Abstract
In Mandarin Chinese, reduplicative classifiers can be used to express plurality, which is closely related to the spatiality of nouns. This paper takes “一CCN” (short for the construction “One + Classifier + Classifier + Noun”) as an example to analyze the spatial presentation of “一CCN” and discusses its semantic consequence. Different from other quantificational expressions such as “Number + Classifier + Noun”, “一CCN” does not express a small quantity and “一CC” cannot fall in the scope of quantitative adverb
 and
and
 . By analyzing the contexts in which it can or cannot appear, and comparing it with
. By analyzing the contexts in which it can or cannot appear, and comparing it with
 (“many”), we conclude that the “many” meaning of “一CCN” is not its literal but inferential meaning.
(“many”), we conclude that the “many” meaning of “一CCN” is not its literal but inferential meaning.
(This study is supported by the project of “Research on the Lexical Semantic Knowledge Representation and Its Computing System within the Framework of Chinese Parataxis Grammar” (Project No. 18JJD740003), and “The Study of International Chinese Language Teaching Resources and Wisdom Education Platform Based on ‘Internet +’” (Project No.18ZDA295). We hereby express our sincere thanks.).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
In [3], “targets” and “referents” are called as “primary objects” and “secondary objects” respectively.
References
Bisang, W.: Classifiers in east and southeast Asian languages: counting and beyond. In: Gvozdanović, J. (ed.) Numeral Types and Changes Worldwide, pp. 113–185. Mouton de Gruyter, Berlin (1999)
Li, W.H.: The interaction between classifier reduplication and construction. Chin. Teach. World 3, 354–362 (2010). (in Chinese)
Talmy, L.: Toward a Cognitive Semantics: Concept Structuring Systems, vol. 1. The MIT Press, Cambridge (2000)
Doetjes, J.: Count/Mass distinction across languages. In: Maienborn, C., Heusinger, K., Portner, P. (eds.) Semantics: An International Handbook of Natural Language Meaning, vol. 3, pp. 2559–2580. Mouton de Gruyter, Berlin and New York (2012)
Zhang, N.: Classifier Structures in Mandarin Chinese. De Gruyter Mouton, Berlin/Boston (2013)
Chen, P.: The tripartite-structure of temporal system in modern Chinese. Stud. Chin. Lang. 6, 401–421 (1988). (in Chinese)
Li, Y.M.: The semantics of reduplication. Lang. Teach. World 1, 10–19 (1996). (in Chinese)
Chu, Z.X.: Study on Spatial Phrases in Chinese. Peking University Press, Beijing (2010). (in Chinese)
Sybesma, R.: Markers of countability in the nominal domain in Mandarin and Cantonese. Essays Linguist. 35, 234–245 (2007). (in Chinese)
Chierchia, G.: Plurality of mass nouns and the notion of “Semantic Parameter”. In: Rothstein, S. (ed.) Events and Grammar, pp. 53–104. Springer Science + Business Media, Dordrecht (1998)
Lü, S.X.: 800 Words in Modern Mandarin Chinese. The Commercial Press, Beijing (1999). (in Chinese)
Yin, H.H.: The scalar usage and noun usage of the focus-sensitive operator “Zhi”
 . Lang. Learn. Linguist. Stud. 1, 49–56 (2009). (in Chinese)
. Lang. Learn. Linguist. Stud. 1, 49–56 (2009). (in Chinese)Xiong, Z.R.: Nominal phrases containing reduplicated classifiers. Lang. Teach. Linguist. Stud. 2, 44–57 (2018). (in Chinese)
Wang, H.:
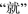 and
and
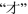 . Chin. Lang. Learn. 12, 35 (1956). (in Chinese)
. Chin. Lang. Learn. 12, 35 (1956). (in Chinese)Song, Y.Z.: Essays on Modern Chinese Grammar. Tianjin People’s Publishing Company, Tianjin (1981). (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sun, J., Yuan, Y. (2020). Spatiality and Its Semantic Consequence of the Quantitative Expression “一CCN” in Mandarin Chinese. In: Hong, JF., Zhang, Y., Liu, P. (eds) Chinese Lexical Semantics. CLSW 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11831. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38189-9_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-38189-9_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-38188-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-38189-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


 . Lang. Learn. Linguist. Stud. 1, 49–56 (2009). (in Chinese)
. Lang. Learn. Linguist. Stud. 1, 49–56 (2009). (in Chinese)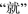 and
and
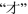 . Chin. Lang. Learn. 12, 35 (1956). (in Chinese)
. Chin. Lang. Learn. 12, 35 (1956). (in Chinese)