Abstract
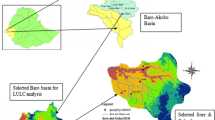
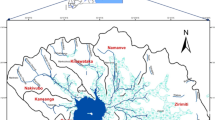
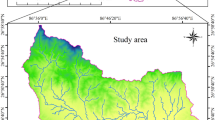
Soil erosion processes remain the principal environmental issue in the arid regions, such as the southern part of Tunisia. Erosion is a real threat not only for soil conservation but also for the sustainability of water harvesting techniques (cisterns, check dams). The quantification of soil loss in Koutine watershed depends on many factors such as human activities, climate variability, topography (slope), and soil resources. The objective of this study is to examine the influence of topography (slope), short-term exceptional rainstorm intensity, and soil texture on erosion at field scale (less than 1 ha). The data used are from field measurements and a survey of sedimentation in 25 cisterns (6 Fesguia and 19 Majel) and erosion simulation in 37 individual sites. Data were collected over a four (04) year period from 2015 to 2018. By combining the two sources of data, we aim to improve the understanding of the erosion processes and to delineate important links between field rainfall (less than 200 mm), topography and soil characteristics, and sediments deposited in the small sediment settlement basins. The results are based on local and spatially distributed observations. The standard deviation values of soil loss/sediment yield (SY) was about 6%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Floret, C., Pontanier, R.: L’aridité en Tunisie présaharienne: Climat, sol, végétation et aménagement, p. 544. ORSTOM, Paris (1982)
Kassab, F.: Les fortes pluies en Tunisie. Publication de l’Université de Tunis I, série Géographie, 234 pp. (1979)
Gaddas, F., Stambouli, T., Derouiche, M.C.: Évaluation du risque d’érosion hydrique. INAT, DGACTA, Revue de l’INAT, Tunisie (2010)
Mtimet, A.: Soils of Tunisia. In: Zdruli, P., Steduto, P., Lacirignola, C., Montanarella, L. (eds.) Soil resources of Southern and Eastern Mediterranean countries, pp. 243–262. Bari, CIHEAM, (2001). (Options Méditerranéennes: Série B. Etudes et Recherches; n. 34)
Jebari, S., Berndtsson, R., Bahri, A., Boufaroua, M.: Exceptional rainfall characteristics related to erosion risk in semiarid Tunisia. Open Hydrology Journal 1, 25–33 (2008)
Nasri, S.: Caractéristiques et impacts hydrologiques de banquettes en cascade sur un versant semi-aride en Tunisie centrale. Hydrol. Sci. J. Sci. Hydrol. 52(6) (2007). Special Section: Dryland Hydrology in Mediterranean Regions
Fersi, M.: Etude hydrologique d’oued Oum Zessar à Koutine. Ministère de l’Agriculture, Tunis (1985)
Wischmeier, W.H., Smith, D.D.: Predicting rainfall erosion losses: guide to conservation planning. USDA, Agriculture Handbook 537. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC (1978)
Bourges, J., Floret, C., Pontanier, R.: Etude d’une topo séquence type du Sud tunisien: Djebel Dissa. Etude spéciale 93, Ministère de l’Agriculture, Division des Sols, République Tunisienne (1974)
Schiettecattea W., Ouessar, M., Gabriels, D., Tanghe, S., Heirman, S., Abdelli, F.: Impact of water harvesting techniques on soil and a water conservation: a case study on a micro catchment in southeastern Tunisia. Journal of Arid Environments 61, 297–313 (2005)
Ennabli, N.: Les aménagements hydrauliques et hydro-agricoles en Tunisie. Imprimerie Officielle de la République Tunisienne, Tunis, 255 pp. (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ben Zaied, M., Ouessar, M., Guied, M., Kerdi, H. (2021). Land Degradation Assessment in the Dry Areas of Tunisia Case Study: Wadi Koutine Watershed. In: Ksibi, M., et al. Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition). EMCEI 2019. Environmental Science and Engineering(). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_198
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_198
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-51209-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-51210-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)