Abstract
We advocate the use of conformal prediction (CP) to enhance rule-based multi-label classification (MLC). In particular, we highlight the mutual benefit of CP and rule learning: Rules have the ability to provide natural (non-)conformity scores, which are required by CP, while CP suggests a way to calibrate the assessment of candidate rules, thereby supporting better predictions and more elaborate decision making. We illustrate the potential usefulness of calibrated conformity scores in a case study on lazy multi-label rule learning.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
 is the indicator function, i.e.,
is the indicator function, i.e.,  if the predicate A is true and \(=0\) otherwise.
if the predicate A is true and \(=0\) otherwise. - 2.
50 random splits into 400 training examples and 196 test examples.
- 3.
Note that the accuracy-rejection curve for random abstention is flat.
References
Aha, D. (ed.): Lazy Learning. Kluwer Academic Publ., Dordrecht (1997)
Auer, P., Cesa-Bianchi, N., Fischer, P.: Finite-time analysis of the multiarmed bandit problem. Mach. Learn. 47(2–3), 235–256 (2002)
Balasubramanian, V., Ho, S., Vovk, V. (eds.): Conformal Prediction for Reliable Machine Learning: Theory, Adaptations and Applications. Morgan Kaufmann, Waltham (2014)
Dembczynski, K., Waegeman, W., Cheng, W., Hüllermeier, E.: On label dependence and loss minimization in multi-label classification. Mach. Learn. 88(1–2), 5–45 (2012)
Friedman, J., Kohavi, R., Yun, Y.: Lazy decision trees. In: Proceedings AAAI 1996. pp. 717–724. Morgan Kaufmann, Menlo Park, California (1996)
Gammerman, A., Vovk, V., Boström, H., Carlsson, L.: Conformal and probabilistic prediction with applications: editorial. Mach. Learn. 108(3), 379–380 (2019)
Mencía, E.L., Fürnkranz, J., Hüllermeier, E., Rapp, M.: Learning interpretable rules for multi-label classification. In: Escalante, H.J., et al. (eds.) Explainable and Interpretable Models in Computer Vision and Machine Learning. TSSCML, pp. 81–113. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98131-4_4
Nguyen, V.L., Hüllermeier, E.: Reliable multi-label classification: Prediction with partial abstention. In: Proceedings of the AAAI 2020, Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA(2020)
Papadopoulos, H.: Inductive conformal prediction: theory and application to neural networks. Tools Artif. Intel. 18(2), 315–330 (2008)
Papadopoulos, H., Vovk, V., Gammerman, A.: Regression conformal prediction with nearest neighbours. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 40, 815–840 (2011)
Parzen, E.: On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 33, 1065–1076 (1962)
Shafer, G., Vovk, V.: A tutorial on conformal prediction. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 371–421 (2008)
Vovk, V., Gammerman, A., Shafer, G.: Algorithmic Learning in a Random World. Springer, Boston (2003)
Wieczorkowska, A., Synak, P., Ras, Z.: Multi-label classification of emotions in music. In: Klopotek, M., Wierzchon, S., Trojanowski, K. (eds.) Intelligent Information Processing and Web Mining. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-33521-8_30
Zhang, M.L., Zhou, Z.H.: A review on multi-label learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 26(8), 1819–1837 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) under grant number 400845550.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hüllermeier, E., Fürnkranz, J., Loza Mencia, E. (2020). Conformal Rule-Based Multi-label Classification. In: Schmid, U., Klügl, F., Wolter, D. (eds) KI 2020: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. KI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12325. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58285-2_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58285-2_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58284-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58285-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


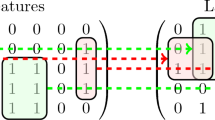


 is the indicator function, i.e.,
is the indicator function, i.e.,  if the predicate A is true and
if the predicate A is true and