Abstract
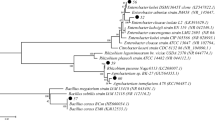
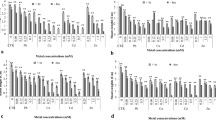
Heavy metal pollution of the soil is a relevant environmental problem. Plant growth promoting and tolerance heavy metal bacteria are a promising technique for phytoremediation. The aim of this study was to isolate heavy metal-tolerant rhizobia from Calobota saharae. Tolerance to a range of heavy metal ions was determined by minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) for Rhizobia which was isolated from Calobota saharae. The Rhizobium leguminosarum GM01 strain exhibited strong tolerance to a range of heavy metals including lead (Pb), Cobalt (Co), and zinc (Zn). R. leguminosarum GM01 have great potentials for plant growth promotion and phytoremediation of contaminated soils.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fagorzi, C., Checcucci, A., diCenzo, G.C., Debiec-Andrzejewska, K., Dziewit, L., Pini, F., Mengoni, A.: Harnessing rhizobia to improve heavy-metal phytoremediation by legumes. Genes 9, 542 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9110542
Dutta, P., Karmakar, A., Majumdar, S., Roy, S.: Klebsiella pneumoniae (HR1) assisted alleviation of Cd(II) toxicity in Vigna mungo: a case study of biosorption of heavy metal by an endophytic bacterium coupled with plant growth promotion. Euro-Mediterranean J. Environ. Integr. 3, 27 (2018)
Das, D., Chakraborty, S., Bhattacharjee, C., Chowdhury, R.: Biosorption of lead ions (Pb2+) from simulated wastewater using residual biomass of microalgae. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 4576–4586 (2016)
Nath, A., Chakraborty, S., Bhattacharjee, C.: Bio-reactorand enzymatic reactions in bioremediation. In: Das, S. (ed.) Microbial Biodegradation and Bioremediation, pp. 455–495. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2014)
Coba de la Peña, T., Fedorova, E., Pueyo, J.J., Lucas, M.M.: The symbiosome: legume and rhizobia co-evolution toward a nitrogen-fixing organelle? Front. Plant Sci. 8, 2229 (2018)
Somasegaran, P., Hoben, H.J.: The Handbook for Rhizobia. Methods in Legume-Rhizobium Technology. Springer, New York (1994)
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., Maniatis, T.: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor (1989)
Ma, Y., Rajkumar, M., Zhang, C., Freitas, H.: Inoculation of Brassica oxyrrhina with plant growth promoting bacteria for the improvement of heavy metal phytoremediation under drought conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 320, 36–44 (2016)
Yu, X., Li, Y., Zhang, C., Liu, H., Liu, J., Zheng, W., Kang, X., Leng, X., Zhao, K., Gu, Y., Zhang, X., Xiang, Q., Chen, Q.: Culturable heavy metal-resistant and plant growth promoting bacteria in V-Ti magnetite mine tailing soil from Panzhihua, China. PLoS ONE 9(9), e106618 (2014)
Khamna, S., Yokota, A., Lumyong, S.: Actinobacteria isolated from medicinal plant rhizosphere soils: diversity and screening of antifungal compounds, indole-3-acetic acid and siderophore production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25(4), 649–655 (2009)
Franco-Correa, M., Quintana, A., Duque, C., Suarez, C., Rodríguez, M.X., Barea, J.-M.: Evaluation of actinomycete strains for key traits related with plant growth promotion and mycorrhiza helping activities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 45, 209–217 (2010)
Schwyn, B., Neilands, J.B.: Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Ann. Biochem. 160, 47–56 (1987)
Guo, J., Chi, J.: Effect of Cd-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobium on plant growth and Cd uptake by Lolium multiflorum Lam. and Glycine max (L.) Merr. in Cd-contaminated soil. Plant Soil 375, 205–214 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ghadbane, M., Benderradji, L., Medjekal, S., Belhadj, H., Daoud, H. (2021). Plant Growth Promoting and Heavy Metal-Tolerant Rhizobia from Algeria. In: Ksibi, M., et al. Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition). EMCEI 2019. Environmental Science and Engineering(). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_110
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_110
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-51209-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-51210-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)