Abstract
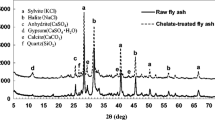
The present research focused on the role of fishbone hydroxyapatite (FB-HAP) in stabilizing heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) Fly ash (FA) particularly Pb and Zn. Bones from a variety of fish species as well as a commercial apatite (Apatite IITM) were used. The effect of both substances was studied under different liquid/solid (L/S) and settling periods. Batch tests were conducted under the fishbone/FA ratios of 0.0 and 1:10 by weight and various contact times of 6, 12, 24, and 672 h (28 days) with two different L/S ratios of 1.0 and 1.5 ml/g. The highest Pb and Zn removal efficiency reached 86.39 and 62.67%, respectively, after 672 h when fishbone dosage was 10% at L/S 1.5. Apatite IITM was also effective for Pb stabilization; however, FB-HAP was more efficient (about 1.5–2 times). The results indicated that both contact time and L/S ratio were the most important factors for enhanced metal stabilization.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Y.M., Chen, T.C., Yeh, K.J., Shue, M.F.: Stabilization of an elevated heavy metal contaminated site. J. Hazard. Mater. 88(1), 63–74 (2001)
Nzihou, A., Sharrock, P.: Calcium phosphate stabilization of fly ash with chloride extraction. Waste Manag. 22(2), 235–239 (2002)
Mu, Y., Saffarzadeh, A., Shimaoka, T.: Utilization of waste natural fishbone for heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 172, 3111–3118 (2018)
Raicevic, S., Kaludjerovic-Radoicic, T., Zouboulis, A.I.: In situ stabilization of toxic metals in polluted soils using phosphates: theoretical prediction and experimental verification. J. Hazard. Mater. 117(1), 41–53 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Saffarzadeh, A., Nag, M., Nomichi, T., Shimaoka, T., Nakayama, H., Komiya, T. (2021). A Novel Approach for Stabilizing Heavy Metals in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Fly Ash Using Waste Fishbone Hydroxyapatite (FB-HAP). In: Ksibi, M., et al. Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition). EMCEI 2019. Environmental Science and Engineering(). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_124
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_124
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-51209-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-51210-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)