Abstract
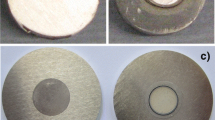
In this paper, the method of quantitative analysis by GDMS of Fe, Si, Cu, and other nine impure elements in pure magnesium was studied. The applicable method for the preparation of samples was confirmed. The isotopes, resolution, and the analysis conditions were optimized. In addition, RSF of these impure elements was obtained using standard samples in order to correct the standard RSF. The results showed that using wire cutting introduces fewer impurities. When the discharge current was 55 mA and the gas flow was 350 mL/min, matrix signal was stable and suitable. Quantitative analysis of samples with the RSF314 showed better precision and accuracy than using the standard RSF. Comparison with the results of ICP-AES, AAS, and ICP-MS, the testing results were closer to the standard value which were obtained by our studies. But our method was more convenient on sample preparation, faster analysis speed, and higher overall accuracy than other means.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y C, Tian Y, Qu T, et al. Purification of Magnesium by Vacuum Distillation and its Analysis[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2014, 788:52–57. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.788.52.
Dai Y, Tao M, Ma C. ICP-AES Determination of 9 Alloying Elements in Magnesium Alloys[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis Part B Chemical Analysis, 2004, 40(3): 155–158.
Ashy M A, Headridge J B, Sowerbutts A. Determination of trace and minor elements in alloys by atomic-absorption spectroscopy using an induction-heated graphite-well furnace as atom source—II[J]. Talanta, 1974, 21(6):649–652. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.788.52. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-9140(74)80205-5,
Tan M E I, Mei-juan T A O, Guo-qiang Y A N. ICP-AES Determination of Silicon in Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys [J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2009, 5.
Welz B. High-resolution continuum source AAS: the better way to perform atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2005, 381(1): 69–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2891-8.
Bogaerts A, Neyts E, Gijbels R, et al. Gas discharge plasmas and their applications[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B Atomic Spectroscopy, 2002, 57(4):609–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0584-8547(01)00406-2.
Harrison W W, Hess K R, Marcus R K, et al. Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1986, 58(2):341A-356A. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-82724-2_17.
Chapman, Brian N. Glow discharge processes[M]. Wiley, 1980.
Beatriz Fernández, Costa J M, Pereiro R, et al. Inorganic mass spectrometry as a tool for characterization at the nanoscale[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2010, 396(1): 15–29.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2959-6.
Dong J, Qian R, Xiong W, et al. Determination of doping elements of synthetic crystals by direct current glow discharge mass spectrometry[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2014, 361:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2014.01.018.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 51734006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhao, J., Wu, J., Xu, B., Yang, Q., Yang, B. (2021). Quantitative Analysis of Impurity Elements in Pure Magnesium by Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry (GDMS). In: Miller, V.M., Maier, P., Jordon, J.B., Neelameggham, N.R. (eds) Magnesium Technology 2021. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65528-0_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65528-0_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-65527-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-65528-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)