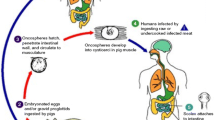
Abstract
Helminth infections are common worldwide and include infections with roundworms (nematodes) and flatworms (cestodes and trematodes). Infections of the central nervous system (CNS) can be caused by a wide range of helminths. As a group, they are common in resource-limited countries, but are rare in wealthy countries. Among these infections, neurocysticercosis is an important cause of seizures worldwide and also a cause of hydrocephalus. Angiostrongylus, Baylisascaris, Toxocara, and Gnathostoma among others can cause eosinophilic meningitis. In this chapter we review epidemiology, presentation, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the common helminthic infections including infections caused by cestodes, nematodes and trematodes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajshekhar V, Raghava MV, Prabhakaran V, Oommen A, Muliyil J. Active epilepsy as an index of burden of neurocysticercosis in Vellore district, India. Neurology. 2006;67(12):2135–9.
Moyano LM, Saito M, Montano SM, Gonzalvez G, Olaya S, Ayvar V, et al. Neurocysticercosis as a cause of epilepsy and seizures in two community-based studies in a cysticercosis-endemic region in Peru. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8(2):e2692.
Debacq G, Moyano LM, Garcia HH, Boumediene F, Marin B, Ngoungou EB, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis estimating association of cysticercosis and neurocysticercosis with epilepsy. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(3):e0005153.
O’Neal SE, Flecker RH. Hospitalization frequency and charges for neurocysticercosis, United States, 2003–2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21(6):969–76.
O’Keefe KA, Eberhard ML, Shafir SC, Wilkins P, Ash LR, Sorvillo FJ. Cysticercosis-related hospitalizations in the United States, 1998–2011. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;92(2):354–9.
Flecker RH, O’Neal SE, Townes JM. Evaluating healthcare claims for neurocysticercosis by using all-payer all-claims data, Oregon, 2010–2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22(12):2168–70.
Ong S, Talan DA, Moran GJ, Mower W, Newdow M, Tsang VC, et al. Neurocysticercosis in radiographically imaged seizure patients in U.S. emergency departments. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8(6):608–13.
Restrepo BI, Llaguno P, Sandoval MA, Enciso JA, Teale JM. Analysis of immune lesions in neurocysticercosis patients: central nervous system response to helminth appears Th1-like instead of Th2. J Neuroimmunol. 1998;89(1–2):64–72.
Restrepo BI, Alvarez JI, Castano JA, Arias LF, Restrepo M, Trujillo J, et al. Brain granulomas in neurocysticercosis patients are associated with a Th1 and Th2 profile. Infect Immun. 2001;69(7):4554–60.
Garcia HH, Nash TE, Del Brutto OH. Clinical symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of neurocysticercosis. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(12):1202–15.
Kramer LD, Locke GE, Byrd SE, Daryabagi J. Cerebral cysticercosis: documentation of natural history with CT. Radiology. 1989;171(2):459–62.
Dumas JL, Visy JM, Belin C, Gaston A, Goldlust D, Dumas M. Parenchymal neurocysticercosis: follow-up and staging by MRI. Neuroradiology. 1997;39(1):12–8.
Nash TE, Pretell EJ, Lescano AG, Bustos JA, Gilman RH, Gonzalez AE, et al. Perilesional brain oedema and seizure activity in patients with calcified neurocysticercosis: a prospective cohort and nested case-control study. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(12):1099–105.
Gupta RK, Awasthi R, Rathore RK, Verma A, Sahoo P, Paliwal VK, et al. Understanding epileptogenesis in calcified neurocysticercosis with perfusion MRI. Neurology. 2012;78(9):618–25.
Nash TE, Ware JM, Mahanty S. Natural history of patients with perilesional edema around Taenia solium calcified granulomas. J Infect Dis. 2017;215(7):1141–7.
Robinson P, Garza A, Weinstock J, Serpa JA, Goodman JC, Eckols KT, et al. Substance P causes seizures in neurocysticercosis. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(2):e1002489.
Nash TE, Bartelt LA, Korpe PS, Lopes B, Houpt ER. Calcified neurocysticercus, perilesional edema, and histologic inflammation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014;90(2):318–21.
Singhi P, Malhi P, Suthar R, Deo B, Khandelwal NK. Long-term cognitive outcome of children with parenchymal neurocysticercosis: a prospective observation study. J Child Neurol. 2018;33(7):468–73.
Garcia HH, Gonzalez AE, Rodriguez S, Tsang VC, Pretell EJ, Gonzales I, et al. Neurocysticercosis: unraveling the nature of the single cysticercal granuloma. Neurology. 2010;75(7):654–8.
Serpa JA, Graviss EA, Kass JS, White AC Jr. Neurocysticercosis in Houston, Texas: an update. Medicine (Baltimore). 2011;90(1):81–6.
Webb CM, White AC Jr. Update on the diagnosis and management of neurocysticercosis. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2016;18(12):44.
Del Brutto OH, Arroyo G, Del Brutto VJ, Zambrano M, Garcia HH. On the relationship between calcified neurocysticercosis and epilepsy in an endemic village: a large-scale, computed tomography-based population study in rural Ecuador. Epilepsia. 2017;58(11):1955–61.
Moyano LM, O’Neal SE, Ayvar V, Gonzalvez G, Gamboa R, Vilchez P, et al. High prevalence of asymptomatic neurocysticercosis in an endemic rural community in Peru. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10(12):e0005130.
Del Brutto OH, Issa NP, Salgado P, Del Brutto VJ, Zambrano M, Lama J, et al. The association between neurocysticercosis and hippocampal atrophy is related to age. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;96(1):243–8.
Qavi A, Garg RK, Malhotra HS, Jain A, Kumar N, Malhotra KP, et al. Disseminated cysticercosis: clinical spectrum, toll-like receptor-4 gene polymorphisms and role of albendazole: a prospective follow-up of 60 cases with a review of 56 published cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(39):e4882.
Rangel-Castilla L, Serpa JA, Gopinath SP, Graviss EA, Diaz-Marchan P, White AC Jr. Contemporary neurosurgical approaches to neurocysticercosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;80(3):373–8.
Torres-Corzo J, Rodriguez-della Vecchia R, Rangel-Castilla L. Bruns syndrome caused by intraventricular neurocysticercosis treated using flexible endoscopy. J Neurosurg. 2006;104(5):746–8.
Marcin Sierra M, Arroyo M, Cadena Torres M, Ramirez Cruz N, Garcia Hernandez F, Taboada D, et al. Extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis: demographic, clinicoradiological, and inflammatory features. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(6):e0005646.
Callacondo D, Garcia HH, Gonzales I, Escalante D, Nash TE. High frequency of spinal involvement in patients with basal subarachnoid neurocysticercosis. Neurology. 2012;78(18):1394–400.
Alsina GA, Johnson JP, McBride DQ, Rhoten PR, Mehringer CM, Stokes JK. Spinal neurocysticercosis. Neurosurg Focus. 2002;12(6):e8.
Pushker N, Bajaj MS, Chandra M, Neena. Ocular and orbital cysticercosis. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2001;79(4):408–13.
Rath S, Honavar SG, Naik M, Anand R, Agarwal B, Krishnaiah S, et al. Orbital cysticercosis: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and outcome. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(3):600–5, 5.e1.
White AC, Coyle CM, Rajshekhar V, Singh G, Hauser WA, Mohanty A, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of neurocysticercosis: 2017 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98(4):945–66.
Bustos JA, Garcia HH, Del Brutto OH. Reliability of diagnostic criteria for neurocysticercosis for patients with ventricular cystic lesions or granulomas: a systematic review. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;97(3):653–7.
Del Brutto OH, Nash TE, White AC Jr, Rajshekhar V, Wilkins PP, Singh G, et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for neurocysticercosis. J Neurol Sci. 2017;372:202–10.
Sharma T, Sinha S, Shah N, Gopal L, Shanmugam MP, Bhende P, et al. Intraocular cysticercosis: clinical characteristics and visual outcome after vitreoretinal surgery. Ophthalmology. 2003;110(5):996–1004.
Lerner A, Shiroishi MS, Zee CS, Law M, Go JL. Imaging of neurocysticercosis. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2012;22(4):659–76.
do Amaral LL, Ferreira RM, da Rocha AJ, Ferreira NP. Neurocysticercosis: evaluation with advanced magnetic resonance techniques and atypical forms. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;16(2):127–44.
Carrillo Mezo R, Lara Garcia J, Arroyo M, Fleury A. Relevance of 3D magnetic resonance imaging sequences in diagnosing basal subarachnoid neurocysticercosis. Acta Trop. 2015;152:60–5.
Tsang VC, Brand JA, Boyer AE. An enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot assay and glycoprotein antigens for diagnosing human cysticercosis (Taenia solium). J Infect Dis. 1989;159(1):50–9.
Wilson M, Bryan RT, Fried JA, Ware DA, Schantz PM, Pilcher JB, et al. Clinical evaluation of the cysticercosis enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot in patients with neurocysticercosis. J Infect Dis. 1991;164(5):1007–9.
Garcia HH, Gilman RH, Catacora M, Verastegui M, Gonzalez AE, Tsang VC. Serologic evolution of neurocysticercosis patients after antiparasitic therapy. Cysticercosis Working Group in Peru. J Infect Dis. 1997;175(2):486–9.
Gonzalez AE, Bustos JA, Garcia HH, Rodriguez S, Zimic M, Castillo Y, et al. Successful antiparasitic treatment for cysticercosis is associated with a fast and marked reduction of circulating antigen levels in a naturally infected pig model. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;93(6):1305–10.
White AC Jr, Garcia HH. Updates on the management of neurocysticercosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018;31(5):377–82.
Bustos JA, Garcia HH, Del Brutto OH. Antiepileptic drug therapy and recommendations for withdrawal in patients with seizures and epilepsy due to neurocysticercosis. Expert Rev Neurother. 2016;16(9):1079–85.
Garcia HH, Evans CA, Nash TE, Takayanagui OM, White AC Jr, Botero D, et al. Current consensus guidelines for treatment of neurocysticercosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002;15(4):747–56.
Zhao BC, Jiang HY, Ma WY, Jin DD, Li HM, Lu H, et al. Albendazole and corticosteroids for the treatment of solitary cysticercus granuloma: a network meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10(2):e0004418.
Garcia HH, Pretell EJ, Gilman RH, Martinez SM, Moulton LH, Del Brutto OH, et al. A trial of antiparasitic treatment to reduce the rate of seizures due to cerebral cysticercosis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(3):249–58.
Romo ML, Wyka K, Carpio A, Leslie D, Andrews H, Bagiella E, et al. The effect of albendazole treatment on seizure outcomes in patients with symptomatic neurocysticercosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2015;109(11):738–46.
Garcia HH, Lescano AG, Gonzales I, Bustos JA, Pretell EJ, Horton J, et al. Cysticidal efficacy of combined treatment with praziquantel and albendazole for parenchymal brain cysticercosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(11):1375–9.
Garcia HH, Gonzales I, Lescano AG, Bustos JA, Zimic M, Escalante D, et al. Efficacy of combined antiparasitic therapy with praziquantel and albendazole for neurocysticercosis: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(8):687–95.
Mejia R, Nash TE. Corticosteroid withdrawal precipitates perilesional edema around calcified Taenia solium cysts. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013;89(5):919–23.
Garcia HH, Gonzales I, Lescano AG, Bustos JA, Pretell EJ, Saavedra H, et al. Enhanced steroid dosing reduces seizures during antiparasitic treatment for cysticercosis and early after. Epilepsia. 2014;55(9):1452–9.
Proano JV, Torres-Corzo J, Rodriguez-Della Vecchia R, Guizar-Sahagun G, Rangel-Castilla L. Intraventricular and subarachnoid basal cisterns neurocysticercosis: a comparative study between traditional treatment versus neuroendoscopic surgery. Childs Nerv Syst. 2009;25(11):1467–75.
Chen G, Xiao Q, Zheng J, Wu J, Ao Q, Liu Y. Endoscopic transaqueductal removal of fourth ventricular neurocysticercosis: report of three cases. Turk Neurosurg. 2015;25(3):488–92.
Kaif M, Husain M, Ojha BK. Endoscopic management of intraventricular neurocysticercosis. Turk Neurosurg. 2019;29(1):59–65.
Nash TE, Ware JM, Mahanty S. Intraventricular neurocysticercosis: experience and long-term outcome from a tertiary referral center in the United States. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98(6):1755–62.
White AC. Controlling the host response in neurocysticercosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019;100(3):483–4.
Nash TE, Ware JM, Coyle CM, Mahanty S. Etanercept to control inflammation in the treatment of complicated neurocysticercosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019;100(3):609–16.
Okello AL, Thomas L, Inthavong P, Ash A, Khamlome B, Keokamphet C, et al. Assessing the impact of a joint human-porcine intervention package for Taenia solium control: results of a pilot study from northern Lao PDR. Acta Trop. 2016;159:185–91.
Garcia HH, Gonzalez AE, Tsang VC, O’Neal SE, Llanos-Zavalaga F, Gonzalvez G, et al. Elimination of Taenia solium transmission in Northern Peru. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(24):2335–44.
Kern P, Menezes da Silva A, Akhan O, Müllhaupt B, Vizcaychipi KA, Budke C, et al. The Echinococcoses: diagnosis, clinical management and burden of disease. Adv Parasitol. 2017;96:259–369.
Wen H, Vuitton L, Tuxun T, Li J, Vuitton DA, Zhang W, et al. Echinococcosis: advances in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;32(2):e00075–18.
Brunetti E, Kern P, Vuitton DA, WHO-IWGE WPft. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop. 2010;114(1):1–16.
Luo K, Luo DH, Zhang TR, Wen H. Primary intracranial and spinal hydatidosis: a retrospective study of 21 cases. Pathog Glob Health. 2013;107(2):47–51.
Altinörs N, Bavbek M, Caner HH, Erdogan B. Central nervous system hydatidosis in Turkey: a cooperative study and literature survey analysis of 458 cases. J Neurosurg. 2000;93(1):1–8.
Stojkovic M, Junghanss T. Cystic and alveolar echinococcosis. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;114:327–34.
Luo X, Jedlicka SS, Jellison KL. Role of wall shear stress in Cryptosporidium parvum Oocyst attachment to environmental biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017;83(24):e01533–17.
Mohindra S, Savardekar A, Gupta R, Tripathi M, Rane S. Varied types of intracranial hydatid cysts: radiological features and management techniques. Acta Neurochir. 2012;154(1):165–72.
Pagnozzi D, Addis MF, Biosa G, Roggio AM, Tedde V, Mariconti M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of antigen 5-based ELISAs for human cystic echinococcosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0004585.
Vidhate MR, Singh D, Sharma P, Singh MK. Cerebral hydatid cyst showing pathognomonic daughter cysts. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2011;14:217–8.
Kim JG, Ahn CS, Sohn WM, Nawa Y, Kong Y. Human sparganosis in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(44):e273.
Liu Q, Li MW, Wang ZD, Zhao GH, Zhu XQ. Human sparganosis, a neglected food borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(10):1226–35.
Hong D, Xie H, Wan H, An N, Xu C, Zhang J. Efficacy comparison between long-term high-dose praziquantel and surgical therapy for cerebral sparganosis: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018;12(10):e0006918.
Liao H, Li D, Zhou B, Liu J, Li Y, Liu H, et al. Imaging characteristics of cerebral sparganosis with live worms. J Neuroradiol. 2016;43(6):378–83.
Yu Y, Shen J, Yuan Z, Xia Z, Gao F, Jiang L, et al. Cerebral sparganosis in children: epidemiologic and radiologic characteristics and treatment outcomes: a report of 9 cases. World Neurosurg. 2016;89:153–8.
Zhang P, Zou Y, Yu FX, Wang Z, Lv H, Liu XH, et al. Follow-up study of high-dose praziquantel therapy for cerebral sparganosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13(1):e0007018.
Barratt J, Chan D, Sandaradura I, Malik R, Spielman D, Lee R, et al. Angiostrongylus cantonensis: a review of its distribution, molecular biology and clinical significance as a human pathogen. Parasitology. 2016;143(9):1087–118.
Wang QP, Lai DH, Zhu XQ, Chen XG, Lun ZR. Human angiostrongyliasis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8(10):621–30.
Ansdell V, Wattanagoon Y. Angiostrongylus cantonensis in travelers: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018;31(5):399–408.
McAuliffe L, Fortin Ensign S, Larson D, Bavaro M, Yetto J, Cathey M, et al. Severe CNS angiostrongyliasis in a young marine: a case report and literature review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019; 19(4): e132–e142.
Liu EW, Schwartz BS, Hysmith ND, DeVincenzo JP, Larson DT, Maves RC, et al. Rat lungworm infection associated with central nervous system disease – eight U.S. states, January 2011–January 2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67(30):825–8.
Clinical Subcommittee of the Hawaii Governor's Joint Task Force on Rat Lungworm Disease. Aug 29, 2018.
Martins YC, Tanowitz HB, Kazacos KR. Central nervous system manifestations of Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Acta Trop. 2015;141(Pt A):46–53.
Jitpimolmard S, Sawanyawisuth K, Morakote N, Vejjajiva A, Puntumetakul M, Sanchaisuriya K, et al. Albendazole therapy for eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Parasitol Res. 2007;100(6):1293–6.
Foster CE, Nicholson EG, Chun AC, Gharfeh M, Anvari S, Seeborg FO, et al. Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection: a cause of fever of unknown origin in pediatric patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63(11):1475–8.
Katchanov J, Sawanyawisuth K, Chotmongkol V, Nawa Y. Neurognathostomiasis, a neglected parasitosis of the central nervous system. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1174–80.
Dzikowiec M, Goralska K, Blaszkowska J. Neuroinvasions caused by parasites. Ann Parasitol. 2017;63(4):243–53.
Herman JS, Chiodini PL. Gnathostomiasis, another emerging imported disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009;22:484–92.
Sawanyawisuth K, Chlebicki MP, Pratt E, Kanpittaya J, Intapan PM. Sequential imaging studies of cerebral gnathostomiasis with subdural hemorrhage as its complication. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2009;103(1):102–4.
Kanpittaya J, Sawanyawisuth K, Intapan PM, Khotsri P, Chotmongkol V, Maleewong W. A comparative study of neuroimaging features between human neuro-gnathostomiasis and angiostrongyliasis. Neurol Sci. 2012;33(4):893–8.
Rostami A, Gamble HR, Dupouy-Camet J, Khazan H, Bruschi F. Meat sources of infection for outbreaks of human trichinellosis. Food Microbiol. 2017;64:65–71.
Gottstein B, Pozio E, Nöckler K. Epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and control of trichinellosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009;22(1):127–45.
Neghina R, Neghina AM, Marincu I, Iacobiciu I. Reviews on trichinellosis (II): neurological involvement. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2011;8(5):579–85.
Taher EE, Meabed EMH, El Akkad DMH, Kamel NO, Sabry MA. Modified dot-ELISA for diagnosis of human trichinellosis. Exp Parasitol. 2017;177:40–6.
Faber M, Schink S, Mayer-Scholl A, Ziesch C, Schönfelder R, Wichmann-Schauer H, et al. Outbreak of trichinellosis due to wild boar meat and evaluation of the effectiveness of post exposure prophylaxis, Germany, 2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60(12):e98–e104.
Krolewiecki A, Nutman TB. Strongyloidiasis: a neglected tropical disease. Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2019;33(1):135–51.
Schär F, Trostdorf U, Giardina F, Khieu V, Muth S, Marti H, et al. Strongyloides stercoralis: global distribution and risk factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7(7):e2288.
Woll F, Gotuzzo E, Montes M. Strongyloides stercoralis infection complicating the central nervous system. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;114:229–34.
Montes M, Sawhney C, Barros N. Strongyloides stercoralis: there but not seen. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2010;23(5):500–4.
Formenti F, La Marca G, Perandin F, Pajola B, Romano M, Santucci B, et al. A diagnostic study comparing conventional and real-time PCR for Strongyloides stercoralis on urine and on faecal samples. Acta Trop. 2019;190:284–7.
Buonfrate D, Requena-Mendez A, Angheben A, Cinquini M, Cruciani M, Fittipaldo A, et al. Accuracy of molecular biology techniques for the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection-a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018;12(2):e0006229.
Henriquez-Camacho C, Gotuzzo E, Echevarria J, White AC Jr, Terashima A, Samalvides F, et al. Ivermectin versus albendazole or thiabendazole for Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;18(1):Cd007745.
Ma G, Holland CV, Wang T, Hofmann A, Fan CK, Maizels RM, et al. Human toxocariasis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):e14–24.
Moreira GM, Telmo Pde L, Mendonca M, Moreira AN, McBride AJ, Scaini CJ, et al. Human toxocariasis: current advances in diagnostics, treatment, and interventions. Trends Parasitol. 2014;30(9):456–64.
Deshayes S, Bonhomme J, de La Blanchardiere A. Neurotoxocariasis: a systematic literature review. Infection. 2016;44(5):565–74.
Sánchez SS, García HH, Nicoletti A. Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging findings of neurotoxocariasis. Front Neurol. 2018;9:53.
LMD S, Magalhaes CG, Telmo PL, Cerqueira MP, Donassolo RA, FPL L, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of recombinant proteins in Toxocara spp. for serodiagnosis in humans: differences in adult and child populations. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(12):e0208991.
Kazacos KR, Jelicks LA, Tanowitz HB. Baylisascaris larva migrans. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;114:251–62.
Graeff-Teixeira C, Morassutti AL, Kazacos KR. Update on baylisascariasis, a highly pathogenic zoonotic infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016;29(2):375–99.
Rascoe LN, Santamaria C, Handali S, Dangoudoubiyam S, Kazacos KR, Wilkins PP, et al. Interlaboratory optimization and evaluation of a serological assay for diagnosis of human baylisascariasis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013;20(11):1758–63.
Sircar AD, Abanyie F, Blumberg D, Chin-Hong P, Coulter KS, Cunningham D, et al. Raccoon roundworm infection associated with central nervous system disease and ocular disease – six states, 2013–2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(35):930–3.
Peters JM, Madhavan VL, Kazacos KR, Husson RN, Dangoudoubiyam S, Soul JS. Good outcome with early empiric treatment of neural larva migrans due to baylisascaris procyonis. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e806–11.
Weerakoon KG, Gobert GN, Cai P, McManus DP. Advances in the diagnosis of human schistosomiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28(4):939–67.
Ross AG, McManus DP, Farrar J, Hunstman RJ, Gray DJ, Li YS. Neuroschistosomiasis. J Neurol. 2012;259(1):22–32.
Ferrari TC, Moreira PR. Neuroschistosomiasis: clinical symptoms and pathogenesis. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(9):853–64.
Coyle CM. Schistosomiasis of the nervous system. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;114:271–81.
Liu H, Lim CC, Feng X, Yao Z, Chen Y, Sun H, et al. MRI in cerebral schistosomiasis: characteristic nodular enhancement in 33 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191(2):582–8.
Furst T, Keiser J, Utzinger J. Global burden of human food-borne trematodiasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12(3):210–21.
Zhang XL, Wang Y, Wang GX, Chen WB, He X, Niu H, et al. Distribution and clinical features of paragonimiasis skrjabini in three gorges reservoir region. Parasitol Int. 2012;61(4):645–9.
Chen J, Chen Z, Lin J, Zhu G, Meng H, Cui G, et al. Cerebral paragonimiasis: a retrospective analysis of 89 cases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013;115(5):546–51.
Calvopina M, Romero-Alvarez D, Macias R, Sugiyama H. Severe pleuropulmonary paragonimiasis caused by paragonimus mexicanus treated as tuberculosis in Ecuador. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017;96(1):97–9.
Lane MA, Marcos LA, Onen NF, Demertzis LM, Hayes EV, Davila SZ, et al. Paragonimus kellicotti Flukes in Missouri, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18(8):1263–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Tanabe, M.B., Schilling, M., White, A.C. (2021). Neurocysticercosis and Other CNS Helminthic Infections. In: Hasbun, MD MPH, R., Bloch, MD MPH, K.C., Bhimraj, MD, A. (eds) Neurological Complications of Infectious Diseases. Current Clinical Neurology. Humana, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56084-3_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56084-3_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-56083-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-56084-3
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)