Abstract
Indian cement industry is rated as one of the best performing industry across various industrial sectors in terms of energy efficiency, quality control, environmental sustainability and adaptive in venturing into new technology. Indian cement industry is contributing to circular economy primarily by (i) Circular Supply Chain, (ii) Recovery and Recycling. Waste from various industries is being utilized by the cement industry as alternative fuels and raw materials (AFR). As cement manufacturing process itself supports the environmentally sustainable waste utilization due to high temperature incineration without leaving any residue, hence it is acting as backbone for waste generating industries. National Council for Cement and Building Materials (NCB) being a leading R&D organization in the field of Cement and Building Materials in India is working to support the cement industry to enhance the waste utilization and sustainable manufacturing for clean and green India. This paper highlights the efforts of Indian cement industry, contribution of NCB towards circular economy and futuristic potential.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
18.1 Introduction
India is among world’s fastest growing economy showing resilient to external factors. The economies of scale have predominantly taken over the narrative around resource use leaving principles of circularity and resource efficiency in the background. The long-term growth perspective is high but with the rise in resource demand. The country’s natural resources are under strain and there is critical need for resource efficiency improvement. Circular economy is emerging approach, which can take the country to newer heights without straining the resource supply. Circular economy looked towards the elimination of any kind of waste in the market. It defines waste to any kind of underutilization of resources or assets rather than its interpretation as junk material (https://niti.gov.in/writereaddata/files/E-WasteStrategy.pdf). The challenge to put circular consumption into practice can be addressed by 3R Principle that is based on Reduce, Recycle and Reuse (Ghosh 2017). There are five streams of circular economy models i.e. (i) Circular Supply Chain; Provide renewable energy, bio-based or fully recyclable input material to replace single-lifecycle inputs, (ii) Recovery and Recycling; Recover useful resources/energy out of disposed products or by-products, (iii) Product Life Extension; Extend working lifecycle of products and components by repairing, upgrading and reselling, (iv) Sharing Platform; Enable increased utilization rate of products by making possible shared use/access/ownership, (v) Product as a Service; Offer product access and retain ownership to internalize benefits of circular resource productivity (https://Circular%20economy/FICCI-Circular-Economy.pdf). Cement industry has been considered as one of the pillar of growth for any nation. Indian cement industry being one of the second largest cement production after China with an installed capacity of 509 MTPA (million tonnes per Annum) in 2018 is constantly contributing for the circular economy of India by various means and this paper highlights Indian cement industry gains through circular economy as well as future potential (https://pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare).
18.2 Achievements of Indian Cement Industry in Last Decade
Indian cement industry is rated as one of the best performing industries across various industrial sectors in terms of energy consumption, quality control, environmental sustainability and adaptive in venturing into new technological options. Some of the recent major strides of Indian cement industry are reduction of CO2 emission factor from 1.12 t of CO2/t of cement in 1996 to 0.670 t of CO2/t of cement in 2017, enhanced blended cement production from 68% in 2010 to 73% of total cement production in 2017. Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) is part replacement of conventional fuel by alternative fuels in terms of thermal energy requirement and is calculated as percentage of heat supplied by alternative fuel from the total heat requirement for pyro-processing in a cement plant. % TSR has improved to 4% now as compared to a dismal 1% only 3–4 years back. Cement plants have adopted technologies to meet the new emission norms for Particulate Matter (PM) and NOX emissions. Plants have installed high efficient bag filters, Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs), hybrid filters to control dust emissions. For NOX reduction, plants have installed secondary control measures like Selective Non Catalytic Reduction (SNCR). All the cement plants have installed continuous emission monitoring system as per the guidelines of Central pollution Control Board. Indian cement sector is most energy efficient worldwide, mainly due to modern technology being implemented in the plants as well as because of efficient monitoring of plant’s performance on a daily basis, focusing on energy savings and CO2 emissions reduction. Indian cement industry growth in next decade looks very promising. Cement demand is projected to grow to 2.5 to 2.7 times the current volumes and reach 550 to 600 MTPA by 2025 (https://www.wbcsd.org/Sector-Projects/Cement-Sustainability-Initiative/Resources/Low-Carbon-Technology-Roadmap-for-the-Indian-Cement-Sector-Status-Review). Per capita consumption is likely to increase from 210 to 580 kg world average. The government of India has launched various new urban development missions including development of 500 cities, setting up of 100 Smart Cities in the country by 2022, Affordable housing under “Housing for All till 2022” and dedicated freight corridors etc. (https://www.ibef.org/industry/cement-presentation).
18.3 Contribution of Indian Cement Industry in Circular Economy
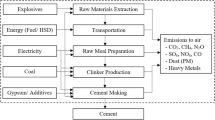
Cement industry contribution to circular economy is primarily under two heads i.e. (i) Circular Supply Chain, (ii) Recovery and Recycling. Figure 18.1 indicates that how the cement industry is contributing in circular economy and sustainable manufacturing.
18.3.1 Circular Supply Chain
In this head of circular economy, Indian cement industry is playing a key role by enhancing the application of Renewable Energy for electrical power generation. The renewable energy installed capacity (wind and solar) in cement plants increased by more than 40% to 276 MW from 2010 to 2017. Out of the total, 42 MW is solar power, while off-site wind installations account for 234 MW. A company has undertaken the target of switching over to renewable energy for 100% of all electrical energy needs by 2030 (https://www.wbcsd.org/Sector-Projects/Cement-Sustainability-Initiative/Resources/Low-Carbon-Technology-Roadmap-for-the-Indian-Cement-Sector-Status-Review). Big players like UltraTech Cement are targeting 25% share of their total power consumption by green energy technologies by 2021 (https://www.thehindubusinessline).
Apart from solar photovoltaic route, cement industry is making efforts to tap solar energy through thermal route. A study has been undertaken in Europe for solar reactor design operating at 800–1000 °C, using rotary kiln and a horizontal bubbling fluidized bed, to manufacture cement (Moumina et al. 2019; https://www.solarpaces.org/new-iea-report/). Another study presents the design of a mini, scalable solar lime kiln which was designed using solar dish collector to calcine small sized (1–5 mm diameter) limestone particles. The heat is focused on a heating element located centrally in a tilted rotary kiln driven by chain drive (Swaminathan and Nadhipite 2017). Some studies have been done for feasibility study for Concentrated Solar Thermal technology in cement industry (Gonzalez and Flamant 2014).
18.3.2 Recovery and Recycling
It has been established that different types of wastes/by products of other industries available worldwide can be utilized as alternative fuels and raw materials for cement production. Moreover, production of blended cements, composite cements and utilizing performance improvers in cement also support circular economy. Use of fly ash and granulated blast furnace slag (GBFS) in the production of blended cements i.e. Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) and Portland Slag Cement (PSC) is also beneficial for conservation of natural resources, lowering in clinker factor in cement and reduction in CO2 emissions along with environmental sustainability. Contribution of Indian Cement Industry in Circular Economy along with their associated challenges are highlighted in following Table 18.1.
18.4 NCB’s Experiences
NCB being a premier R&D organization for cement and construction sector in Inida has executed a number of R&D and consultancy projects related to waste utilization and energy conservation. Outcomes of these project is helping to Indian cement industry for contributing towards the circular economy and sustainable manufacturing. Some of them are highlighted below.
18.4.1 Production of Synthetic Slag from Low Grade Limestone
A Study were carried out at NCB laboratory for development of Synthetic Slag using low-grade limestone. Laboratory slag samples prepared with low-grade limestones and other additive materials, which found to be conforming the IS: 12089-1987. These laboratories made synthetic slag samples as shown in Fig. 18.2 were also investigated by optical microscopy as shown in Fig. 18.3 and found to have maximum 92% glass content, which is greater than 85% as specified in IS-12089. PSC samples were prepared with 40 and 60% synthetic slag replacing equal quantity of clinker. The performance of PSC blends prepared using synthetic slag sample were found as per requirements of Indian Standard Specification, IS: 455-1989 for PSC. As the limestone, which is getting depleted and has reached to an alarming level where the availability of cement grade limestone in India has reduced to 8949 million tones only, Synthetic Slag may play a vital role to replace clinker or indirectly cement grade limestone. However, main challenge would be to produce this slag at industrial scale.
18.4.2 Alternative Fuels Utilization
NCB has vast experience of analytical studies, trial runs and system design for Alternative Fuels (AFs) utilization. NCB has carried out various studies, which covers the impact assessment of AFs on overall process. Recently, number of studies have been carried out for cement plants. One study for utilization of Tyre Derived Fuel (TDF) as alternative fuel for co-processing. TDF ash sample was tested at NCB laboratory, and Zinc content was found to be around 4.06%, which is equivalent to 0.03% by weight in clinker. Several investigations have already revealed that zinc concentration above 500 ppm in clinker impact the workability of cement. Considering the impact of addition of Zinc in clinker, plant can achieve around 21% Thermal Substitution Rate (TSR) however, TSR beyond 21% may not be feasible due to higher zinc content in TDF. Another study was done for a cement plant (located in North Karnataka, India) to handle more than 25 types of alternative fuels, plant was commissioned a year back and now utilizing waste as a fuel with more than 10% TSR. NCB is also doing projects for system design to handle five different types of alternative fuels for a cement plant located in South & Central part of India.
18.4.3 Dolomitic Limestone Utilization
NCB in one of its recent projects has successfully utilized of up to 15% dolomite as an additive replacing equal quantity of clinker. The cement performance was found to be similar to that of control cement prepared without dolomite.
18.4.4 Performance Improvers in Cement Manufacturing
Based on studies on number of industrial wastes by NCB, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has permitted the use of copper slag, LD slag, lead-zinc slag and catalytic waste from petroleum refinery as performance improvers in manufacture of OPC.
18.4.5 Bottom Ash Utilization
In a recent R & D work, NCB has developed tiles and bricks by utilization of ~30% bottom ash along with fly ash. Cementitious binders with consistent strength property were prepared using rationalized formulations and curing conditions. The pre-cast bodies like tiles (150 × 75 × 25 mm) were meeting test limits of IS 2690 (Part 2):1992 and bricks having dimensions of 190 × 90 × 40 mm were meeting the requirement of strength and water absorption of Class 15 of IS 1077 (Part 2):1992. In another research activity at NCB, Bottom Ash is also successfully utilized as 50% replacement of fine aggregate in concrete.
18.4.6 Composite Cement Production
NCB has carried out several studies on composite cement wherein combinations of fly ash and granulated blast furnace slag were used for preparing composite cement blends. BIS has brought out standard specification IS: 16415-2015 for composite cement on recommendations of NCB.
18.4.7 Alternative Raw Materials Utilization
NCB has done an investigative study to utilize 15 inorganic industrial wastes including limes sludge, Wolstanite, leather sludge, Jarosite, LD slag, red mud and marble slurry in cement manufacture and as aggregate in concrete.
18.5 Comparison with Other Countries
One of the major aspects of circular economy for Indian cement industry is Alternative Fuels & Raw Materials (AFR). India’s Thermal Substitution rate is comparable with other countries such as 100% TSR in Australia and 100% TSR in France. Following Table 18.2 indicates that India has fourth position in the world to utilize Waste as Fuel on the basis of Quantity.
Above table indicates that waste utilization as fuel in India is still reasonable good considering high cement production capacity but still has huge potential to achieve high TSR. In terms of WHR, Cogeneration systems are well established in cement industry all over the world with Japan, China, India and Southeast Asian countries taking the lead in this development (http://www.ciiwasteexchange).
18.6 Futuristic Scenario
Development of Portland Composite Cement (Fly ash/Slag and Limestone based), Development of Portland Limestone Cement (PLC), utilization of low grade limestone and mines rejects, Utilization of Construction and demolished waste (C&D) waste based aggregates in concrete structures and pavements are some of the key areas, where Indian Cement Industry & NCB is working together towards resource conservation and boost to circular economy in India (Table 18.3).
As a latest development, Indian government is planning to ban the single use plastic very soon. Government is looking towards Indian cement industry to burn the existing plastic waste and the industry is quite capable to do so due to some of the inherent features of cement manufacturing process. A typical analysis of entire single use plastic waste consumption in Indian cement industry as fuel considering existing production and fuel usage is shown in Table 18.4.
It is encouraging to see in Table 18.5 that % TSR of the Indian cement industry can go up by 5.5% with overall TSR of around 9.5% by utilizing 90% of single use plastic as fuel and replacing conventional fuel like coal and petcoke. This will provide a steady path to achieve 25% TSR by year 2025 and will encourage the circular economy in near future (http://www.ciiwasteexchange.org/doc/annexure_6.pdf).
Another potential area for Indian Cement industry is Geopolymer cements; Geo-polymeric cements are eco-friendly binders and being produced from non-limestone bearing raw materials and wastes such as fly ash and slag. Thermal Power plants (TPP) in India are also in the process of installation of Flue Gas Desulphurization (FGD) systems to control SOx emissions. By product of this system is FGD gypsum which can be a partial/fully replacement of natural gypsum used to control setting time of Portland cements (Caillahua and Moura 2018). Cements plants in India, which are facing the issue of gypsum availability, may procure FGD gypsum from power plants in future.
18.7 Conclusions
Indian cement industry has to play a catalyst role in future towards resource conservation and providing impetus to circular economy. All stakeholders including cement plants, research organizations (Like-NCB), Government Bodies (Pollution Control Boards, Municipal Corporation etc.) etc. have to work together in one direction to achieve goals of circular economy. In coming years, Circular economy will gain further momentum in Indian cement industry by utilizing Gypsum generated from FGD in TPP, Consumption of Non-recyclable plastic waste, Production of High Volume Flyash cement, Utilizing Steel slag, reduction clinker factor by Alternative raw materials and increasing TSR by the use of AFs. However, Solar Thermal Calcination and Geopolymer cement will take time to establish. Some newer avenues need to be explored in this area like product as a service where cement industry can also work out to buy compressed air and other utilities instead of procuring compressors, pumps etc. It may lead to opportunities of futuristic technologies like oxy fuel combustion. Some companies can sell pure oxygen to cement plants cluster at a reasonable price. Another interesting aspect of circular economy, which remains unexplored in context of cement industry is product life extension, at present uses of C&D waste is taking momentum which helps form product life cycle extension.
References
Agarwal SK, Vanguri S, Chaturvedi SK, Kumar A, Reddy AS (2017) Performance evaluation of granulated BF slag—steel slag based Portland slag cement. In: 15th International seminar on cement, concrete and building materials, New Delhi
Caillahua MC, Moura FJ (2018) Technical feasibility for use of FGD gypsum as an additive setting time retarder for Portland Cement. J Mater Res Technol 7(2):190–197
CII Homepage. http://www.ciiwasteexchange.org/doc/afr2018.pdf. Last accessed 8 June 2019
CII Homepage. http://www.ciiwasteexchange.org/doc/annexure_6.pdf. Last accessed 8 June 2019
CEA Homepage. http://www.cea.nic.in/reports/others/thermal/tcd/flyash_201617.pdf
FICCI Homepage. http://ficci.in/spdocument/22977/FICCI-Circular-Economy.pdf. Last accessed 12 June 2019.
Ghosh SK (2017) Circular economy and 3Rs—reduce, reuse, recycle, for efficient use of resources in the Asia and the Pacific. In: Proceedings of the WasteSafe 2017—5th international conference on solid waste management in the developing countries, 25–27 February 2017, Khulna, Bangladesh
Gonzalez RS, Flamant G (2014) Technical and economic feasibility analysis of using concentrated solar thermal technology in the cement production process: hybrid approach—a case study. J Solar Energy Eng 136:025001-1 to 12
IBEF Homepage. https://www.ibef.org/industry/cement-presentation. Last accessed 18 Oct 2019
Julie D (2004) Resource recovery, SSW synthesis part 3, good practices and recommendations on SSW use. Julie, Lafarge Res Recov 26–28
Mohapatra BN, Vyas SK, Shekhar C (2014) Indian experience of using AFR. In: Cement kiln. Industrial Angles, vol 3, pp 7–13
Moumina G, Tescarib S, Sundarrajb P, Oliveirab L, Roebb M, Sattlerb C (2019) Solar treatment of cohesive particles in a directly irradiated rotary kiln. Solar Energy 182:480–490
NITI Aayog Homepage. https://niti.gov.in/writereaddata/files/E-WasteStrategy.pdf. Last accessed 15 June 2019
PIB Homepage. https://pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=1562754. Last accessed 15 June 2019
Raju A (2019) Plastic waste management and marine plastic pollution in South Asia. In: Second sub-regional workshop on preparation of status report and sub-regional roadmap for implementing the global waste management goals towards addressing SDGS in South Asia, Dhaka
SolarPACES Homepage. https://www.solarpaces.org/new-iea-report/. Last accessed 8 June 2019
Shaw SK, Saxena A, Kukreja K, Rao MVR, Venkatesh V (2017) Feasibility study for enhancement of solid alternate fuels in Indian cement plant. In: Proceeding of the 15th NCB international seminar on cement and building materials, New Delhi
Swaminathan R, Nadhipite S (2017) Design of solar lime kiln. Innov Energy Res. https://doi.org/10.4172/2576-1463.s1-001
The HINDU Business Line Homepage. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/companies/by-2021-ultratech-aims-to-source-25-of-energy-from-renewable-sources/article27689331.ece. Last accessed 12 June 2019
WBCSD HomePage. https://www.wbcsd.org/Sector-Projects/Cement-Sustainability-Initiative/Resources/Low-Carbon-Technology-Roadmap-for-the-Indian-Cement-Sector-Status-Review-2018. Last accessed 12 June 2019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Copyright information
© 2020 The Author(s)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kukreja, K., Sharma, P., Mohapatra, B., Saxena, A. (2020). Indian Cement Industry: A Key Player in the Circular Economy of India. In: Sangwan, K., Herrmann, C. (eds) Enhancing Future Skills and Entrepreneurship. Sustainable Production, Life Cycle Engineering and Management. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44248-4_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-44248-4_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-44247-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-44248-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)