Abstract
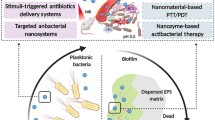
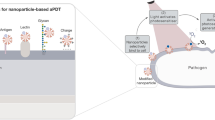
Unprecedented explosion of research in the field of nanotechnology has gained importance in the treatment, prevention, and eradication of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains. The emerging multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDRB) pose a major threat to the modern health-care system. The MDRB strains cannot be treated with conventional antibiotics due to their rapid mutations and resistance. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria that produce biofilm are responsible for approximately 700,000 deaths each year. One of the biggest problems faced by research society is to find alternatives to combat the increasing number of resistant variants. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) was established recently and remains a successful treatment modality for infectious diseases caused by microbial strains and biofilms. Light-mediated inactivation through photodynamic therapy provides new dimensions to eradicate antibiotic-resistant microbes. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) has gained interest in nanotechnology where the effectiveness of photosensitizers (PS) can be enhanced by the use of nanoparticles (NPs). In the last two decades, different techniques have been raised for aPDT in combination with nanoparticles. Nanoparticles are used in aPDT either as photosensitizing agents or as PS delivery agents. Nanoparticles used in aPDT improve the dispersion and selective delivery of PS to the target cells. Over last decades, various nanoparticles are utilized in aPDT as nanocarriers. Polymeric nanovehicles, nanomicelles, and liposome are used to encapsulate PS molecules. The inorganic metallic nanoparticles are extensively studied for the photoinactivation of resistant microorganisms and their biofilms. The four types of combinations between nanoparticles and PS are categorized as nanoparticles embedded with PS, nanoparticles with PS bound to the surface, nanoparticles as the PS, and PS alongside nanoparticles. Nanoparticles have enhanced the activity of aPDT by encapsulating the PS in nanoparticles or binding the PS on the surface of nanoparticles covalently. The photoactive nanoparticles were successful as antimicrobial agents and more effective against antibiotic-resistant microbial strains and their biofilms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E (2009) Photocatalytic reduction of graphene oxide nanosheets on TiO2 thin film for photoinactivation of bacteria in solar light irradiation. J Phys Chem C 113:20214–20220. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp906325q
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E (2010) Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 4:5731–5736. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn101390x
Aoshima H, Kokubo K, Shirakawa S et al (2009) Antimicrobial activity of fullerenes and their hydroxylated derivatives. Biocontrol Sci 14:69–72. https://doi.org/10.4265/bio.14.69
Aziz N, Fatma T, Varma A, Prasad R (2014) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Scenedesmus abundans and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. J Nanopart 2014:689419. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/689419
Aziz N, Faraz M, Pandey R, Sakir M, Fatma T, Varma A, Barman I, Prasad R (2015) Facile algae-derived route to biogenic silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial and photocatalytic properties. Langmuir 31:11605−11612. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03081
Aziz N, Pandey R, Barman I, Prasad R (2016) Leveraging the attributes of Mucor hiemalis-derived silver nanoparticles for a synergistic broad-spectrum antimicrobial platform. Front Microbiol 7:1984. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01984
Banerjee I, Douaisi MP, Mondal D, Kane RS (2012) Light-activated nanotube–porphyrin conjugates as effective antiviral agents. Nanotechnology 23:105101. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/23/10/105101
Bhuyan T, Mishra K, Khanuja M, Prasad R, Varma A (2015) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater Sci Semicond Process 32:55–61
Bjarnsholt T (2013) The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS 121:1–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12099
Ceri H, Olson ME, Turner RJ (2010) Needed, new paradigms in antibiotic development. Expert Opin Pharmacother 11:1233–1237. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656561003724747
Chadha T (2012) Antibiotic resistant genes in natural environment. Agrotechnology 01:1–3. https://doi.org/10.4172/2168-9881.1000104
Costerton JW, Lewandowski Z, Caldwell DE et al (1995) Microbial biofilms. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:711–745. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.mi.49.100195.003431
Dai T, Tegos GP, Zhiyentayev T et al (2010) Photodynamic therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in a mouse skin abrasion model. Lasers Surg Med 42:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20887
Dakal TC, Kumar A, Majumdar RS, Yadav V (2016) Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front Microbiol 7:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01831
Davies D (2003) Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1008
De Freitas LM, Calixto GMF, Chorilli M et al (2016) Polymeric nanoparticle-based photodynamic therapy for chronic periodontitis in vivo. Int J Mol Sci 17:769. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050769
De la Fuente-Nunez C, Torres MD, Mojica FJ, Lu TK (2017) Next-generation precision antimicrobials: towards personalized treatment of infectious diseases. Curr Opin Microbiol 37:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2017.05.014
Derycke A (2004) Liposomes for photodynamic therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56:17–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2003.07.014
Donlan RM (2002) Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg Infect Dis 8:881–890. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0809.020063
Drenkard E (2003) Antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microbes Infect 5:1213–1219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2003.08.009
Drenkard E, Ausubel FM (2002) Pseudomonas biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance are linked to phenotypic variation. Nature 416:740–743. https://doi.org/10.1038/416740a
Durán N, Durán M, de Jesus MB et al (2016) Silver nanoparticles: a new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 12:789–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2015.11.016
Fathi A, Rasekaran R et al (2013) Influence of hydrogen peroxide or gold nanoparticles in protoporphyrin IX mediated antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on Staphylococcus aureus. Afr J Microbiol Res 7:4617–4624. https://doi.org/10.5897/2013.5885
Fernandes P, Martens E (2017) Antibiotics in late clinical development. Biochem Pharmacol 133:152–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2016.09.025
Foster HA, Ditta IB, Varghese S, Steele A (2011) Photocatalytic disinfection using titanium dioxide: spectrum and mechanism of antimicrobial activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1847–1868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3213-7
Hah HJ, Kim G, Lee Y-EK et al (2011) Methylene blue-conjugated hydrogel nanoparticles and tumor-cell targeted photodynamic therapy. Macromol Biosci 11:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201000231
Holmstrup P, Klausen B (2018) The growing problem of antimicrobial resistance. Oral Dis 24:291–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12610
Huang L, Xuan Y, Koide Y et al (2012a) Type I and type II mechanisms of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy: an in vitro study on Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Lasers Surg Med 44:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.22045
Huang Y-Y, Sharma SK, Dai T et al (2012b) Can nanotechnology potentiate photodynamic therapy? Nanotechnol Rev 1:111–146. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2011-0005
Huang Y-Y, Choi H, Kushida Y et al (2016) Broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects of photocatalysis using titanium dioxide nanoparticles are strongly potentiated by addition of potassium iodide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:5445–5453. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00980-16
Hwang YY, Ramalingam K, Bienek DR et al (2013) Antimicrobial activity of nanoemulsion in combination with cetylpyridinium chloride in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:3568–3575. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02109-12
Jasovský D, Littmann J, Zorzet A, Cars O (2016) Antimicrobial resistance—a threat to the world’s sustainable development. Ups J Med Sci 121:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/03009734.2016.1195900
Jing H, Mezgebe B, Aly Hassan A et al (2014) Experimental and modeling studies of sorption of ceria nanoparticle on microbial biofilms. Bioresour Technol 161:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.015
Jori G, Fabris C, Soncin M et al (2006) Photodynamic therapy in the treatment of microbial infections: basic principles and perspective applications. Lasers Surg Med 38:468–481. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20361
Junqueira JC, Jorge AOC, Barbosa JO et al (2012) Photodynamic inactivation of biofilms formed by Candida spp., Trichosporon mucoides, and Kodamaea ohmeri by cationic nanoemulsion of zinc 2,9,16,23-tetrakis(phenylthio)-29H, 31H-phthalocyanine (ZnPc). Lasers Med Sci 27:1205–1212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-012-1050-2
Kang S, Herzberg M, Rodrigues DF, Elimelech M (2008) Antibacterial effects of carbon nanotubes: size does matter. Langmuir 24:6409–6413. https://doi.org/10.1021/la800951v
Käsermann F, Kempf C (1998) Buckminsterfullerene and photodynamic inactivation of viruses. Rev Med Virol 8:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1654(199807/09)8:3<143::AID-RMV214>3.0.CO;2-B
Kashef N, Huang Y-Y, Hamblin MR (2017) Advances in antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation at the nanoscale. Nanophotonics 6:853–879. https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2016-0189
Khan S, Khan AU, Azam A, Alam F (2012) Gold nanoparticles enhance methylene blue-induced photodynamic therapy: a novel therapeutic approach to inhibit Candida albicans biofilm. Int J Nanomedicine 2012:3245–3257. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S31219
Klepac-Ceraj V, Patel N, Song X et al (2011) Photodynamic effects of methylene blue-loaded polymeric nanoparticles on dental plaque bacteria. Lasers Surg Med 43:600–606. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.21069
Kubheka G, Uddin I, Amuhaya E et al (2016) Synthesis and photophysicochemical properties of BODIPY dye functionalized gold nanorods for use in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. J Porphyr Phthalocyanines 20:1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1142/S108842461650070X
Kuo W-S, Chang C-Y, Chen H-H et al (2016) Two-photon photoexcited photodynamic therapy and contrast agent with antimicrobial graphene quantum dots. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:30467–30474. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12014
Lewis K (2001) Riddle of biofilm resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:999–1007. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.45.4.999-1007.2001
Li X-Z, Nikaido H (2009) Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. Drugs 69:1555–1623. https://doi.org/10.2165/11317030-000000000-00000
Lipovsky A, Gedanken A, Nitzan Y, Lubart R (2011) Enhanced inactivation of bacteria by metal-oxide nanoparticles combined with visible light irradiation. Lasers Surg Med 43:236–240. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.21033
Llor C, Bjerrum L (2014) Antimicrobial resistance: risk associated with antibiotic overuse and initiatives to reduce the problem. Ther Adv Drug Saf 5:229–241. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042098614554919
Lucky SS, Soo KC, Zhang Y (2015) Nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy. Chem Rev 115:1990–2042. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr5004198
Magadla A, Oluwole DO, Managa M, Nyokong T (2019) Physicochemical and antimicrobial photodynamic chemotherapy (against E. Coli) by indium phthalocyanines in the presence of silver-iron bimetallic nanoparticles. Polyhedron 40:2710–2721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2019.01.032
Mah T-FC, O’Toole GA (2001) Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol 9:34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-842X(00)01913-2
Maisch T, Santarelli F, Schreml S et al (2009) Fluorescence induction of protoporphyrin IX by a new 5-aminolevulinic acid nanoemulsion used for photodynamic therapy in a full-thickness ex vivo skin model. Exp Dermatol 19:e302–e305. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2009.01001.x
Majik M, Parvatkar P (2013) Next generation biofilm inhibitors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: synthesis and rational design approaches. Curr Top Med Chem 14:81–109. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026613666131113152257
Matsumura Y, Yoshikata K, Kunisaki S, Tsuchido T (2003) Mode of bactericidal action of silver zeolite and its comparison with that of silver nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4278–4281. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.7.4278-4281.2003
McAdam AJ, Hooper DC, DeMaria A et al (2012) Antibiotic resistance: how serious is the problem, and what can be done? Clin Chem 58:1182–1186. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2011.181636
Misba L, Kulshrestha S, Khan AU (2016) Antibiofilm action of a toluidine blue O-silver nanoparticle conjugate on Streptococcus mutans: a mechanism of type I photodynamic therapy. Biofouling 32:313–328. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2016.1141899
Mizuno K, Zhiyentayev T, Huangv L et al (2011) Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with functionalized fullerenes: quantitative structure-activity relationships. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 02:1–9. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000109
Mroz P, Tegos GP, Gali H et al (2007) Photodynamic therapy with fullerenes. Photochem Photobiol Sci 6:1139–1149. https://doi.org/10.1039/b711141j
Nakonechny F, Firer MA, Nitzan Y, Nisnevitch M (2010) Intracellular antimicrobial photodynamic therapy: a novel technique for efficient eradication of pathogenic bacteria. Photochem Photobiol 86:1350–1355. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.2010.00804.x
National Collaborating Centre for Infectious Diseases (2010) Proceedings of Community-Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Consultation Notes, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 10–11 February 2010 Available at: http://www.nccid.ca/files/caAMR_ConsultationNotes_final.pdf
Nombona N, Antunes E, Chidawanyika W et al (2012) Synthesis, photophysics and photochemistry of phthalocyanine-ɛ-polylysine conjugates in the presence of metal nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 233:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.02.012
Pagonis TC, Chen J, Fontana CR et al (2010) Nanoparticle-based endodontic antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. J Endod 36:322–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2009.10.011
Paramanantham P, Antony AP, Sruthil Lal SB et al (2018) Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation of fungal biofilm using amino functionalized mesoporous silica-rose bengal nanoconjugate against Candida albicans. Sci Afr e00007:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2018.e00007
Parasuraman P, Anju VT, Sruthil Lal S et al (2019) Synthesis and antimicrobial photodynamic effect of methylene blue conjugated carbon nanotubes on E. coli and S. aureus. Photochem Photobiol Sci 1(8):563–576. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PP00369F
Paulo J, Longo F, Muehlmann LA, De Azevedo RB (2011) Nanostructured carriers for photodynamic therapy applications in microbiology, pp 189–196
Pissuwan D, Cortie CH, Valenzuela SM, Cortie MB (2010) Functionalised gold nanoparticles for controlling pathogenic bacteria. Trends Biotechnol 28:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.12.004
Pourhajibagher M, Salehi Vaziri A, Takzaree N, Ghorbanzadeh R (2019) Physico-mechanical and antimicrobial properties of an orthodontic adhesive containing cationic curcumin doped zinc oxide nanoparticles subjected to photodynamic therapy. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 25:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.01.002
Prasad R, Pandey R, Varma A, Barman I (2017) Polymer based nanoparticles for drug delivery systems and cancer therapeutics. In: Natural Polymers for Drug Delivery (eds. Kharkwal H and Janaswamy S), CAB International, UK. 53–70
Rehman S, Ullah R, Butt AM, Gohar ND (2009) Strategies of making TiO2 and ZnO visible light active. J Hazard Mater 170:560–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.064
Ribeiro APD, Andrade MC, Bagnato VS et al (2015) Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy against pathogenic bacterial suspensions and biofilms using chloro-aluminum phthalocyanine encapsulated in nanoemulsions. Lasers Med Sci 30:549–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1354-x
Rud Y, Buchatskyy L, Prylutskyy Y et al (2012) Using C 60 fullerenes for photodynamic inactivation of mosquito iridescent viruses. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 27:614–617. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2011.601303
Sadekuzzaman M, Yang S, Mizan MFR, Ha SD (2015) Current and recent advanced strategies for combating biofilms. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 14:491–509. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12144
Sakima V, Barbugli P, Cerri P et al (2018) Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy mediated by curcumin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles in a murine model of oral candidiasis. Molecules 23:2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082075
Santajit S, Indrawattana N (2016) Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Biomed Res Int 2016:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2475067
Sharma SK, Chiang LY, Hamblin MR (2011) Photodynamic therapy with fullerenes in vivo: reality or a dream? Nanomedicine 6:1813–1825. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.11.144
Singh S, Singh SK, Chowdhury I, Singh R (2017) Understanding the mechanism of bacterial biofilms resistance to antimicrobial agents. Open Microbiol J 11:53–62. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874285801711010053
Spagnul C, Turner LC, Boyle RW (2015) Immobilized photosensitizers for antimicrobial applications. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 150:11–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.04.021
Sperandio F, Huang Y-Y, Hamblin M (2013) Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy to kill Gram-negative bacteria. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov 8:108–120. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574891X113089990012
St. Denis TG, Dai T, Izikson L et al (2011) All you need is light. Virulence 2:509–520. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.2.6.17889
Tawfik AA, Alsharnoubi J, Morsy M (2015) Photodynamic antibacterial enhanced effect of methylene blue-gold nanoparticles conjugate on Staphylococcal aureus isolated from impetigo lesions in vitro study. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 12:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2015.03.003
Torchilin V (2005) Fluorescence microscopy to follow the targeting of liposomes and micelles to cells and their intracellular fate. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2004.06.002
Tsai T, Yang Y-T, Wang T-H et al (2009) Improved photodynamic inactivation of Gram-positive bacteria using hematoporphyrin encapsulated in liposomes and micelles. Lasers Surg Med 41:316–322. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20754
Tuchina ES, Tuchin VV (2010) TiO2 nanoparticle enhanced photodynamic inhibition of pathogens. Laser Phys Lett 7:607–612. https://doi.org/10.1002/lapl.201010030
Vilsinski BH, Gerola AP, Enumo JA et al (2015) Formulation of aluminum chloride phthalocyanine in pluronic TM P-123 and F-127 block copolymer micelles: photophysical properties and photodynamic inactivation of microorganisms. Photochem Photobiol 91:518–525. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12421
Vrany JD, Stewart PS, Suci PA (1997) Comparison of recalcitrance to ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin exhibited by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms displaying rapid-transport characteristics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41:1352–1358
Vt A, Paramanantham P, Sb SL et al (2018) Antimicrobial photodynamic activity of rose bengal conjugated multi walled carbon nanotubes against planktonic cells and biofilm of Escherichia coli. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 24:300–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2018.10.013
Wang X, Li Q, Xie J et al (2009) Fabrication of ultralong and electrically uniform single-walled carbon nanotubes on clean substrates. Nano Lett 9:3137–3141. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl901260b
Wang Y, Li Z, Wang J et al (2011) Graphene and graphene oxide: biofunctionalization and applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 29:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.01.008
Wang Z, Bai H, Lu C et al (2019) Light controllable chitosan micelles with ROS generation and essential oil release for the treatment of bacterial biofilm. Carbohydr Polym 205:533–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.095
Weissleder R (2001) A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat Biotechnol 19:316–317. https://doi.org/10.1038/86684
Wilson DN (2014) Ribosome-targeting antibiotics and mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:35–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3155
Wright G (2005) Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: enzymatic degradation and modification. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:1451–1470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2005.04.002
Wu M-C, Deokar AR, Liao J-H et al (2013) Graphene-based photothermal agent for rapid and effective killing of bacteria. ACS Nano 7:1281–1290. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn304782d
Yang K, Gitter B, Rüger R et al (2011) Antimicrobial peptide-modified liposomes for bacteria targeted delivery of temoporfin in photodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy. Photochem Photobiol Sci 10:1593. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1pp05100h
Yang M, Chang K, Chen L et al (2018) Blue light irradiation triggers the antimicrobial potential of ZnO nanoparticles on drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 180:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.02.003
Yin R, Agrawal T, Khan U et al (2015) Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation in nanomedicine: small light strides against bad bugs. Nanomedicine 10:2379–2404. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.15.67
Zane A, Zuo R, Villamena F et al (2016) Biocompatibility and antibacterial activity of nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles for use in dental resin formulations. Int J Nanomedicine 11:6459–6470. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S117584
Zhao J, Lin Z, Fang S et al (2019) Photoexcitation of self-n-doped fullerene ammonium halides: the role of halide ion and a possible synergistic dual-redox cycle mechanism within their aggregate. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 373:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.01.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Anju, V.T., Siddhardha, B., Dyavaiah, M. (2020). Nanostructures for Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Photodynamic Therapy. In: Prasad, R., Siddhardha, B., Dyavaiah, M. (eds) Nanostructures for Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Applications. Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-40337-9_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-40337-9_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-40336-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-40337-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)