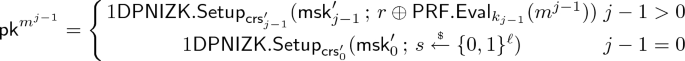Abstract
We present a novel tree-based technique that can convert any designated-prover NIZK proof system (DP-NIZK) which maintains zero-knowledge only for single statement, into one that allows to prove an unlimited number of statements in ZK, while maintaining all parameters succinct. Our transformation requires leveled fully-homomorphic encryption. We note that single-statement DP-NIZK can be constructed from any one-way function. We also observe a two-way derivation between DP-NIZK and attribute-based signatures (ABS), and as a result derive now constructions of ABS and homomorphic signatures (HS).
Our construction improves upon the prior construction of lattice-based DP-NIZK by Kim and Wu (Crypto 2018) since we only require leveled FHE as opposed to HS (which also translates to improved LWE parameters when instantiated). Alternatively, the recent construction of NIZK without preprocessing from either circular-secure FHE (Canetti et al. STOC 2019) or polynomial Learning with Errors (Peikert and Shiehian, Crypto 2019) could be used to obtain a similar final statement. Nevertheless, we note that our statement is formally incomparable to these works (since leveled FHE is not known to imply circular secure FHE or the hardness of LWE). We view this as evidence for the potential in our technique, which we hope can find additional applications in future works.
Z. Brakerski and R. Tsabary—Supported by the Binational Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016726), and by the European Union Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program via ERC Project REACT (Grant 756482) and via Project PROMETHEUS (Grant 780701).
S. Garg—Supported in part from AFOSR Award FA9550-19-1-0200, NSF CNS Award 1936826, DARPA SIEVE Award, and research grants by the Sloan Foundation, Visa Inc., and Center for Long-Term Cybersecurity (CLTC, UC Berkeley). Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the funding agencies.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
In non-interactive zero-knowledge proof systems for NP (NIZK) [BFM88], a prover can provide a non-interactive proof of the validity of an NP statement (efficiently, using a witness), that convinces a verifier, without revealing any information about the witness or anything other than the validity of the statement. This is not possible to achieve in the plain model, and therefore usually some common setup is considered, in particular it is often assumed that an honestly generated common reference string (CRS) is accessible to both the prover and the verifier [FLS90]. In this work we consider proof systems with statistical soundness and computational zero-knowledge.
NIZK with Preprocessing. In some cases it suffices to consider a relaxed notion, NIZK with preprocessing [SMP87], where the trusted party that generates the CRS also produces additional secret information either for the prover or for the verifier or for both. As pointed out by Kim and Wu [KW18], multi-theorem preprocessing NIZK could replace plain NIZK in a number of applications, e.g. for achieving MPC with low round complexity.
In the case of secret information for the prover, known as designated-prover NIZK or DP-NIZK, the prover’s key should be kept secret in order to maintain zero-knowledge. In the mirror case of designated-verifier NIZK (DV-NIZK), the verifier’s secret is for the purposes of securing the soundness. In both cases, the preprocessing might make the CRS non-reusable. That is, if the same secret key of the prover (resp. verifier) is used in the proofs of multiple statements then ZK (resp. soundness) might not hold for all of these statements. Therefore, we make the distinction between single-theorem and multi-theorem NIZK in the preprocessing model. We note that throughout this introduction, writing DP/DV-NIZK refers by default to the multi-theorem version.
The seminal work of [FLS90] shows, among other things, how to transform any single-statement NIZK proof system into a multi-statement NIZK. [KNYY19] recently showed that a similar bootstrapping strategy works also in the designated-verifier model. As pointed out by [KW18], the transformation fails to work in the designated-prover model since it critically relies on the fact that the prover algorithm is publicly computable. In this work we focus on multi-statement DP-NIZK.
1.1 Our Results
We present a new technique for bootstrapping DP-NIZK from single-theorem to multi-theorem, using leveled fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) as a building block. We recall that leveled FHE schemes are ones that allow to evaluate depth d circuits, for any (polynomially bounded) d specified at key generation time. We start by noticing that single-theorem DP-NIZK can be constructed straightforwardly from any one-way function using garbled circuits and commitment schemes (we did not find this simple construction in the literature). We then apply a succinctness transformation similar to that proposed by Gentry et al. [Gen09, GGI+15] to shrink the CRS size and make it independent of the complexity of the statement that needs to be proven. This transformation uses (leveled) FHE. Finally, as our main contribution, we present a tree based construction which transforms single-theorem succinct DP-NIZK into multi-theorem (succinct) DP-NIZK, essentially by committing to an implicit tree of CRS values, each of which is used to prove the validity of its children. We provide more information and a technical overview in Sect. 1.3 below.
In addition, in this work, we observe a two-way implication between DP-NIZK and the notion of attribute-based signatures (ABS) [MPR11, BF14, BZ14, BGI13], assuming one-way functions exist. Combining this new observation with the known connection between ABS and HS [Tsa17], we get a construction of homomorphic signatures from leveled FHE. We note the parameters of the obtained HS scheme are fairly unfavorable, in particular the length of the signature grows with the size of the evaluated function. However, this schemes has the so-called context-hiding property. Such HS schemes suffice for some applications (not surprisingly, the [KW18] construction of DP-NIZK is an example of such as application). See Sect. 1.4 below.
1.2 Our Parameters and Assumptions Compared to Prior Work
Comparison with DP-NIZK Constructions from LWE. [KW18] presented a construction of DP-NIZK using homomorphic signatures for \({\mathbf {NC}^1}\) as building block. Such HS schemes were constructed under the learning with errors (LWE) assumption [Reg05] by Gorbunov, Vaikuntanathan and Wee [GVW15]. Comparing our result with their work, we point out that our techniques are very different. Succinctness and bootstrapping that play a central role in our construction, do not appear to be a component of the [KW18] construction. In terms of assumptions, we require leveled FHE and they require homomorphic signatures. The two assumptions are formally incomparable, but when instantiating concretely with LWE, our construction is favorable in terms of the required assumption. Leveled FHE can be constructed based on the hardness of LWE, with a fixed polynomial modulus-to-noise ratio, and with parameters that grow moderately with d [BV14]. The modulus-to-noise ratio (when measured as a function of the dimension of the LWE problem) effectively determines the hardness of the LWE instance at hand. The smaller the ratio is, the harder the problem becomes, and the better approximation to worst-case lattice problems one will be able to achieve if the assumption is broken. In terms of parameter growth, the only parameter effected by d is the public key, which grows linearly with d. In contrast to FHE, it is not known how to bootstrap homomorphic signatures. Bootstrapping allows the modulus-to-noise ratio to be fixed, regardless of the evaluation depth. Therefore, since [KW18] requires the use of HS rather than FHE, they require modulus to noise ratio of \(\mathrm{poly}(s)\), where s is the size of the verification circuit for the \({\mathbf {NP}}\) relation for which proofs are provided. This is worse than the parameters presented in this work.
We should also compare our construction to the recent constructions of NIZK without preprocessing by Canetti et al. [CCH+19] and by Peikert and Shiehian [PS19]. The former constructs NIZK from any circular secure FHE scheme. That is, one that can securely encrypt its own secret key. This is not known to be implied by LWE, but it is an assumption that is fairly common in the FHE literature. The latter constructs NIZK from LWE with fixed polynomial modulus-to-noise ratio. Their construction uses LWE-based leveled FHE as building block, but then uses specific properties of the LWE-based scheme so their construction is not generic. Formally, none of these constructions are implied by generic leveled FHE, which suggests that our techniques have a novel aspect that hopefully can serve as stepping stone for future contributions.
Other DP-NIZK Constructions. Katsumata et al. [KNYY19] showed how to construct DP-NIZK (with computational soundness) based on a (new) assumption on groups with bilinear maps, however a later work by these authors [KNYY20] subsumed that result and showed how to remove the preprocessing and remain with essentially the same properties.
1.3 Technical Overview
As we outlined above, our construction has three components:
-
1.
A single-theorem DP-NIZK construction from any one-way function via garbled circuits and commitments.
-
2.
A succinctness transformation from single-theorem DP-NIZK to succinct single-theorem DP-NIZK. This is similar to the succinctness transformations in [Gen09, GGI+15].
-
3.
Tree-based bootstrapping from succinct single-theorem NIZK to (succinct) multi-theorem DP-NIZK.
In what follows, we describe each of these components in more detail. We consider an \({\mathbf {NP}}\) language L and we let V be the verifier for an \({\mathbf {NP}}\) relation of L. That is, V is a polynomial time algorithm s.t. \(V(x,w)=1\) if and only if w is a valid witness for \(x \in L\). We slightly overload the notation and also use V to denote the circuit that implements the algorithm V on instances x of length n, where n is clear from the context.
Single-Theorem DP-NIZK from OWF. We create a DP-NIZK scheme for instances of size n with respect to the language L. The DP-NIZK setup generates a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\) and prover secret key \({k_{P}}\) as follows. We start by generating a garbled circuit G of the circuit V. We then commit to each of the labels of the garbled circuit, let \(c_{i,b}\) be a commitment to the label \(\ell _{i,b}\). The garbled circuit G and the committed labels are placed in \(\textsf {crs}\), and the openings of all commitments are provided as the secret \({k_{P}}\). In order to prove that \(x\in L\) for some instance x, a prover P with witness w simply opens the commitments to the labels corresponding to (x, w). The verifier executes the garbled circuit and verifies that the output is indeed 1. One minor subtlety is that the verifier needs to be convinced that the prover indeed opened to the correct x, but needs to know nothing about w. This is achieved by providing the labels corresponding to x in the “correct” order, i.e. \(c_{i,0}\) followed by \(c_{i,1}\), but for the w labels \(c_{i,0}\) and \(c_{i,1}\) will be randomly permuted.
Remark 1
As was pointed out to us by TCC 2020 reviewers, there is an alternative way to obtain single-theorem DP-NIZK from OWF by instantiating the hidden-bit model [FLS90]. The hidden bit-model requires that the CRS constitutes a commitment to a sequence of bits drawn (by a trusted party) from a certain distribution, which can be opened by the prover. This can be instantiated for designated prover straightforwardly by having in the CRS commitments to the hidden bits, and giving the openings of the commitments to the prover.
This alternative has the advantage of not requiring use of garbled circuits, but it has the drawback of being designated for a specific \(\mathbf {NP}\) complete language such as hamiltoniciy, or variants of SAT [KP95]. Although in a different context, [Dam92] also considers the goal of constructing proofs directly for arbitrary circuits. In contrast, the garbled circuit approach can apply directly to any witness relation and does not require an \(\mathbf {NP}\) reduction to be used.
Succinctness Transformation. The idea here is to use (leveled) FHE as follows. In the setup process, generate \(\textsf {crs}^0, {k_{P}}^0\) for a non-compact scheme, and also generate a key pair for the FHE scheme \(( \mathsf {hpk}, \mathsf {hsk})\). Place \( \mathsf {hpk}, \textsf {crs}^0\) and a commitment c for \( \mathsf {hsk}\) in the new CRS and \( \mathsf {hsk}, {k_{P}}^0\) and the opening for the commitment c in the new \({k_{P}}\). Now, to prove that \(x\in L\) using w, encrypt w using the FHE, let \(\mathsf {ct}_w\) be the encryption. Then consider the ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}\) which is the homomorphic evaluation of \(V(x,\cdot )\) on the ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}_w\). The prover will use \({k_{P}}^0\) to prove that when decrypting \(\mathsf {ct}\) with the \( \mathsf {hsk}\) committed to by the commitment c, the outcome is 1. The verifier will calculate \(\mathsf {ct}\) locally using homomorphic evaluation, and then will verify the proof using \(\textsf {crs}^0\). This guarantees that soundness holds, up to subtleties like ensuring that any ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}_w\), even dishonestly generated, corresponds to some encrypted value. We note that soundness for DP-NIZK is easier to show than for NIZK without preprocessing as in [Gen09, GGI+15] since the homomorphic encryption keys, and commitments thereof, are guaranteed to be honestly generated.
In terms of succinctness, we only use the underlying scheme to prove statements about the decryption circuit of the FHE scheme, which is independent of the statement length n, and therefore we would hope that the complexity of V does not play a role in the parameters of the new scheme. This is not entirely correct since in leveled FHE, the length of \( \mathsf {hpk}\) can depend on the depth of V. However, we note that \( \mathsf {hpk}\) is reusable, and we can generate many instances of the proof system with the same \( \mathsf {hpk}\). Thus, the parameters contain a part which may not be succinct but is reusable, and another part that is succinct but possibly not reusable. This will suffice for our purposes as we see below.
Tree-Based Bootstrapping. The basic idea is to implicitly generate exponentially many (in the security parameter) single-theorem \((\textsf {crs}, {k_{P}})\) values, so that the prover can use a fresh value for each new theorem. Of course the verifier will need a way to retrieve the correct \(\textsf {crs}\) and verify that it is indeed one of those implicit \(\textsf {crs}\) values and not some value maliciously chosen by a dishonest prover. To resolve this issue, we generate additional instances of the single-theorem DP-NIZK and use them to prove that the \(\textsf {crs}\) values were generated honestly according to some predetrmined (pseudo)randomness that is given via a PRF.
In more detail, we consider a depth-\(\lambda \) binary tree, where each node is associated with an independent instance of the single-theorem DP-NIZK, and all of those instances are implicitly determined by a PRF seed that generates the randomness for the DP-NIZK setup algorithm. Every intermediate node is used in order to prove the (single) statement that the CRS of its two children were generated honestly according to the PRF seed, and the CRS of the tree-root is given as part of the CRS of the multi-theorem DP-NIZK. To prove a statement, the prover randomly chooses one of the tree leaves and uses the corresponding CRS to generate the proof for the statement. It then provides, in addition, all of the proofs on the path from the tree root to this leaf, as an evidence that this leaf indeed appears in the predetermined tree.
Note that the setup algorithm of any node is encoded into the NP relation that is proved by its parent node, and a non-efficient setup might cause a blow-up that is exponential with the tree depth. This is where we crucially use the decomposability of the setup algorithm that was discussed when we described the succinctness transformation. In the tree construction, we will generate the reusable-but-not-succinct part of the single-statement CRS once for all of the nodes in a given level of the tree, and then each node will be associated with a new instance of the succinct-but-not-reusable part of the single-statement CRS.
The zero-knowledge comes from the zero-knowledge of the single-statement DP-NIZK (as long as the prover does not choose the same leaf more than once) and from the pseudorandomness of the PRF seed. In fact, we have to generate a fresh PRF seed for every level of the tree, and to use the pseudorandomness of the seed of the ith level to claim that the single-statement DP-NIZK instances of the ith level are zero-knowledge. We then can claim that the zero-knowledge of the ith level instances guarantees that the PRF seed of the \(i+1\)th level remains secret since it is only used as a witness, and the proof proceed via \(2\lambda \) similar hybrids.
If we only cared about zero-knowledge, we could let the prover sample the PRF seeds on its own (or even to use real randomness instead of PRF outputs). But such scheme would not be sound, since the prover can possibly sample a bad CRS of the single-statement DP-NIZK for which soundness does not hold. To resolve this issue, during setup we sample a random string r along with the PRF seeds for all of the tree levels, and publish r and commitments to the seeds. The prover is then forced to use as “randomness” for the single-statement DP-NIZK setup the PRF outputs XORed with the truly random string r, where we enforce this as part of the NP relation that is verified. That is, we require that the witnesses of all of the proofs along the tree will include the proper decommitments to the PRF seeds. With this approach the PRF seeds remain hidden from the verifier due to the hiding of the commitments, so we don’t compromise zero-knowledge, and in addition the truly random string r restricts the prover to use as “randomness” for the single-statement DP-NIZK setup only strings which the marginal distribution of each of them independently is uniform. We therefore need the underlying single-statement DP-NIZK to be sound for any set of \(2^{\lambda }\) CRS values that were sampled with “randomness” that is randomized via the same uniform string r. To obtain this, we use the fact that the underlying single-statement DP-NIZK is statistically sound and therefore its soundness can be amplified via parallel repetition \(\lambda \) times.
1.4 DP-NIZK, Attribute-Based Signatures and Homomorphic Signatures
An attribute-based signatures scheme (ABS, [MPR11, BGI13, BF14, BZ14]) is a digital signature scheme that supports multiple keys with varying permissions, where signatures do not reveal information about the permissions of the signing key that was used. A homomorphic signature (HS, [CJL09, BFKW09, GKKR10, BF11a, BF11b, GVW15]) is a digital signature that supports homomorphic evaluations over the signed message, where evaluated signatures should not reveal information about the message associated with the pre-evaluated signature other than the result of the function that was computed homomomorphically.
The relation between ABS, HS and NIZK was studied in various works. [MPR11, BF14, SAH16, SKAH18] show reductions of the form “OWF+NIZK \(\rightarrow \) ABS”, [KW18] show that “HS \(\rightarrow \) DPNIZK” and [Tsa17] shows that “ABS \(\leftrightarrow \) HS” for certain types of ABS and HS. Our new DPNIZK construction can be translated to new ABS and HS constructions as follows.
Attribute-Based Signatures from OWF and DP-NIZK. While we believe that some of the aforementioned constructions [MPR11, BF14, SAH16, SKAH18] of ABS from OWF+NIZK can possibly be initialized from OWF+DPNIZK (and in turn also imply HS from OWF+DPNIZK via [Tsa17]), to the best of our knowledge a statement of the flavor “OWF+DPNIZK \(\rightarrow \) ABS” does not explicitly appear in previous literature, so we briefly describe such a reduction now.
The ABS public key and master secret key are an instance of a standard signature scheme. To generate an ABS key for a policy f, generate and instance of DPNIZK and a commitment scheme. Commit to f and use the master secret key to sign (with a standard signature) the DPNIZK CRS and the commitment to f. To sign a message x with a constrained key, provide a DPNIZK proof respective to the instance that appears in the key, proving that “there exists a valid decommitment for some f such that \(f(x) = 1\)”. The commitments scheme and standard signature schemes can be instantiated from one-way functions.
Attribute-Based Signatures from FHE. Applying the transformation which is described above to our DPNIZK construction results in an ABS scheme with the following characteristics:
-
Efficiency. The size of public parameters and the master key is some \(\mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) and in particular independent of the message and policy space, while keys and signatures grow with the policy size.
-
Unforgeability. The unforgeability is based on the statistical soundness of DPNIZK, the (possibly statistical) binding of the commitment scheme and the unforgeability of the standard signature scheme. Since any ABS is in particular a standard signature scheme, this is the best possible unforgeability.
-
Policy Privacy. The privacy is based on the hiding of the commitment and on the zero-knowledge of DPNIZK, which in turn relies on the security of the underlying FHE.
Homomorphic Signatures from FHE. We apply the “ABS \(\rightarrow \) HS” transformation of [Tsa17] and derive a single-hop HS scheme with the following characteristics:
-
Efficiency. The size of public parameters and the master key is some \(\mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) and in particular independent of the message and policy space. However, both post-evaluation and pre-evaluation signatures grow with the function to be computed. That is, when one signs a message they also commit to the maximal size of functions to be homomorphically-computed over it.
-
Unforgeability. Can be based on any OWF.
-
Context-Hiding. Relies on the security of the FHE.
DP-NIZK from Attribute-Based Signatures. As mentioned above, the work of [Tsa17, KW18] implies a derivation of the form “ABS \(\rightarrow \) DPNIZK”. To simplify and complete the picture, we now briefly describe a direct and simple transformation. In the setup of the DP-NIZK scheme, sample a symmetric key \( \mathsf {sk}\) and initialize the ABS scheme. If \(V(\cdot ,\cdot )\) is the verification circuit of the NP relation, then consider the circuit \(V'(\cdot ,\cdot ) = V(\cdot ,\mathsf {Dec}_{ \mathsf {sk}}(\cdot ))\) and generate an ABS key for the policy \(V'\). The secret prover key consists of \( \mathsf {sk}\) and the ABS key for \(V'\). To prove a statement x with a witness w, consider \(w'\) the encryption of w under key \( \mathsf {sk}\) and provide an ABS signature for the message \((x,w')\).
2 Preliminaries
2.1 Notations
For \(n \in {\mathbb {N}}\) we let [n] denote the ordered set \(\{1,\dots ,n\}\). For a bit-string \(m \in \{0,1\}^n\) we let \(U_m^d\) denote the universal circuit that takes as input a description of a circuit \(f : \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) of depth at most d, and outputs f(m). for a bit-string \(m \in \{0,1\}^n\) we let \(m_i\) denote the ith bit of m.
2.2 Pseudorandom Function (PRF)
Definition 1
A Pseudorandom Function (PRF) is a pair of polynomial-time algorithms \((\mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Eval})\) where \(\mathsf {Setup}\) is randomized and \(\mathsf {Eval}\) is deterministic, such that for any \(\text{ ppt }\) adversary \(\mathcal{A}\) it holds that
where the probability is over \(k \leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda })\) and the coins of \(\mathcal{A}\), and \(\mathcal{O}(\cdot )\) is a random function.
2.3 Collision Resistant Hash Function (CRH)
Definition 2
An efficient function family ensemble \(\mathcal{H}= \{ \mathcal{H}_{n,\lambda }: \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}^{\lambda } \}_{n,\lambda \in {\mathbb {N}}}\) is a secure collision-resistant hash (CRH) function family if for any \(\text{ ppt }\) algorithm \(\mathcal{A}\) and any n, for large enough \(\lambda \) it holds that
2.4 Statistically Binding Equivocable Commitments
Definition 3
A commitment scheme \((\mathsf {Gen},\mathsf {Commit},\mathsf {Ver})\) is a tuple of \(\text{ ppt }\) algorithms as follows.
-
\(\mathsf {Gen}(1^{\lambda },1^n) \rightarrow \textsf {crs}\) takes as input a security parameter \(\lambda \) and message length n, and outputs a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\).
-
\(\mathsf {Commit}(\textsf {crs},m) \rightarrow (c,d)\) takes as input a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\) and a message \(m \in \{0,1\}^n\), and outputs a commitment c and decommitment d.
-
\(\mathsf {Ver}(\textsf {crs},c,m,d) \rightarrow \{accept,reject\}\) takes as input a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\), a commitment c, a message m and a decommitment d, and either accepts or rejects.
Correctness. A commitment scheme is correct if for every \(m \in \{0,1\}^n\) it holds that
where \(\textsf {crs}\leftarrow \mathsf {Gen}(1^{\lambda },1^n) ~\text {and}~~ (c,d)\leftarrow \mathsf {Commit}(\textsf {crs},m)\). Statistical Binding. A commitment scheme is statistically binding if for any sufficiently large \(\lambda \) and any n the following holds
Hiding. A commitment scheme is hiding if for any sufficiently large \(\lambda \) and any n, for any \(\text{ ppt }\) adversary \(\mathcal{A}\) and any pair of messages \(m_0,m_1 \in \{0,1\}^n\) it holds that
where \(\textsf {crs}\leftarrow \mathsf {Gen}(1^{\lambda },1^n)\), \((c_b,d_b) \leftarrow \mathsf {Commit}(\textsf {crs},m_b)\) for \(b \in \{0,1\}\) and the probability is over the coins of \(\mathsf {Gen}\), \(\mathsf {Commit}\) and \(\mathcal{A}\).
Equivocability. A commitment scheme is equivocable if there exists a \(\text{ ppt }\) simulator \(\mathcal{S}= (\mathcal{S}^A,\mathcal{S}^B)\) such that for any sufficiently large \(\lambda \) and any n, for any \(\text{ ppt }\) distinguisher \(\varPsi \), any pair of messages \(m_0,m_1 \in \{0,1\}^n\) and any \(b \in \{0,1\}\) it holds that
where \(\textsf {crs}\leftarrow \mathsf {Gen}(1^{\lambda },1^n)\), \((c_b,d_b) \leftarrow \mathsf {Commit}(\textsf {crs},m_b)\) for \(b \in \{0,1\}\), \((\textsf {crs}',c',\mathsf {td}_{c'}) \leftarrow \mathcal{S}^A(1^{\lambda },1^n)\) and \(d'_b \leftarrow \mathcal{S}^B(\textsf {crs}',c',\mathsf {td}_{c'},m_b)\) for \(b \in \{0,1\}\), and the probability is over the coins of \(\mathsf {Gen}\), \(\mathsf {Commit}\), \(\mathcal{S}\) and \(\varPsi \).
2.5 Garbled Circuits
Definition 4
A garbling scheme for circuits is a tuple of \(\text{ ppt }\) algorithms \((\mathsf {Garble},\mathsf {Eval})\) with the following syntax.
-
\(\mathsf {Garble}(1^{\lambda },C) \rightarrow (\widetilde{C}, \{\mathsf {lab}_{i,b}\}_{i \in [n],b\in \{0,1\}})\) is a probabilistic algorithm that takes as input a security parameter \(\lambda \) and a boolean circuit \(C : \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}\), and outputs a garbled circuit \(\widetilde{C}\) and 2n labels \(\{\mathsf {lab}_{i,b}\}_{i \in [n],b\in \{0,1\}}\), where each of the labels is of size \(\lambda = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) for some fixed polynomial \(\mathrm{poly}\).
-
\(\mathsf {Eval}(\widetilde{C},\{\mathsf {lab}_{i}\}_{i \in [n]}) \rightarrow b\) is a deterministic algorithm that takes as input a garbled circuit \(\widetilde{C}\) and n labels \(\{\mathsf {lab}_{i}\}_{i \in [n]}\), and outputs a bit \(b \in \{0,1\}\).
Correctness. The scheme is correct if for every circuit \(C : \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}\), every input \(x \in \{0,1\}^n\) and every \(\left( \widetilde{C}, \{\mathsf {lab}_{i,b}\}_{i \in [n],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) \leftarrow \mathsf {Garble}(1^{\lambda },C)\), it holds that
Security. The scheme is secure if there exists a \(\text{ ppt }\) simulator \(\mathcal{S}\) such that for every circuit \(C : \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) and every input \(x \in \{0,1\}^n\) it holds that
where \(\left( \widetilde{C}, \{\mathsf {lab}_{i,b}\}_{i \in [n],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) \leftarrow \mathsf {Garble}(1^{\lambda },C)\) and \(\equiv _{\lambda }\) denotes computational indistinguishability with respect to the security parameter \(\lambda \).
2.6 Homomorphic Encryption
Definition 5
A leveled fully homomorphicencryption scheme \(\mathrm {FHE}\) is a tuple of \(\text{ ppt }\) algorithms \((\mathsf {Keygen},\mathsf {Enc},\mathsf {Eval},\mathsf {Dec})\) with the following syntax.
-
\(\mathsf {Keygen}(1^{\lambda },1^d) \rightarrow ( \mathsf {pk}, \mathsf {sk})\) is a probabilistic algorithm that takes as input a security parameter \(\lambda \) and depth d, and outputs a public key \( \mathsf {pk}\) and secret key \( \mathsf {sk}\).
-
\(\mathsf {Enc}( \mathsf {pk},m) \rightarrow \mathsf {ct}\) is a probabilistic algorithm that takes as input a public key \( \mathsf {pk}\) and a message \(m \in \{0,1\}^*\), and outputs a ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}\).
-
\(\mathsf {Eval}(\mathsf {ct},C) \rightarrow \mathsf {ct}'\) is a deterministic algorithm that takes as input a ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}\) and a boolean circuit \(C : \{0,1\}^* \rightarrow \{0,1\}\), and outputs an evaluated ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}'\).
-
\(\mathsf {Dec}( \mathsf {sk}, \mathsf {ct}')\) is a deterministic algorithm that takes as input a secret key \( \mathsf {sk}\) and an evaluated ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}'\), and outputs a bit \(b \in \{0,1\}\).
Correctness. The scheme is correct if for every \(n,d \in {\mathbb {N}}\), every message \(m \in \{0,1\}^n\) and every circuit \(C : \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) of depth at most d, it hold that
where the probability is over the coins of \(\mathsf {Keygen}\) and \(\mathsf {Enc}\).
Security. The scheme is secure if for any \(\text{ ppt }\) adversary \(\mathcal{A}\), any \(n \in {\mathbb {N}}\) and any pair of messages \(m_0,m_1 \in \{0,1\}^n\), it holds that
where \( \mathsf {pk}\leftarrow \mathsf {Keygen}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\) and the probability is over the coins of \(\mathsf {Keygen}\), \(\mathsf {Enc}\) and \(\mathcal{A}\).
Compactness. The scheme is compact if there exists a polynomial \(p = p(\cdot )\) such that for all security parameters \(\lambda \) and all \(n,d \in {\mathbb {N}}\), \(m \in \{0,1\}^n\) and \(C : \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) of depth at most d, for all \(( \mathsf {pk}, \mathsf {sk}) \leftarrow \mathsf {Keygen}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\), the output length of \(\mathsf {Eval}(\widetilde{m},C)\) is at most p bits long where \(\widetilde{m} \leftarrow \mathsf {Enc}\left( \mathsf {pk},m\right) \), and the size of \( \mathsf {sk}\) is at most p bits.
For our application we need an \(\mathrm {FHE}\) scheme where the correctness also holds for maliciously chosen ciphertexts. Formally,
Definition 6
(FHE with correctness for all ciphertexts). An \(\mathrm {FHE}\) shceme has correctness for all ciphertexts if for all \(n,d \in {\mathbb {N}}\), for every string \(\mathsf {ct}\in \{0,1\}^p\) and every circuit \(C : \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) of depth at most d, it holds that
where I is the identity circuit and the probability is over the coins of \(\mathsf {Keygen}\).
We now show that any FHE scheme with standard correctness implies a scheme with correctness for all ciphertexts (which preserves the compactness property).
Lemma 1
Let \(\mathrm {FHE}= (\mathsf {Keygen},\mathsf {Enc},\mathsf {Eval},\mathsf {Dec})\) be an FHE scheme with standard correctness and let \(\mathrm {PKE}= (\mathsf {Keygen},\mathsf {Enc},\mathsf {Dec})\) be a public-key encryption scheme. hen there exists an FHE scheme \(\mathrm {FHE}' = (\mathsf {Keygen}',\mathsf {Enc}',\mathsf {Eval}',\mathsf {Dec}')\) with correctness for all ciphertexts.
Proof
Define \(\mathrm {FHE}' = (\mathsf {Keygen}',\mathsf {Enc}',\mathsf {Eval}',\mathsf {Dec}')\) as follows:
-
\(\mathsf {Keygen}'(1^{\lambda },1^d)\): Sample \(( \mathsf {hpk}, \mathsf {hsk}) \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Keygen}(1^{\lambda },1^{d'})\) and \(( \mathsf {pk}, \mathsf {sk}) \leftarrow \mathrm {PKE}.\mathsf {Keygen}(1^{\lambda })\), then compute \(\tilde{ \mathsf {sk}} \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Enc}( \mathsf {hpk}, \mathsf {sk})\) and output \(( \mathsf {pk}', \mathsf {sk}') := (( \mathsf {hpk}, \mathsf {pk},\tilde{ \mathsf {sk}}), \mathsf {hsk})\) where \(d' = \mathrm{poly}(d,\lambda )\) is the maximal depth of \(C'\) as defined in \(\mathsf {Eval}'\) below.
-
\(\mathsf {Enc}'( \mathsf {pk}',m)\): Compute and output \(\mathsf {ct}' := m' \leftarrow \mathrm {PKE}.\mathsf {Enc}( \mathsf {pk},m)\).
-
\(\mathsf {Eval}'(\mathsf {ct}',C)\): Define the circuit \(C_{\mathsf {ct}'}(\circ ) := C(\mathrm {PKE}.\mathsf {Dec}_{\circ }(\mathsf {ct}'))\). Compute and output \(\mathsf {ct}'' := \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Eval}(\tilde{ \mathsf {sk}},C_{\mathsf {ct}'})\).
-
\(\mathsf {Dec}'( \mathsf {sk}',\mathsf {ct}')\): Output \(\mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Dec}( \mathsf {hsk},\mathsf {ct}')\).
Fix \(n,d \in {\mathbb {N}}\), a string \(\mathsf {ct}' \in \{0,1\}^p\) and a circuit \(C : \{0,1\}^n \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) of depth at most d. Consider \(( \mathsf {pk}', \mathsf {sk}') \leftarrow \mathsf {Keygen}'(1^{\lambda },1^d)\), \(\mathsf {ct}''_I \leftarrow \mathsf {Eval}'(\mathsf {ct}',I)\) and \(\mathsf {ct}''_C \leftarrow \mathsf {Eval}'(\mathsf {ct}',C)\), then it holds that
and therefore
and
3 Definitions of Designated-Prover NIZK
Definition 7
(DP-NIZK Proofs). A designated-prover non-interactive zero-knowledge (DP-NIZK) proof \(\varPi _{\mathsf {DPNIZK}}\) for an ensemble of \(\mathbf {NP}\) languages \(\mathcal{C}\subseteq \{C : \{0,1\}^* \times \{0,1\}^* \rightarrow \{0,1\}\}\) (where C is a verification circuit and \(\mathcal{L}_C = \{ x ~:~ \exists w ~~ C(x,w) = 1 \}\) is the \(\mathbf {NP}\) language determined by C) is defined by a tuple of \(\text{ ppt }\) algorithms with the following syntax.
-
\(\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params}) \rightarrow (\textsf {crs},k_P)\) takes as input the security parameter \(\lambda \) and possibly some parameters \(\mathsf {params}\) of \(\mathcal{C}\) (e.g. the maximal circuit depth), and outputs a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\) and a proving key \(k_P\).
-
\(\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,k_P,x,w) \rightarrow \pi \) takes as input a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\), a circuit \(C \in \mathcal{C}\), a proving key \(k_P\), a statement x and a witness w. It outputs a proof \(\pi \).
-
\(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,x,\pi ) \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) takes as input a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\), a circuit \(C \in \mathcal{C}\), a statement x and a proof \(\pi \), and either accepts (with output 1) or rejects (with output 0) the proof.
Moreover, \(\varPi _{\mathsf {DPNIZK}}\) should satisfy the following properties:
(Perfect) Completeness. For all sufficiently large \(\lambda \), for all circuits \(C \in \mathcal{C}\), for all pairs (x, w) for which \(C(x,w) = 1\) and for all \((\textsf {crs},k_P) \leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params})\), it holds that
(Statistical) Soundness. For all sufficiently large \(\lambda \) and for all \(C \in \mathcal{C}\) it holds that
(Programmable CRS) Zero-Knowledge. For all \(\text{ ppt }\) adversaries \(\mathcal{A}\) there exists a \(\text{ ppt }\) simulator \(\mathcal{S}= (\mathcal{S}_1,\mathcal{S}_2)\) such that
where \((\textsf {crs},k_P) \leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params})\), \((\textsf {crs}',\tau ) \leftarrow \mathcal{S}_1(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params})\) and
and the probability is over the coins of \(\mathcal{A},\mathcal{S},\mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Prove}\). We also consider the a relaxed notion of single-statement zero knowledge, in which the (programmable CRS) zero-knowledge condition holds only for adversaries \(\mathcal{A}\) that make at most a single query to the oracle.
We sometimes require the following additional property.
Efficient Setup. A DP-NIZK proof system is efficient if for all \(\lambda \) there exists a \(p = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) such that for all \(\mathsf {params}\), the complexity of \(\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params})\) is p (and in particular does not depend on \(\mathsf {params}\)).
3.1 Single-Statement Global-Setup DP-NIZK Proofs
Definition 8
(Single-Statement Global-Setup DP-NIZK Proofs). A single-statement global-setup DP-NIZK proof \(\varPi _{1\mathsf {DPNIZK}}\) for an ensemble of \(\mathbf {NP}\) languages \(\mathcal{C}\subseteq \{C : \{0,1\}^* \times \{0,1\}^* \rightarrow \{0,1\}\}\) (where C is a verification circuit and \(\mathcal{L}_C = \{ x ~:~ \exists w ~~ C(x,w) = 1 \}\) is the \(\mathbf {NP}\) language determined by C) is defined by a tuple of \(\text{ ppt }\) algorithms with the following syntax.
-
\(\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params}) \rightarrow (\textsf {crs}, \mathsf {msk})\) takes as input the security parameter \(\lambda \) and possibly some parameters \(\mathsf {params}\) of \(\mathcal{C}\) (e.g. the maximal circuit depth), and outputs a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\) and a master secret key \( \mathsf {msk}\).
-
\(\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}}( \mathsf {msk}) \rightarrow ( \mathsf {pk},k_P)\) takes as input a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\) and a master secret key \( \mathsf {msk}\), and outputs a public key \( \mathsf {pk}\) and a proving key \(k_P\).
-
\(\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,( \mathsf {pk},k_P),x,w) \rightarrow \pi \) takes as input a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\), a circuit \(C \in \mathcal{C}\), a public key \( \mathsf {pk}\), a proving key \(k_P\), a statement x and a witness w. It outputs a proof \(\pi \).
-
\(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}(C, \mathsf {pk},x,\pi ) \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) takes as input a common reference string \(\textsf {crs}\), a circuit \(C \in \mathcal{C}\), a public key \( \mathsf {pk}\), a statement x and a proof \(\pi \), and either accepts (with output 1) or rejects (with output 0) the proof.
Moreover, \(\varPi _{1\mathsf {DPNIZK}}\) should satisfy the following properties:
(Perfect) Completeness. For all sufficiently large \(\lambda \), for all \(C \in \mathcal{C}\) and for all pairs (x, w) for which \(C(x,w) = 1\), it holds that
(Statistical) Soundness. For all sufficiently large \(\lambda \), for all \(C \in \mathcal{C}\) and for all \((\textsf {crs}, \mathsf {msk}) \leftarrow \mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda })\) it holds that
(Statistical) \(\epsilon \)-Soundness. We also define a generalized notion of soundness as follows. For all sufficiently large \(\lambda \), for all \(C \in \mathcal{C}\) for all \((\textsf {crs}, \mathsf {msk}) \leftarrow \mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda })\) it holds that
(Programmable CRS) Single-Statement Zero-Knowledge. For all \(\text{ ppt }\) adversaries \(\mathcal{A}\) there exists a \(\text{ ppt }\) simulator \(\mathcal{S}= (\mathcal{S}_1,\mathcal{S}_2)\) such that
where
and
the probability is over the coins of \(\mathcal{A},\mathcal{S},\mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Prove}\) and \(\textsf {crs}\leftarrow \mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params})\), and for every i the adversary \(\mathcal{A}\) makes at most a single query of the form \(\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}}(\cdot , \mathsf {pk}^i,k_P^i,\cdot ,\cdot )\).
Efficiency. For all \(\lambda \) there exists a \(p = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) such that for all \(\mathsf {params}\) and all \((\textsf {crs}, \mathsf {msk}) \leftarrow \mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params})\), the complexity of \(\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}}( \mathsf {msk})\) is p (and in particular does not depend on \(\mathsf {params}\)).
Remark 2
A global-setup DP-NIZK can be viewed as a generalization of standard DP-NIZK in the following manner. When the algorithm \(\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}\) is trivial (i.e. when it outputs \(\textsf {crs}= \mathsf {msk}= 1^{\lambda }\)), then the tuple of algorithms \((\mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Prove},\mathsf {Verify})\) qualify as a DP-NIZK proof system with efficient setup and single-statement zero-knowledge.
Remark 3
Every \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) with standard statistical soundness can be amplified to \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) with statistical \(\epsilon \)-soundness for any \(\epsilon = \frac{1}{2^{\mathrm{poly}(\lambda )}}\) via parallel composition of \(\mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Prove},\mathsf {Verify}\) for \(log \left( \frac{1}{\epsilon }\right) =\mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) times. The single-statement zero-knowledge simulator of the amplified proof system is derived via parallel composition of the simulator of the underlying \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) proof system.
4 Our Construction
4.1 Single-Statement Global-Setup DP-NIZK from FHE
Theorem 1
Assuming the existence of the following building blocks, for every \(d \in {\mathbb {N}}\) there exists a single-statement global-setup DP-NIZK proof system as in Definition 8 for the ensemble \(\mathcal{C}_d\) of \(\mathbf {NP}\) relations that are verifiable by circuits C of depth at most d.
-
1.
A leveled fully-homomorphic scheme \(\mathrm {FHE}= (\mathsf {Keygen},\mathsf {Enc},\mathsf {Eval},\mathsf {Dec})\) with correctness for all ciphertexts as in Definitions 5 and 6. For every \(\lambda \) let \(p = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) denote the size of \(\mathrm {FHE}\) evaluated-ciphertexts and secret-keys as described in the “compactness” section of Definition 5.
-
2.
A garbing scheme \(\mathsf {GC}= (\mathsf {Garble},\mathsf {Eval})\) as in Definition 4 where each label is of size \(\lambda = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) bits.
-
3.
A statistically-binding equivocable commitment scheme \(\mathsf {SBCS}= (\mathsf {Gen},\mathsf {Commit},\mathsf {Ver})\) as in Definition 3.
In the rest of this section we prove Theorem 1. We let \(\mathsf {params}= d\) be the depth bound of circuits in \(\mathcal{C}_d\).
Construction 9
(Single-Statement Global-Setup DP-NIZK).
-
\(\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\):
-
1.
Compute \(( \mathsf {hpk}, \mathsf {hsk}) \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Keygen}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\).
-
2.
Output \(\textsf {crs}:= \mathsf {hpk}\) and \( \mathsf {msk}:= \mathsf {hsk}\).
-
1.
-
\(\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}}( \mathsf {msk})\):
-
1.
Parse \( \mathsf {msk}= \mathsf {hsk}\) and let \(D_{ \mathsf {hsk}} : \{0,1\}^{p} \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) be the boolean circuit that has \( \mathsf {hsk}\) hard-wired in it, takes as input an \(\mathrm {FHE}\) evaluated-ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}\), and decrypts \(\mathsf {ct}\) with \( \mathsf {hsk}\). Compute
$$\left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}, \{\mathsf {lab}_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) \leftarrow \mathsf {GC}.\mathsf {Garble}\left( 1^{\lambda }, D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}\right) .$$ -
2.
For \(i \in [p]\) and \(b \in \{0,1\}\) compute \(\textsf {crs}_{i,b} \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^{\lambda })\) and \( \left( c_{i,b}, d_{i,b}\right) \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Commit}(\textsf {crs}_{i,b},\mathsf {lab}_{i,b})\).
-
3.
Output
$$ \mathsf {pk}:= \left( \widetilde{D_{h \mathsf {sk}}}, \{\textsf {crs}_{i,b}, c_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) , \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ k_P := \left\{ \mathsf {lab}_{i,b},~ d_{i,b} \right\} _{i\in [p],b \in \{0,1\}}. $$
-
1.
-
\(\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,( \mathsf {pk},k_P),x,w)\):
-
1.
If \(C \notin \mathcal{C}_d\) or \(C(x,w) \ne 1\) then output \(\perp \).
-
2.
Encrypt \(\mathsf {ct}_{w} \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Enc}_ \mathsf {hpk}(w)\).
-
3.
Let \(C'_x\) be the circuit \(C_x(\circ ) := C(x,\circ )\) and compute homomorphically
$$\mathsf {ct}_b \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Eval}_{ \mathsf {hpk}}(\mathsf {ct}_{w}, C_x).$$ -
4.
Note that \(\mathsf {ct}_b \in \{0,1\}^{p}\). For \(i \in [p]\) let \(\widetilde{b}_i\) denote the ith bit of \(ct_b\). Output
$$ \pi := \left( \mathsf {ct}_{w}, \{ \mathsf {lab}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i},~ d_{i,\widetilde{b}_i} \}_{i \in [p]}\right) .$$
-
1.
-
\(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}(C, \mathsf {pk},x,\pi )\):
-
1.
Parse \(\textsf {crs}= \mathsf {hpk}\), \( \mathsf {pk}= \left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}, \{\textsf {crs}_{i,b}, c_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) \) and \(\pi = \left( \mathsf {ct}_{w}, \{ \mathsf {lab}_{i},~ d_{i} \}_{i \in [p]}\right) \).
-
2.
Compute \(\mathsf {ct}_b \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Eval}_{ \mathsf {hpk}}(\mathsf {ct}_{w}, C_x)\) (where \(C_x\) is as defined above).
-
3.
Note that \(\mathsf {ct}_{b} \in \{0,1\}^{p}\). For \(i \in [p]\) let \(\widetilde{b}_i\) denote the ith bit of \(\mathsf {ct}_{b}\). Verify the label decommitments: for \(i \in [p]\) compute
$$ \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Ver}\left( \textsf {crs}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i}, c_{i,\widetilde{b}_i},\mathsf {lab}_{i}, d_{i}\right) , $$if any of those verifications fail then output 0 (reject).
-
4.
Compute and output \(\mathsf {GC}.\mathsf {Eval}\left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {sk}}}, \{ \mathsf {lab}_{i}\}_{i \in [p]} \right) \).
-
1.
Proof of Completeness. Fix \(\lambda ,d,C,x,w\) where \(C \in \mathcal{C}_d\) and \(C(x,w) = 1\). Consider
Parse \(\textsf {crs}= \mathsf {hpk}\), \( \mathsf {pk}= \left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}, \{\textsf {crs}_{i,b}, c_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) \) and \(\pi = \left( \mathsf {ct}_{w}, \{ \mathsf {lab}_{i},~ d_{i} \}_{i \in [p]}\right) \).
Consider the execution of \(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}\left( C, \mathsf {pk},x,\pi \right) \). Since \(\mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Eval}\) is deterministic, the value \(\mathsf {ct}_b\) that is computed in \(\mathsf {Prove}\) and in \(\mathsf {Verify}\) is identical. Therefore the correctness of \(\mathsf {SBCS}\) implies that all of the decommitment verifications in step (3) of \(\mathsf {Verify}\) pass. Moreover, due to the correctness of \(\mathrm {FHE}\) it holds that
and the correctness of \(\mathsf {GC}\) implies that the output in step (4) of \(\mathsf {Verify}\) is \(\mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Dec}_{ \mathsf {hsk}}(\mathsf {ct}_b) = 1\). \(\square \)
Proof of Soundness. Fix \(\lambda ,d \in {\mathbb {N}}\), \(C\in \mathcal{C}_d\) and \((\textsf {crs}, \mathsf {msk}) \leftarrow \mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\), and consider the random variable \( \mathsf {pk}\leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}}( \mathsf {msk})\). Assume that there exist \((x,\pi )\) such that \(x \notin \mathcal{L}_C\) and \(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}(C, \mathsf {pk},x,\pi )=1\).
Parse \(\textsf {crs}= \mathsf {hpk}\), \( \mathsf {pk}= \left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}, \{\textsf {crs}_{i,b}, c_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) \) and \(\pi = \left( \mathsf {ct}_{w}, \{ \mathsf {lab}'_{i},~ d'_{i} \}_{i \in [p]}\right) \), and recall that the values in the \( \mathsf {pk}\) were computed as follows
and
Let \(\mathsf {ct}_b \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Eval}_{ \mathsf {hpk}}(\mathsf {ct}_{w}, C_x)\) be the value that is computed during \(\mathsf {Verify}\) and for \(i \in [p]\) let \(\widetilde{b}_i\) denote the ith bit of \(\mathsf {ct}_{b}\).
Assume towards contradiction that for all \(i \in [p]\) it holds that \(\mathsf {lab}'_i = \mathsf {lab}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i}\), then by the correctness of GC and FHE, and since \(\mathsf {Verify}\) outputs 1, it holds that
and therefore the string \(w := \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Dec}_{ \mathsf {hsk}}(\mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Eval}_{ \mathsf {hpk}}(\mathsf {ct}_w,I))\) satisfies \(C(x,w) = 1\), with contradiction to the assumption that \(x \notin \mathcal{L}_C\).
Therefore, it must be the case that there exists some \(j \in [p]\) for which \(\mathsf {lab}'_j \ne \mathsf {lab}_{j,\widetilde{b}_j}\). Since all of the verifications in step (3) of \(\mathsf {Verify}\) pass successfully, it in particular holds that
Therefore, denoting \(\textsf {crs}^* := \textsf {crs}_{j,\widetilde{b}_j}\), \(m^*_0 := \mathsf {lab}_{j,\widetilde{b}_j}\), \(m^*_1 := \mathsf {lab}'_j\) and \(d^* := d'_j\), and letting \(r^*\) be the randomness used during \( \mathsf {pk}\leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}}( \mathsf {msk})\) when computing \( c_{j,\widetilde{b}_j} \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Commit}(\textsf {crs}_{j,\widetilde{b}_j}, \mathsf {lab}_{j,\widetilde{b}_j} ~;~ r^*)\), it holds that
where the last equation is due to the binding of \(\mathsf {SBCS}\). \(\square \)
Proof of Single-Statement Zero-Knowledge. Let \(\mathsf {SBCS}.\mathcal{S}= (\mathsf {SBCS}.\mathcal{S}^A,\mathsf {SBCS}.\mathcal{S}^B)\) be the equivocability simulator of \(\mathsf {SBCS}\) and let \(\mathsf {GC}.\mathcal{S}\) be the simulator of the garbling scheme. Define the single-statement zero-knowledge simulator \(\mathcal{S}= (\mathcal{S}_1,\mathcal{S}_2)\) as follows:
-
\(\mathcal{S}_1(\textsf {crs})\):
-
1.
Set \( \mathsf {hsk}:= 0^p\) , where p is the upper-bound on the size of FHE secret-keys and evaluated ciphertexts, as in Definition 5.
-
2.
Let \(D_{ \mathsf {hsk}} : \{0,1\}^{p} \rightarrow \{0,1\}\) be the boolean circuit that has \( \mathsf {hsk}\) hard-wired in it, takes as input an \(\mathrm {FHE}\) evaluated-ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}\), and decrypts \(\mathsf {ct}\) with \( \mathsf {hsk}\). Compute
$$\left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}, \{\mathsf {lab}_{i} \}_{i \in [p] }\right) \leftarrow \mathcal{S}_{\mathsf {GC}}\left( 1^{\lambda }, 1^{\left| {D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}} \right| },1\right) .$$ -
3.
For \(i \in [p]\) and \(b \in \{0,1\}\) compute \(\left( \textsf {crs}_{i,b},c_{i,b},\mathsf {td}^{c}_{i,b}\right) \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathcal{S}^A(1^{\lambda },1^{\lambda })\).
-
4.
Set
$$ \mathsf {pk}:= \left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}, \{ c_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) , \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \tau := \left( \{\mathsf {lab}_{i} \}_{i \in [p] }, \{\mathsf {td}^{c}_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}} \right) . $$
-
1.
-
\(\mathcal{S}_2(\textsf {crs}, C, \mathsf {pk},\tau ,x)\):
-
1.
Parse \(\textsf {crs}= \mathsf {hpk}\), \( \mathsf {pk}= \left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}, \{ c_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}}\right) \) and \(\tau = \left( \{\mathsf {lab}_{i} \}_{i \in [p] }, \{\mathsf {td}^{c}_{i,b} \}_{i \in [p],b\in \{0,1\}} \right) \).
-
2.
Encrypt \(\mathsf {ct}_{w} \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Enc}_ \mathsf {hpk}(0^k)\), where k is the bit-length of witnesses as determined by C.
-
3.
Compute homomorphically \(\mathsf {ct}_b \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Eval}_{ \mathsf {hpk}}(\mathsf {ct}_{w}, C_x)\), where \(C_x\) is the circuit \(C_x(\circ ) := C(x,\circ )\).
-
4.
Note that \(\mathsf {ct}_b \in \{0,1\}^{p}\). For \(i \in [p]\) let \(\widetilde{b}_i\) denote the ith bit of \(ct_b\) and compute
$$ d_i \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathcal{S}^B\left( \textsf {crs}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i},c_{i,\widetilde{b}_i},\mathsf {td}^{c}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i},\mathsf {lab}_i\right) $$ -
5.
Output
$$ \pi := \left( \mathsf {ct}_{w}, \{ \mathsf {lab}_{i},~ d_{i} \}_{i \in [p]}\right) .$$
-
1.
We now prove indistinguishability via a sequence of hybrids:
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{0}\) . The real \(\mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Prove}\) algorithms.
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{1}\) . We change the way that the values \(\{\textsf {crs}_{i,b},c_{i,b}\}_{i \in [p],b \in \{0,1\}}\) and \(\{d_{i,\widetilde{b}_i} \}_{i \in [p]}\) are computed in \(\mathsf {Setup}\) and \(\mathsf {Prove}\) respectively:
-
1.
In \(\mathsf {Setup}\), for \(i \in [p]\) and \(b \in \{0,1\}\) compute \(\left( \textsf {crs}_{i,b},c_{i,b},\mathsf {td}^{c}_{i,b}\right) \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathcal{S}^A(1^{\lambda },1^{\lambda })\).
-
2.
In \(\mathsf {Prove}\), for \(i \in [p]\) compute
$$ d_i \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathcal{S}^B\left( \textsf {crs}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i},c_{i,\widetilde{b}_i},\mathsf {td}^{c}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i},\mathsf {lab}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i}\right) . $$
Hybrids \(\mathcal {H}_{1}\) and \(\mathcal {H}_{0}\) are computationally indistinguishable due to the equivocability of \(\mathsf {SBCS}\).
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{2}\) . Note that in Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{1}\) the values \(\{\mathsf {lab}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i} \}_{i \in [p]}\) are only used during \(\mathsf {Prove}\), and the other p GC labels are never used. In this hybrid we change the way that the values \(\widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}\) and \(\{\mathsf {lab}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i} \}_{i \in [p]}\) are computed in \(\mathsf {Setup}\) and \(\mathsf {Prove}\) respectively:
-
1.
In \(\mathsf {Setup}\), compute
$$\left( \widetilde{D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}}, \{\mathsf {lab}_{i} \}_{i \in [p] }\right) \leftarrow \mathcal{S}_{\mathsf {GC}}\left( 1^{\lambda }, 1^{\left| {D_{ \mathsf {hsk}}} \right| },1\right) .$$ -
2.
In \(\mathsf {Prove}\), for \(i \in [p]\) set \(\mathsf {lab}_{i,\widetilde{b}_i} := \mathsf {lab}_i\) and proceed as in the previous hybrid.
Hybrids \(\mathcal {H}_{2}\) and \(\mathcal {H}_{1}\) are computationally indistinguishable due to the security of \(\mathsf {GC}\).
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{3}\) . Note that in Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{2}\) the value \( \mathsf {hsk}\) is only used when computing the FHE ciphertext \(\mathsf {ct}_{w}\) in \(\mathsf {Prove}\). In this hybrids we change the way that \(\mathsf {ct}_{w}\) is computed: Encrypt \(\mathsf {ct}_{w} \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Enc}_ \mathsf {hpk}(0^k)\), where k is the bit-length of witnesses as determined by C. Hybrids \(\mathcal {H}_{3}\) and \(\mathcal {H}_{2}\) are computationally indistinguishable due to the security of \(\mathrm {FHE}\).
Note that this hybrid is identical to the simulators \(\mathcal{S}_1,\mathcal{S}_2\). \(\square \)
Efficiency. Fix \(\lambda \) and note that by the compactness of \(\mathrm {FHE}\), there exists some \(p = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) such that for all \(\mathsf {params}= d\) and \(( \mathsf {hpk}, \mathsf {hsk}) \leftarrow \mathrm {FHE}.\mathsf {Keygen}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\), the size of \(\mathrm {FHE}\) evaluated-ciphertexts and \( \mathsf {hsk}\) is at most p. Denote \((\textsf {crs}, \mathsf {msk}) = ( \mathsf {hpk}, \mathsf {hsk})\) and note that the running time of \(\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}}( \mathsf {msk})\) is bounded by some \(p' = \mathrm{poly}(p,\lambda ) = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\), i.e. for all \(\mathsf {params}=d\) and all \((\textsf {crs}, \mathsf {msk}) \leftarrow \mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\), the complexity of \(\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}}( \mathsf {msk})\) is at most \(p'\).
4.2 DP-NIZK from Single-Statement Global-Setup DP-NIZK
Theorem 2
Assuming the existence of the following building blocks, for every \(d \in {\mathbb {N}}\) there exists a \(\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) proof system as in Definition 7 for the ensemble \(\mathcal{C}_d\) of \(\mathbf {NP}\) relations that are verifiable by circuits C of depth at most d.
-
1.
A pseudo-random function \(\mathsf {PRF}= (\mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Eval})\) where w.l.o.g. for every \(k \leftarrow \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda })\) it holds that \(k \in \{0,1\}^{\lambda }\).
-
2.
A single-statement global-setup DPNIZK proof system \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}= (\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}, \mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Prove},\mathsf {Verify})\) for \(\{\mathcal{C}_d\}_d\), where w.l.o.g. for every \((\textsf {crs}, \mathsf {msk}) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\) it holds that the randomness used by \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}}( \mathsf {msk})\) is of size \(\ell = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\), the size of \( \mathsf {msk}\) is some \(p = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) and the scheme satisfies \((2^{\lambda -\ell },\lambda )\)-soundness.
-
3.
A statistically-binding commitment scheme \(\mathsf {SBCS}= (\mathsf {Gen},\mathsf {Commit},\mathsf {Ver})\) as in Definition refdef:comm.
In the rest of this section we prove Theorem 2.
Construction 10
(DP-NIZK from 1-DP-NIZK).
-
\(\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\):
-
1.
For \(i = 0,\dots ,\lambda \) compute \((\textsf {crs}'_i, \mathsf {msk}'_i) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^{d'_i})\) where \(d'_i\) is defined in the paragraph bellow.
-
2.
Sample \(r {\mathop {\leftarrow }\limits ^{\scriptscriptstyle {\$}}}\{0,1\}^{\ell }\) and for \(i \in [\lambda ]\) sample \(k_i \leftarrow \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda })\).
-
3.
Compute \(\textsf {crs}^* \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Gen}(1^{\lambda },1^{p+\lambda })\) and for \(i \in [\lambda ]\) sample \((c^*_i,d^*_i) \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Commit}(\textsf {crs}^*,( \mathsf {msk}'_i,k_i))\).
-
4.
Sample \(\left( \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset },k_P^{\emptyset }\right) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}'_0}( \mathsf {msk}'_0)\).
-
5.
Output \(\textsf {crs}:= (\{\textsf {crs}'_i\}_{i=0,\dots ,\lambda },\textsf {crs}^*,\{c^*_i\}_{i \in [\lambda ]}, \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset },r)\) and \(k_P := \left( \{ \mathsf {msk}'_i\}_{i=0,\dots ,\lambda }, \{k_i,d^*_i\}_{i \in [\lambda ]}, k_P^{\emptyset }\right) \).
-
1.
-
\(\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,k_P,x,w)\):
-
1.
Parse \(\textsf {crs}= (\{\textsf {crs}'_i\}_{i=0,\dots ,\lambda },\textsf {crs}^*,\{c^*_i\}_{i \in [\lambda ]}, \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset },r)\) and \(k_P = \left( \{ \mathsf {msk}'_i\}_{i=0,\dots ,\lambda }, \{k_i,d^*_i\}_{i \in [\lambda ]}, k_P^{\emptyset }\right) \).
-
2.
Sample \(m {\mathop {\leftarrow }\limits ^{\scriptscriptstyle {\$}}}\{0,1\}^{\lambda }\) and for \(i \in [\lambda ]\) let \(m^i\) denote length-i prefix of m (i.e. \(m^i = m_1m_2\dots m_i\)). In particular denote \(m^0 = \emptyset \) and \(m^{\lambda } = m\).
-
3.
For \(i = 0, \dots , \lambda -1\) do:
-
(a)
For \(b \in \{0,1\}\) compute
$$r^{m^i\Vert b} := r \oplus \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Eval}_{k_{i+1}}(m^i\Vert b)$$and sample a 1-DPNIZK instance respective to \((\textsf {crs}'_{i+1}, \mathsf {msk}'_{i+1})\) with \(r^{m^i\Vert b}\) as randomness:
$$\left( \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert b},k_P^{m^i\Vert b}\right) := 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}'_{i+1}}( \mathsf {msk}'_{i+1} ~;~ r^{m^i\Vert b}).$$ -
(b)
Let \(C'_i\) be the relation that takes as a statement a pair \((\circ _0,\circ _1)\) and as a witness a 3-tuple \((\bullet _0,\bullet _1,\bullet _2)\), and outputs 1 iff
$$\begin{aligned}&\mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Ver}\left( \textsf {crs}^*,c^*_{i+1},(\bullet _0,\bullet _1),\bullet _2\right) = accept ~~~ \wedge \\&\forall b \in \{0,1\}, ~~ \circ _b = 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}'_{i+1}}\left( \bullet _0~;~ r \oplus \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Eval}_{\bullet _1}(m^i\Vert b)\right) .\end{aligned}$$Compute
$$\begin{aligned}&\pi ^{m^i} \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}'_i}\left( C'_i,( \mathsf {pk}^{m^i}, k_P^{m^i}),\right. \\&\quad \left. ( \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 0}, \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 1}), ( \mathsf {msk}'_{i+1},k_{i+1},d^*_{i+1})\right) . \end{aligned}$$
-
(a)
-
4.
Compute
$$\pi ^{m} \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}'_{\lambda }}\left( C,( \mathsf {pk}^m,k_P^{m}), x, w\right) .$$ -
5.
Output \(\pi := \left( m, \{ \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert b} \}_{i = 0,\dots ,\lambda -1, b \in \{0,1\}}, \{ \pi ^{m^i} \}_{i = 0,\dots ,\lambda } \right) \).
-
1.
-
\(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,x,\pi )\):
-
1.
Parse \(\textsf {crs}= (\{\textsf {crs}'_i\}_{i=0,\dots ,\lambda },\textsf {crs}^*,\{c^*_i\}_{i \in [\lambda ]}, \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset },r)\) and \(\pi = \left( m, \{ \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert b} \}_{i = 0,\dots ,\lambda -1, b \in \{0,1\}}, \{ \pi ^{m^i} \}_{i = 0,\dots ,\lambda } \right) \).
-
2.
For \(i = 0,\dots ,\lambda - 1\) compute
$$ 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}'_i}\left( C'_i, \mathsf {pk}^{m^i}, ( \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 0}, \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 1}), \pi ^{m^i} \right) $$and if it rejects (outputs 0) then reject (output 0).
-
3.
Compute and output
$$ 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}'_{\lambda }}\left( C, \mathsf {pk}^m, x, \pi ^{m} \right) .$$
-
1.
Choice of Parameters. Note that by the efficiency of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) there is some fixed polynomial \(p = p(\lambda )\) such that for all \(\lambda ,d\) and \((\textsf {crs}', \mathsf {msk}') \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\) the complexity of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}'}( \mathsf {msk}')\) is p. Therefore, there is some fixed polynomial \(p' = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda ,p) = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) such that for all \(\lambda ,d\) and \((\textsf {crs},k_P) \leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\), the complexity of \(\{C'_i\}_{i}\) (the circuits defined in step (b) of \(\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}}(\cdot ,k_P,\cdot ,\cdot )\)) is at most \(p'\). It follows that there is also some \(d'' = \mathrm{poly}(\lambda )\) such that for all \(\lambda ,d\) and \((\textsf {crs},k_P) \leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\), the depth of \(\{C'_i\}_{i}\) is at most \(d^{''}\). For \(i < \lambda \) we set \(d'_i := d^{''}\) and for \(i = \lambda \) we set \(d'_{\lambda } := d\).
Proof of Completeness. Fix \(\lambda ,d,C,x,w\) where C is of depth at most d and \(C(x,w) = 1\). Consider \((\textsf {crs},k_P) \leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\) and \(\pi \leftarrow \mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,k_P,x,w)\). Parse
Consider the execution of \(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}\left( C,x,\pi \right) \). For \(i = 0,\dots ,\lambda -1\) it holds that
and therefore \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}'_i}\left( C'_i, ( \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 0}, \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 1}), \pi ^{m^i} \right) =1\).
Moreover, since \(C(x,w) =1\), it holds that \( 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}'_{\lambda }}\left( C, x, \pi ^{m} \right) = 1\). \(\square \)
Proof of (Statistical) Soundness.
Notation. For any fixed pair \((\textsf {crs}', \mathsf {msk}') \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Global}.\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },\mathsf {params})\) we divide the space \(\{0,1\}^{\ell }\) into “good randomness” and “bad’ randomness”, where a string \(s' \in \{0,1\}^{\ell }\) is “bad randomness” respective to \((\textsf {crs}', \mathsf {msk}')\) if it breaks its soundness, i.e. if
where \( \mathsf {pk}' \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}'}( \mathsf {msk}' ~;~ s')\), and otherwise \(s'\) is “good randomness”.
The following lemma follows immediately from the \(\epsilon \)-soundness of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) if \(\epsilon (\lambda ) = 2^{-\lambda } \cdot \mathrm{negl}(\lambda )\):
Lemma 2
For every pair \((\textsf {crs}', \mathsf {msk}') \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Global}.\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\) and every set \(S \subset \{0,1\}^{\ell }\) of size at most \(2^{\lambda }\),
We now proceed with the proof of soundness. Fix \(\lambda \), d and a circuit \(C \in \mathcal{C}_d\). Consider the random variable \(\textsf {crs}\leftarrow \mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^d)\) and the corresponding circuits \(\{C'_i\}_{i = 0,\dots ,\lambda -1}\) as described in step (b) of \(\mathsf {Prove}_{\textsf {crs}}\). Parse
and recall that \(\textsf {crs}'_i\) was computed as \(\left( \textsf {crs}'_i, \mathsf {msk}'_i\right) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^{d'_i})\) and \(r {\mathop {\leftarrow }\limits ^{\scriptscriptstyle {\$}}}\{0,1\}^{\ell }\). Moreover, the values \(\{c^*_i\}_{i \in [\lambda ]}\) were compute as
where \(\textsf {crs}^* \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Gen}(1^{\lambda },1^{p+\lambda })\) and \(k_i \leftarrow \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda })\).
For all \(i \in [\lambda ]\) consider the set of strings \(S^i := \{ \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Eval}_{k_i}(m^i)\}_{m^i \in \{0,1\}^i}\). Then due to Lemma 2, it holds that
Assume that there exist \((x,\pi )\) such that \(x \notin \mathcal{L}_{C}\) and \(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,x,\pi )=1\). Parse
-
Assume that there exists some \(j \in [\lambda ]\) such that the value \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}}\) (as appears in \(\pi \)) was computed “honestly” and the value \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^j}\) (as appears in \(\pi \)) wasn’t computed “honestly”, i.e. assume that
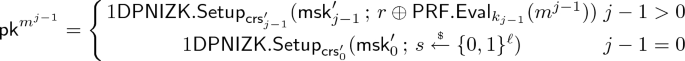
and
$$ \mathsf {pk}^{m^j} \ne 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}'_{j}}( \mathsf {msk}'_{j} ~;~ r \oplus \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Eval}_{k_{j}}(m^j)) . $$Due to soundness of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) respective to \((\textsf {crs}'_{j-1}, \mathsf {msk}'_{j-1})\) and \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}}\) (which holds with all but negl. prob due to Eq. (1)), and since we assume that \(\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}}(C,x,\pi )=1\) and in particular that \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Verify}_{\textsf {crs}'_{j-1}}\left( C'_{j-1}, \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}}, ( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}\Vert 0}, \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}\Vert 1}), \pi ^{m^{j-1}} \right) =1\), with all but negl. prob, there exists a a string \(\hat{w}_{j-1}\) such that
$$\begin{aligned} C'_{j-1}\left( ( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}\Vert 0}, \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}\Vert 1}),\hat{w}_{j-1}\right) = 1. \end{aligned}$$(2)Parse \(\hat{w}_{j-1} = (\widehat{ \mathsf {msk}}_{j},\hat{k}_j,\hat{d}^*_j)\), then Eq. (2) in particular means that
$$ \mathsf {pk}^{m^j} = 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}'_{j}}(\widehat{ \mathsf {msk}}_{j} ~;~ r \oplus \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Eval}_{\hat{k}_j}(m^j)) . $$Since we assume that \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^j}\) wasn’t generated honestly, i.e. that
$$ \mathsf {pk}^{m^j} \ne 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Setup}_{\textsf {crs}'_{j}}( \mathsf {msk}'_{j} ~;~ r \oplus \mathsf {PRF}.\mathsf {Eval}_{k_{j}}(m^j)) , $$it follows that \((\widehat{ \mathsf {msk}}_{j},\hat{k}_j) \ne ( \mathsf {msk}'_j,k_j)\). However, Eq. (2) also implies that
$$\mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Ver}\left( \textsf {crs}^*,c^*_{j},(\widehat{ \mathsf {msk}}_{j},\hat{k}_j),\hat{d}^*_j\right) = accept,$$and therefore the decommitment \(\hat{d}^*_j\) breaks the soundness of \(\mathsf {SBCS}\) respective to \((\textsf {crs}^*, c^*_j)\) and the pair of messages \(( \mathsf {msk}'_j,k_j)\) and \((\widehat{ \mathsf {msk}}_{j},\hat{k}_j)\). Since the soundness of \(\mathsf {SBCS}\) respective to \((\textsf {crs}^*, c^*_j)\) holds with all but negligible probability, it follows that the probability that \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}}\) was computed “honestly” and \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^j}\) wasn’t computed “honestly” is negligible.
Since for \(j-1 = 0\) the value \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{j-1}}\) is always generated honestly during \(\mathsf {Setup}\), an inductive argument implies that with all but negligible probability all of the values \( \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset }, \mathsf {pk}^{m^{1}},\dots , \mathsf {pk}^{m^{\lambda -1}}, \mathsf {pk}^{m} \in \pi \) were generated honestly.
Lastly, the soundness of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) respective to \((\textsf {crs}'_{\lambda }, \mathsf {msk}'_{\lambda })\) and \( \mathsf {pk}^{m}\) implies that with all but negligible probability there is no \((x,C,\pi ^m)\) such that
\(\square \)
Proof of (Programmable CRS) Zero-Knowledge. Let \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}= (\mathcal{S}_1,\mathcal{S}_2)\) be the single-statement zero-knowledge simulator of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) and define the zero-knowledge simulator \(\mathcal{S}= (\mathcal{S}_1,\mathcal{S}_2)\) as follows:
-
\(\mathcal{S}_1(1^{\lambda })\):
-
1.
For \(i = 0,\dots ,\lambda \) compute \((\textsf {crs}'_i, \mathsf {msk}'_i) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathsf {Global}\mathsf {Setup}(1^{\lambda },1^{d'_i})\).
-
2.
Sample \(r {\mathop {\leftarrow }\limits ^{\scriptscriptstyle {\$}}}\{0,1\}^{\ell }\).
-
3.
Compute \(\textsf {crs}^* \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Gen}(1^{\lambda },1^{p+\lambda })\) and for \(i \in [\lambda ]\) sample \((c^*_i,d^*_i) \leftarrow \mathsf {SBCS}.\mathsf {Commit}(\textsf {crs}^*,0^{p+\lambda })\).
-
4.
Compute \(( \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset }, \tau ^{\emptyset }) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_1(\textsf {crs}'_0)\).
-
5.
Output \(\textsf {crs}:= (\{\textsf {crs}'_i\}_{i=0,\dots ,\lambda },\textsf {crs}^*,\{c^*_i\}_{i \in [\lambda ]}, \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset },r)\) and \(\tau := \tau ^{\emptyset }\).
-
1.
-
\(\mathcal{S}_2(C,\textsf {crs},\tau ,x)\):
-
1.
Parse \(\textsf {crs}= (\{\textsf {crs}'_i\}_{i=0,\dots ,\lambda },\textsf {crs}^*,\{c^*_i\}_{i \in [\lambda ]}, \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset },r)\) and \(\tau = \tau ^{\emptyset }\).
-
2.
Compute \(m {\mathop {\leftarrow }\limits ^{\scriptscriptstyle {\$}}}\{0,1\}^{\lambda }\) and for \(i \in [\lambda ]\) let \(m^i\) denote length-i prefix of m (i.e. \(m^i = m_1m_2\dots m_i\)). In particular denote \(m^0 = \emptyset \) and \(m^{\lambda } = m\).
-
3.
For \(i = 0, \dots , \lambda -1\) do:
-
(a)
For \(b \in \{0,1\}\) compute
$$( \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert b} ,\tau ^{m^i\Vert b} )\leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_1(\textsf {crs}'_{i+1}).$$ -
(b)
Compute
$$\pi ^{m^i} \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_2\left( \textsf {crs}'_i,C'_i, \mathsf {pk}^{m^i},\tau ^{m^i}, ( \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 0}, \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 1})\right) .$$
-
(a)
-
4.
Compute
$$\pi ^{m} \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_2\left( \textsf {crs}'_{\lambda },C, \mathsf {pk}^m,\tau ^m, x\right) .$$ -
5.
Output \(\pi := \left( m, \{ \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert b} \}_{i = 0,\dots ,\lambda -1, b \in \{0,1\}}, \{ \pi ^{m^i} \}_{i = 0,\dots ,\lambda } \right) \).
-
1.
We now prove indistinguishability via a sequence of \(2+3\lambda \) hybrids:
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{0}\) . The real \(\mathsf {Setup},\mathsf {Prove}\) algorithms.
For \(i = 0,\dots ,\lambda -1\) we define the hybrids \(\{\mathcal {H}_{i,j}\}_{j \in [3]}\) and consider the sequence
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{i,1}\) . Note that in the previous hybrid, \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) public-keys respective to \(\textsf {crs}'_i\) are sampled with real randomness, and \( \mathsf {msk}'_i\) is not used elsewhere. We therefore can simulate them and proofs respective to them. Formally, we change the way that values of the form \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{i-1}\Vert b}\) and \(\pi ^{m^i}\) are generated:
-
If \(i = 0\), change the way that \( \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset }\) is generated during \(\mathsf {Setup}\):
$$( \mathsf {pk}^{\emptyset },\tau ^{\emptyset }) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_1(\textsf {crs}'_0).$$If \(i > 0\), change the way that \( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{i-1}\Vert b}\) is generated during the \((i-1)\)th iteration of Step (3) of \(\mathsf {Prove}\):
$$( \mathsf {pk}^{m^{i-1}\Vert b},\tau ^{m^{i-1}\Vert b}) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_1(\textsf {crs}'_i).$$ -
Change the way that \(\pi ^{m^i}\) is generated during the ith iteration of Step (3) of \(\mathsf {Prove}\):
$$\pi ^{m^i} \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_2\left( \textsf {crs}'_i,C'_i, \mathsf {pk}^{m^i},\tau ^{m^i}, (pk^{m^i\Vert 0}, \mathsf {pk}^{m^i\Vert 1})\right) .$$
Hybrids \(\mathcal {H}_{i-1,3}\) and \(\mathcal {H}_{i,1}\) are indistinguishable due to the single-statement zero-knowledge of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) respective to \(\textsf {crs}'_i\).
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{i,2}\) . Note that in the previous hybrid, the value \(d^*_{i+1}\) is never used. In this hybrid we change the way that the commitment \(c^*_{i+1}\) is computed:
Hybrids \(\mathcal {H}_{i,1}\) and \(\mathcal {H}_{i,2}\) are indistinguishable due to the hiding of \(\mathsf {SBCS}\).
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{i,3}\) . Note that in the previous hybrid, the value \(k_{i+1}\) is only used when computing
during \(\mathsf {Prove}\). In this hybrid we sample instead \(r^{m^i\Vert b} {\mathop {\leftarrow }\limits ^{\scriptscriptstyle {\$}}}\{0,1\}^{\ell }\). Hybrids \(\mathcal {H}_{i,2}\) and \(\mathcal {H}_{i,3}\) are indistinguishable due to the pseudorandomness of \(\mathsf {PRF}\).
Hybrid \(\mathcal {H}_{\lambda }\) . Note that in the previous hybrid (\(\mathcal {H}_{\lambda -1,3}\)), \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) public-keys respective to \(\textsf {crs}'_{\lambda }\) are sampled with real randomness, and \( \mathsf {msk}'_{\lambda }\) is not used elsewhere.
Moreover, the values m which are used by the prover when answering proof queries are sampled uniformly at random from \(\{0,1\}^{\lambda }\). Since the adversary is allowed to make at most a polynomial number of queries, with all but negligible probability the prover does not sample the same m for two different proof queries. In that case, for every \( \mathsf {pk}^m\) that is sampled respective to \(\textsf {crs}'_{\lambda }\), the prover generates at most a single proof.
We therefore can simulate those proofs with the single-statement zero-knowledge simulator of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\). Formally, we change the way that values of the form \( \mathsf {pk}^{m}\) and \(\pi ^{m}\) are generated:
-
Change the way that \( \mathsf {pk}^{m}\) is generated during the \((\lambda -1)\)th iteration of Step (3) of \(\mathsf {Prove}\):
$$( \mathsf {pk}^{m},\tau ^{m}) \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_1(\textsf {crs}'_{\lambda }).$$ -
Change the way that \(\pi ^{m}\) is generated during Step (4) of \(\mathsf {Prove}\):
$$\pi ^{m} \leftarrow 1\mathsf {DPNIZK}.\mathcal{S}_2\left( \textsf {crs}'_{\lambda },C, \mathsf {pk}^{m},\tau ^{m}, x\right) .$$
Hybrids \(\mathcal {H}_{\lambda -1,3}\) and \(\mathcal {H}_{\lambda }\) are indistinguishable due to the single-statement zero-knowledge of \(1\mathsf {DPNIZK}\) respective to \(\textsf {crs}'_{\lambda }\). This hybrid is identical to the simulator, which completes the proof. \(\square \)
References
Boneh, D., Freeman, D.M.: Homomorphic signatures for polynomial functions. In: Paterson, K.G. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 2011. LNCS, vol. 6632, pp. 149–168. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20465-4_10
Boneh, D., Freeman, D.M.: Linearly homomorphic signatures over binary fields and new tools for lattice-based signatures. In: Catalano, D., Fazio, N., Gennaro, R., Nicolosi, A. (eds.) PKC 2011. LNCS, vol. 6571, pp. 1–16. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19379-8_1
Bellare, M., Fuchsbauer, G.: Policy-based signatures. In: Krawczyk [Kra14], pp. 520–537
Boneh, D., Freeman, D., Katz, J., Waters, B.: Signing a linear subspace: signature schemes for network coding. In: Jarecki, S., Tsudik, G. (eds.) PKC 2009. LNCS, vol. 5443, pp. 68–87. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00468-1_5
Blum, M., Feldman, P., Micali, S.: Non-interactive zero-knowledge and its applications (extended abstract). In: Simon, J. (ed.) Proceedings of the 20th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, 2–4 May 1988, Chicago, Illinois, USA, pp. 103–112. ACM (1988)
Boyle, E., Goldwasser, S., Ivan, I.: Functional signatures and pseudorandom functions. In: Krawczyk [Kra14], pp. 501–519. IACR ePrint (2013). http://eprint.iacr.org/2013/401
Brakerski, Z., Vaikuntanathan, V.: Lattice-based FHE as secure as PKE. In: Naor, M. (ed.) Innovations in Theoretical Computer Science, ITCS 2014, Princeton, NJ, USA, 12–14 January 2014, pp. 1–12. ACM (2014)
Boneh, D., Zhandry, M.: Multiparty key exchange, efficient traitor tracing, and more from indistinguishability obfuscation. In: Garay, J.A., Gennaro, R. (eds.) CRYPTO 2014. LNCS, vol. 8616, pp. 480–499. Springer, Heidelberg (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44371-2_27
Canetti, R., et al.: from practice to theory. In: Charikar, M., Cohen, E. (eds.) Proceedings of the 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing, STOC 2019, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 23–26 June 2019, pp. 1082–1090. ACM (2019)
Charles, D.X., Jain, K., Lauter, K.E.: Signatures for network coding. IJICoT 1(1), 3–14 (2009)
Damgård, I.: Non-interactive circuit based proofs and non-interactive perfect zero-knowledge with preprocessing. In: Rueppel, R.A. (ed.) EUROCRYPT 1992. LNCS, vol. 658, pp. 341–355. Springer, Heidelberg (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-47555-9_28
Feige, U., Lapidot, D., Shamir, A.: Multiple non-interactive zero knowledge proofs based on a single random string (extended abstract). In: 31st Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, St. Louis, Missouri, USA, 22–24 October 1990, vol. I, pp. 308–317. IEEE Computer Society (1990)
Gentry, C.: A fully homomorphic encryption scheme. PhD thesis, Stanford University (2009). crypto.stanford.edu/craig
Gentry, C., Groth, J., Ishai, Y., Peikert, C., Sahai, A., Smith, A.D.: Using fully homomorphic hybrid encryption to minimize non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs. J. Cryptol. 28(4), 820–843 (2015)
Gennaro, R., Katz, J., Krawczyk, H., Rabin, T.: Secure network coding over the integers. In: Nguyen, P.Q., Pointcheval, D. (eds.) PKC 2010. LNCS, vol. 6056, pp. 142–160. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13013-7_9
Gorbunov, S., Vaikuntanathan, V., Wichs, D.: Leveled fully homomorphic signatures from standard lattices. In: Servedio, R.A., Rubinfeld, R. (eds.) Proceedings of the Forty-Seventh Annual ACM on Symposium on Theory of Computing, STOC 2015, Portland, OR, USA, 14–17 June 2015, pp. 469–477. ACM (2015)
Katsumata, S., Nishimaki, R., Yamada, S., Yamakawa, T.: Designated verifier/prover and preprocessing NIZKs from Diffie-Hellman assumptions. In: Ishai, Y., Rijmen, V. (eds.) EUROCRYPT 2019. LNCS, vol. 11477, pp. 622–651. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-17656-3_22
Katsumata, S., Nishimaki, R., Yamada, S., Yamakawa, T.: Compact NIZKs from standard assumptions on bilinear maps. In: Canteaut, A., Ishai, Y. (eds.) EUROCRYPT 2020. LNCS, vol. 12107, pp. 379–409. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45727-3_13
Kilian, J., Petrank, E.: An efficient non-interactive zero-knowledge proof system for NP with general assumptions. Electron. Colloq. Comput. Complex. 2(38) (1995)
Krawczyk, H. (ed.): PKC 2014. LNCS, vol. 8383. Springer, Heidelberg (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54631-0
Kim, S., Wu, D.J.: Multi-theorem preprocessing NIZKs from lattices. In: Shacham, H., Boldyreva, A. (eds.) CRYPTO 2018. LNCS, vol. 10992, pp. 733–765. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96881-0_25
Maji, H.K., Prabhakaran, M., Rosulek, M.: Attribute-based signatures. In: Kiayias, A. (ed.) CT-RSA 2011. LNCS, vol. 6558, pp. 376–392. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19074-2_24
Peikert, C., Shiehian, S.: Noninteractive zero knowledge for NP from (plain) learning with errors. In: Boldyreva, A., Micciancio, D. (eds.) CRYPTO 2019. LNCS, vol. 11692, pp. 89–114. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26948-7_4
Regev, O.: On lattices, learning with errors, random linear codes, and cryptography. In: Gabow, H.N., Fagin, R. (eds.) STOC, pp. 84–93. ACM (2005). Full version in [?]
Sakai, Y., Attrapadung, N., Hanaoka, G.: Attribute-based signatures for circuits from bilinear map. In: Cheng, C.-M., Chung, K.-M., Persiano, G., Yang, B.-Y. (eds.) PKC 2016. LNCS, vol. 9614, pp. 283–300. Springer, Heidelberg (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49384-7_11
Sakai, Y., Katsumata, S., Attrapadung, N., Hanaoka, G.: Attribute-based signatures for unbounded languages from standard assumptions. In: Peyrin, T., Galbraith, S. (eds.) ASIACRYPT 2018. LNCS, vol. 11273, pp. 493–522. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03329-3_17
De Santis, A., Micali, S., Persiano, G.: Non-interactive zero-knowledge proof systems. In: Pomerance, C. (ed.) CRYPTO 1987. LNCS, vol. 293, pp. 52–72. Springer, Heidelberg (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-48184-2_5
Tsabary, R.: An equivalence between attribute-based signatures and homomorphic signatures, and new constructions for both. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive 2017:723 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 International Association for Cryptologic Research
About this paper
Cite this paper
Brakerski, Z., Garg, S., Tsabary, R. (2020). FHE-Based Bootstrapping of Designated-Prover NIZK. In: Pass, R., Pietrzak, K. (eds) Theory of Cryptography. TCC 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12550. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64375-1_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64375-1_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-64374-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-64375-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)