Abstract
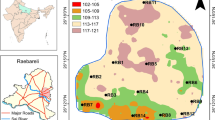
Assessment of the groundwater quality of the Kangsabati river basin confined with both agricultural and arid parts reside at Paschim Medinipur, West Bengal, India. Total 50 water samples were analyzed for studying the three different major seasons. Then the collected samples from the river basin were studied for electrical conductivity, TDS, pH, and major cations like sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium as well as anions like carbonate, bicarbonate, chloride, nitrate and sulphate (followed by the American Public Health Association’s protocol). The specified locations were selected to cover the whole study area and specific consideration was given to the region where contamination is expected. The usual groundwater contaminants were nitrate, chloride, TDS, Na and K elements. The results were assessed in relation to the drinking water quality standardized by the World Health Organization. To find out the precise distribution pattern of the concentration of different elements and targeted to differentiate the higher pollutants concentration, multiple statistical approaches also carried out, discussed, and presented in zone-based classification. Though the polluted areas in this are surveyed out but groundwater of Kangsabati river basin will be managed by applying the proper management practices.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, M., Samie, S. A., & Badawy, H. (2013). Factors controlling mechanisms of groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in the Quaternary aquifer of the Eastern Nile Delta. Egypt Environmental Earth Sciences, 68, 369–394.
Apha, A. (1995). WEF, 1998 Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater 20.
Austen, M., et al. (2002). Biodiversity links above and below the marine sediment–water interface that may influence community stability. Biodiversity & Conservation, 11, 113–136.
Famiglietti, J. S. (2014). The global groundwater crisis. Nature Climate Change, 4 945.
Harrison, R. M. (2015). Pollution: causes, effects and control. Royal Society of Chemistry.
Kar, A., Bhattacharya, M., Ghorai, M., Patra, S., & Patra, B. C. (2017). Ichthyofaunal diversity of Kangsabati River at Paschim Medinipur District, West Bengal, India. In Proceedings of the Zoological Society (pp. 165–173). Springer.
Kisku, S., Chini, D. S., Bhattacharya, M., Kar, A., Parua, S., Das, B. K., & Patra, B. C. (2017). A cross-sectional study on water quality in relation to fish diversity of Paschim Medinipur, West Bengal, India through geoinformatics approaches. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 43, 283–289.
Kumar, C. (2001). Simulation of sea water intrusion and tidal influence ISH. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 7, 1–11.
Kumar, M., Ramanathan, A., Rao, M., & Kumar, B. (2006). Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environmental Geology, 50, 1025–1039.
Nag, S., & Ghosh, P. (2013). Variation in groundwater levels and water quality in Chhatna Block, Bankura district, West Bengal—A GIS approach. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 81, 261–280.
Organization WH. (1993). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization.
Otieno, F. A. O., Olumuyiwa, I. O., Ochieng, G. M. (2012). Groundwater: Characteristics, qualities, pollutions and treatments: An overview.
Ravikumar, P., Somashekar, R., & Angami, M. (2011). Hydrochemistry and evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in the Markandeya River basin, Belgaum District, Karnataka State, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173, 459–487.
Ritter, K. S., Sibley, P., Hall, K., Keen, P., Mattu, G., Linton, B., et al. (2002). Sources, pathways, and relative risks of contaminants in surface water and groundwater: A perspective prepared for the Walkerton inquiry. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part A, 65, 1–142.
Sen, J., Sen, S., & Bandyopadhyay, S. (2004). Geomorphological investigation of badlands: A case study at Garhbeta, West Medinipur District, West Bengal, India. Geomorphology and Environment, 204–234.
Shit, P., Bhunia, G., & Maiti, R. (2014). Vegetation influence on runoff and sediment yield in the lateritic region: An experimental study. Journal of Geography and Natural Disasters, 4 116.
Spalding, R., & Exner, M. (1991). Nitrate contamination in the contiguous United States. In Nitrate contamination (pp. 13–48). Springer.
Swartjes, F. A. (2011). Introduction to contaminated site management. In Dealing with contaminated sites (pp. 3–89). Springer.
Toda, H., Mochizuki, Y., Kawanishi, T., & Kawashima, H. (2002). Denitrification in shallow groundwater in a coastal agricultural area in Japan. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 63, 167–173.
Zahid, A., Hassan, M. Q., Balke, K.-D., Flegr, M., & Clark, D. W. (2008). Groundwater chemistry and occurrence of arsenic in the Meghna floodplain aquifer, southeastern Bangladesh. Environmental Geology, 54, 1247–1260.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kar, A., Chini, D.S., Patra, B.C., Bhattacharya, M. (2021). Assessment of Groundwater Resource Pollution in Kangsabati River Basin, Paschim Medinipur, West Bengal, India. In: Adhikary, P.P., Shit, P.K., Santra, P., Bhunia, G.S., Tiwari, A.K., Chaudhary, B.S. (eds) Geostatistics and Geospatial Technologies for Groundwater Resources in India. Springer Hydrogeology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62397-5_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62397-5_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-62396-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-62397-5
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)