Abstract
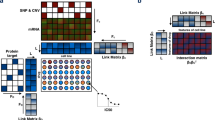
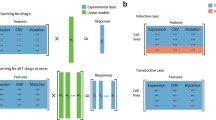
The molecular characterization of tumor samples by multiple omics data sets of different types or modalities (e.g. gene expression, mutation, CpG methylation) has become an invaluable source of information for assessing the expected performance of individual drugs and their combinations. Merging relevant information from the omics data modalities provides the statistical basis for determining suitable therapies for specific cancer patients. Different data modalities may each have their own specific structures that need to be taken into account during inference. In this paper, we assume that each omics data modality has a low-rank structure with only a few relevant features that affect the prediction and we propose to use a composite local nuclear norm penalization for learning drug sensitivity. Numerical results show that the composite low-rank structure can improve the prediction performance compared to using a global low-rank approach or elastic net regression.
The first two authors contributed equally. L.R. is supported by The Norwegian Research Council 237718 through the Big Insight Center for research-driven innovation. The research of T.T.M. and J.C. are supported by the European Research Council (SCARABEE, no. 742158).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M., Aittokallio, T.: Machine learning and feature selection for drug response prediction in precision oncology applications. Biophys. Rev. 11(1), 31–39 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-018-0446-z
Ali, M., Khan, S.A., Wennerberg, K., Aittokallio, T.: Global proteomics profiling improves drug sensitivity prediction: results from a multi-omics, pan-cancer modeling approach. Bioinformatics 34(8), 1353–1362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx766
Ammad-Ud-Din, M., Khan, S.A., Wennerberg, K., Aittokallio, T.: Systematic identification of feature combinations for predicting drug response with Bayesian multi-view multi-task linear regression. Bioinformatics 33(14), i359–i368 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx266
Barretina, J., et al.: The cancer cell line encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 483(7391), 603 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11003
Chang, Y., et al.: Cancer drug response profile scan (CDRscan): a deep learning model that predicts drug effectiveness from cancer genomic signature. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27214-6
Chen, J., Zhang, L.: A survey and systematic assessment of computational methods for drug response prediction. Brief. Bioinform. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbz164
Chen, K., Dong, H., Chan, K.S.: Reduced rank regression via adaptive nuclear norm penalization. Biometrika 100(4), 901–920 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/ast036
Costello, J.C., et al.: A community effort to assess and improve drug sensitivity prediction algorithms. Nat. Biotechnol. 32(12), 1202 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2877
Ammad-ud din, M., et al.: Drug response prediction by inferring pathway-response associations with kernelized Bayesian matrix factorization. Bioinformatics 32(17), i455–i463 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw433
Dugger, S.A., Platt, A., Goldstein, D.B.: Drug development in the era of precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17(3), 183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2017.226
Garnett, M.J., et al.: Systematic identification of genomic markers of drug sensitivity in cancer cells. Nature 483(7391), 570 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11005
Geeleher, P., et al.: Discovering novel pharmacogenomic biomarkers by imputing drug response in cancer patients from large genomics studies. Genome Res. 27(10), 1743–1751 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.221077.117
Güvenç Paltun, B., Mamitsuka, H., Kaski, S.: Improving drug response prediction by integrating multiple data sources: matrix factorization, kernel and network-based approaches. Brief. Bioinform. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbz153
Hasin, Y., Seldin, M., Lusis, A.: Multi-omics approaches to disease. Genome Biol. 18(1), 83 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1215-1
Li, G., Liu, X., Chen, K.: Integrative multi-view regression: bridging group-sparse and low-rank models. Biometrics (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/biom.13006
Roses, A.D.: Pharmacogenetics in drug discovery and development: a translational perspective. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 7(10), 807–817 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2593
Suphavilai, C., Bertrand, D., Nagarajan, N.: Predicting cancer drug response using a recommender system. Bioinformatics 34(22), 3907–3914 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty452
Tibshirani, R.: Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 58(1), 267–288 (1996)
Wang, L., Li, X., Zhang, L., Gao, Q.: Improved anticancer drug response prediction in cell lines using matrix factorization with similarity regularization. BMC Cancer 17(1), 513 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3500-5
Yadav, B., et al.: Quantitative scoring of differential drug sensitivity for individually optimized anticancer therapies. Sci. Rep. 4(1) (2014).https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05193
Yang, W., et al.: Genomics of drug sensitivity in cancer (GDSC): a resource for therapeutic biomarker discovery in cancer cells. Nucl. Acids Res. 41(D1), D955–D961 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1111
Yuan, M., Lin, Y.: Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 68(1), 49–67 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9868.2005.00532.x
Zhang, Y., Yang, Q.: A survey on multi-task learning. CoRR abs/1707.08114 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1707.08114
Zhao, Z., Zucknick, M.: Structured penalized regression for drug sensitivity prediction. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/rssc.12400
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mai, T.T., Rønneberg, L., Zhao, Z., Zucknick, M., Corander, J. (2020). Learning Cancer Drug Sensitivities in Large-Scale Screens from Multi-omics Data with Local Low-Rank Structure. In: Cazzaniga, P., Besozzi, D., Merelli, I., Manzoni, L. (eds) Computational Intelligence Methods for Bioinformatics and Biostatistics. CIBB 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12313. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63061-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63061-4_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-63060-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-63061-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)