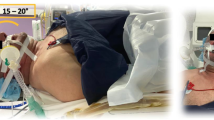
Abstract
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN), or tic douloureux, is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by recurrent attacks of lancinating facial pain occurring in the distribution of one or more divisions of the trigeminal Nerve. When trigeminal neuralgia becomes refractory to medical management, surgery becomes imminent. Glycerol rhizolysis, thermocoagulation, and Percutaneous balloon compression (PBC) are well established in the treatment of TN. It is indicated in patients who have failed medical therapy, TN in association with multiple sclerosis (MS), young patients willing to accept the associated mild numbness occurring after surgery. Should be avoided in patients with atypical facial pain or post-herpetic pain and contralateral masseter weakness. Light sedation with anxiolytics such as benzodiazepines and fast-acting opioids such as Fentanyl is used at some settings, although the majority of the patients require general anesthesia with intratracheal intubation. Long-term pain recurrence varies between 20 and 43%, and immediate pain relief is higher than 90%. Late regeneration of damaged nerves might be a factor leading to higher recurrence rates. Studies often reported longer pain relief with balloon compression than glycerol rhizolysis and thermocoagulation. PBC leads to numbness and a few minor and transitory complications. PBC following previous percutaneous procedures was found to be highly effective.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Montano N, Conforti G, Di Bonaventura R, Meglio M, Fernandez E, Papacci F. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;11:289–99.
Krafft RM. Trigeminal neuralgia. Am Fam Physician. 2008;77:1291–6.
McMillan R. Trigeminal neuralgia—a debilitating facial pain. Rev pain. 2011;5:26–34.
Cruccu G, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS, Scholz J, Sindou M, Svensson P, et al. Trigeminal neuralgia: new classification and diagnostic grading for practice and research. Neurology. 2016;87:220–8. Describing a new classification system for TN
Mullan S, Lichtor T. Percutaneous microcompression of the trigeminal ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1983;59(6):1007–12.
Shelden CH, Pudenz RH, Freshwater DB, Crue BL. Compression rather decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1955;12:123–6.
Brown JA, Hoeflinger B, Long PB, Gunning WT, Rhoades R, Bennet-Clarke CA, et al. Axon and ganglion cell injury in rabbits after percutaneous trigeminal balloon compression. Neurosurgery. 1996;38:993–1004.
Abdennebi B, Guenane L. Technical considerations and outcome assessment in retrogasserian balloon compression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Series of 901 patients. Surg Neurol Int. 2014;5:118.
Tibano AT, de Siqueira SRDT, da Nóbrega JCM, et al. Cardiovascular response during trigeminal ganglion compression for trigeminal neuralgia according to the use of local anesthetics. Acta Neurochir. 2010;152:1347–51.
Kefalopoulou Z, Markaki E, Constantoyannis C. Avoiding abducens nerve palsy during the percutaneous balloon compression procedure. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2009;87(2):101–4.
AsPlund P, Linderoth B, Bergenhei AT. The predictive power of balloon shape and change of sensory functions on outcome of percutaneous balloon compression for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2010;113:498–507.
Lee S-T, Chen J-F. Percutaneous trigeminal ganglion balloon compression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia—part I: pressure recordings. Surg Neurol. 2003;59:63–7.
Lee ST, Chen JF. Percutaneous trigeminal ganglion balloon compression for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia—part II: results related to compression duration. Surg Neurol. 2003;60:149–54.
Brown JA, Pilitsis JG. Percutaneous balloon compression for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: results in 56 patients based on balloon compression pressure monitoring. Neurosurg Focus. 2005;18:E10.
Noorani I, Lodge A, Vajramani G, Sparrow O. Comparing percutaneous treatments of trigeminal neuralgia: 19 years of experience in a single centre. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2016;94(2):75–85. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445077.
Montano N, Papacci F, Cioni B, et al. The role of percutaneous balloon compression in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia recurring after other surgical procedures. Acta Neurol Belg. 2014;114:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-013-0263-x.
Martin S, Teo M, Suttner N. The effectiveness of percutaneous balloon compression in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurosurg. 2015;123(6):1507–11. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.11.jns14736.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Roychoudhury, P., Di Grazia, V., Orhurhu, V., Abd-Elsayed, A. (2021). Balloon Compression of the Trigeminal Nerve. In: Abd-Elsayed, A. (eds) Trigeminal Nerve Pain. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60687-9_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60687-9_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-60686-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-60687-9
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)