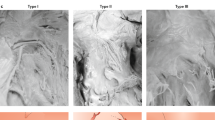
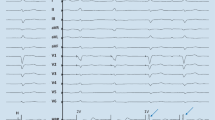
Abstract
Long-term RV apical pacing has been associated with increased risk of atrial fibrillation, heart failure hospitalizations, pacing-induced cardiomyopathy, and associated mortality. The search for an alternative site of pacing for ventricular activation has led us to His–Purkinje conduction system pacing (HP-CSP) which presently includes His bundle pacing (HBP) and left bundle branch pacing (LBBP). HP-CSP results in synchronized ventricular activation by direct stimulation of the His–Purkinje network and may result in prevention of some of the adverse clinical outcomes. HP-CSP can also overcome bundle branch block patterns and might be an option for cardiac resynchronization therapy. In this chapter, we review the anatomy of the conduction system and mechanisms of QRS narrowing with HP-CSP and review some of the best practices during implantation to allow for better long-term performance and outcomes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sweeney MO, et al. Adverse effect of ventricular pacing on heart failure and atrial fibrillation among patients with normal baseline QRS duration in a clinical trial of pacemaker therapy for sinus node dysfunction. Circulation. 2003;107:2932–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Cir.0000072769.17295.B1.
Khurshid S, et al. Incidence and predictors of right ventricular pacing-induced cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm. 2014;11:1619–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2014.05.040.
Kiehl EL, et al. Incidence and predictors of right ventricular pacing-induced cardiomyopathy in patients with complete atrioventricular block and preserved left ventricular systolic function. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13:2272–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2016.09.027.
Sharma PS, et al. Permanent His-bundle pacing is feasible, safe, and superior to right ventricular pacing in routine clinical practice. Heart Rhythm. 2015;12:305–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2014.10.021.
Abdelrahman M, et al. Clinical outcomes of his bundle pacing compared to right ventricular pacing. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:2319–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.02.048.
Vijayaraman P, et al. Outcomes of his bundle pacing upgrade after long-term right ventricular pacing and / or pacing-induced cardiomyopathy: insights into disease progression. Heart Rhythm J. 2019;16(10):1554–61.
Lustgarten DL, et al. His-bundle pacing versus biventricular pacing in cardiac resynchronization therapy patients: a crossover design comparison. Heart Rhythm. 2015;12:1548–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.03.048.
Sharma PS, et al. Permanent His-bundle pacing as an alternative to biventricular pacing for cardiac resynchronization therapy: a multicenter experience. Heart Rhythm. 2017;15:413–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2017.10.014.
Upadhyay GA, et al. His corrective pacing or biventricular pacing for cardiac resynchronization in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:157–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2019.04.026.
Scherlag BJ, Lazzara R. Functional aspects of His bundle physiology and pathophysiology: clinical implications. J Electrocardiol. 2017;50:151–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2016.07.011.
Elizari MV. The normal variants in the left bundle branch system. J Electrocardiol. 2017;50:389–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2017.03.004.
Kawashima T, Sasaki H. A macroscopic anatomical investigation of atrioventricular bundle locational variation relative to the membranous part of the ventricular septum in elderly human hearts. Surg Radiol Anat. 2005;27:206–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-004-0302-7.
Narula OS. Longitudinal dissociation in the His bundle. Bundle branch block due to asynchronous conduction within the His bundle in man. Circulation. 1977;6:996–1006.
El-Sherif N. Normalization of bundle branch block patterns by distal His bundle pacing. Clinical and experimental evidence of longitudinal dissociation in the pathologic His bundle. Circulation. 1978;57:473–83.
Sharma PS, Huizar J, Ellenbogen KA, Tan AY. Recruitment of bundle branches with permanent His bundle pacing in a patient with advanced conduction system disease: what is the mechanism? Heart Rhythm. 2016;13:623–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.11.012.
Sharma PS, Ellison K, Patel HN, Trohman RG. Overcoming left bundle branch block by permanent His bundle pacing: evidence of longitudinal dissociation in the His via recordings from a permanent pacing lead. Heart Rhythm Case Rep. 2017;3:499–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrcr.2017.08.002.
Deshmukh P, Casavant DA, Romanyshyn M, Anderson K. Permanent, direct His-bundle pacing : a novel approach to cardiac pacing in patients with normal His-Purkinje activation. Circulation. 2000;101:869–77. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.8.869.
Dandamudi G, Vijayaraman P. How to perform permanent His bundle pacing in routine clinical practice. Heart Rhythm. 2016;13:1362–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2016.03.040.
Vijayaraman P, Dandamudi G. How to perform permanent His bundle pacing: tips and tricks. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2016;39:1298–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/pace.12904.
Sharma PS, Vijayaraman P, Ellenbogen KA. Permanent His bundle pacing: shaping the future of physiological ventricular pacing. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-019-0224-z.
Vijayaraman P, Dandamudi G, Ellenbogen KA. Electrophysiological observations of acute His bundle injury during permanent His bundle pacing. J Electrocardiol. 2016;49:664–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2016.07.006.
Huang W, et al. A beginner’s guide to permanent left bundle branch pacing. Heart Rhythm. 2019; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2019.06.016.
Vijayaraman P, et al. Permanent His bundle pacing: recommendations from a Multicenter His Bundle Pacing Collaborative Working Group for standardization of definitions, implant measurements, and follow-up. Heart Rhythm. 2017; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2017.10.039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sharma, P.S., Vijayaraman, P. (2021). His Purkinje Conduction System Pacing: Methods, Mechanisms, and Best Practices. In: Efimov, I.R., Ng, F.S., Laughner, J.I. (eds) Cardiac Bioelectric Therapy. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63355-4_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63355-4_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-63354-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-63355-4
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)