Abstract
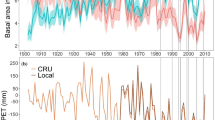
Climate changes reflect an increase in temperature and a decrease in annual rainfall, with high variability between regions, which will generate hotter, drier environments. Under these conditions, it is projected that forest ecosystems will be severely affected, and recent studies have accumulated evidence for drought-induced tree mortality, especially in North Africa (Tunisia). Consequently, many studies have attempted to explain mechanisms of survival and mortality in forest species. However, the physiological mechanisms that underlie drought-induced mortality are not completely understood. The aim of the present study is to analyze the effect of an extremely dry year on the cause of mortality and decline of cork oak forest in the northwest of Tunisia, during the period 1988–1995. Extreme-drought years with significant effects on tree growth were registered. Cork oak mortality was recorded for up to 63,622 trees.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jazzar, L., Rzigui, T., Ben Fradj, R., Touhami, I., Nasr, Z.: Leaf gas exchange variation under summer drought in Tunisian cork oak from geographically central and marginal populations. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr. 4, 17 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-019-0105-1
Bonan, G.B.: Forests and climate change: forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 320, 1444–1449 (2008)
Touhami, I., Chirino, E., Aouinti, H., El Khorchani, A., Elaieb, M.T., Khaldi, A., Nasr, Z.: Decline and dieback of cork oak (Quercus suber L.) forests in the Mediterranean basin: a case study of Kroumirie, Northwest Tunisia. J. Forest Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-00974-1
Allen, C.D., et al.: A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. Forest Ecol. Manage. 259, 660–684 (2010)
McKee, T.B.N., Doesken, J., Kleist, J.: The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In: Eight Conferences on Applied Climatology. American Meteorological Society, Anaheim, CA, pp. 179–184 (1993)
Ben Jamâa, M.L., Hasnaoui, B.: Le dépérissement du chêne-liège (Quercus suber L.) en Tunisie. Ann. Rech. For., Maroc, No special: 1–10 (1996)
McDowell, N., et al.: Mechanisms of plant survival and mortality during drought: Why do some plants survive while others succumb to drought? New Phytol. 178, 719–739 (2008)
Breshears, D.D., et al.: Tree die-off in response to global-change-type drought: mortality insights from a decade of plant water potential measurements. Front. Ecol. Environ. 7, 185–189 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Institute for Rural Engineering, Waters, and Forestry, Tunisia. This research is part of the project: HYDROMED (PID-2019-111332RB-C21): Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Touhami, I. et al. (2021). Drought Disturbance from Climate Change: Response of Cork Oak (Quercus Suber L.) Forests in North Africa (Tunisia). In: Ksibi, M., et al. Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition). EMCEI 2019. Environmental Science and Engineering(). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_155
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_155
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-51209-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-51210-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)