from Raw Text to Universal Dependencies, pp. 45–54. Association for Computational Linguistics, Brussels (2018). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/K18-2004
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., Le, Q.V.: Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In: Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N.D., Weinberger, K.Q. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 27, pp. 3104–3112. Curran Associates, Inc. (2014). http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5346-sequence-to-sequence-learning-with-neural-networks.pdf
Vulić, I., Mrkšić, N., Reichart, R., Ó Séaghdha, D., Young, S., Korhonen, A.: Morph-fitting: fine-tuning word vector spaces with simple language-specific rules. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 56–68. Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver (2017). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P17-1006
Wróblewska, A.: Polish dependency parser trained on an automatically induced dependency bank. Ph.D. dissertation, ICS PAS, Warsaw (2014)
Wróblewska, A., Rybak, P.: Dependency Parsing of Polish. Poznań Stud. Contemp. Linguist. 55(2), 305–337 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1515/psicl-2019-0012
Acknowledgments
The presented research was supported by SONATA 8 grant no 2014/15/D/HS2/03486 from the National Science Centre Poland. The computing was performed at Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wróblewska, A., Krasnowska-Kieraś, K., Rybak, P. (2020). Towards the Evaluation of Feature Embedding Models of the Fusional Languages. In: Vetulani, Z., Paroubek, P., Kubis, M. (eds) Human Language Technology. Challenges for Computer Science and Linguistics. LTC 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12598. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66527-2_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66527-2_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-66526-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-66527-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


 in Russian
in Russian
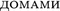 (‘house’.
(‘house’.