Abstract
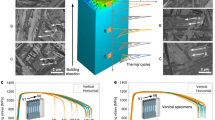
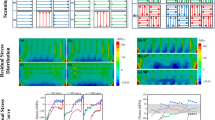
Additive manufacturing of metals has opened a whole new range of complex functional geometries inaccessible by convectional production methods which are called to revolutionise several sectors (i.e., biomedical, aerospace, energy). These parts usually include a wide variety of characteristic elemental length scales from thin walls/struts to bulk regions. The different intrinsic aspects of the manufacturing process (heat fluxes) make the properties of the material strongly size dependent. These dependencies are still unclear, and further investigations are needed in order to ensure the quality of the produced parts. In this work, the variation of the mechanical properties as a function of the component size and build orientation is addressed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horn TJ, Harrysson OLA (2012) Overview of current additive manufacturing technologies and selected applications. Sci Prog 95(3):255–282
Frazier WE (2014) Metal additive manufacturing: a review. J Mater Eng Perform 23(6):1917–1928
Simonelli M, Tse YY, Tuck C (2014) On the texture formation of selective laser melted Ti–6Al–4V. Metall Mater Trans A, 45(6):2863–2872
Murr LE, Quinones SA, Gaytan SM, Lopez MI, Rodela A, Martinez EY, Hernandez DH, Martinez E, Medina F, Wicker RB (2009) Microstructure and mechanical behavior of Ti–6Al–4V produced by rapilayer manufacturing, for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2(1):20–32
Zhao X, Li S, Zhang M, Liu Y, Sercombe TB, Wang S, Hao Y, Yang R, Murr LE (2016) Comparison of the microstructures and mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V fabricated by selective laser melting and electron beam melting. Mater Des 95:21–31
Song B, Zhao X, Li S, Han C, Wei Q, Wen S, Liu J, Shi Y (2015) Differences in microstructure and properties between selective laser melting and traditional manufacturing for fabrication of metal parts: a review. Front Mech Eng 10(2):111–125
Yadroitsev I, Bertrand Ph, Smurov I (2007) Parametric analysis of the selective laser melting process. Appl Surf Sci 253(19):8064–8069
Simonelli M, Tse YY, Tuck C (2014) Effect of the build orientation on the mechanical properties and fracture modes of SLM Ti–6Al–4V. Mater Sci Eng A 616:1–11
Wauthle R, Vrancken B, Beynaerts B, Jorissen K, Schrooten J, Kruth J-P, Van Humbeeck J (2015) Effects of build orientation and heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V lattice structures. Addit Manuf 5:77–84
Simonelli M, Tse YY, Tuck C (2014) Effect of the build orientation on the mechanical properties and fracture modes of SLM Ti–6Al–4V. Mater Sci Eng: A 616:1–11
Wang D, Yang Y, Liu R, Xiao D, Sun J (2013) Study on the designing rules and processability of porous structure based on selective laser melting (SLM). J Mater Process Technol 213(10):1734–1742
Wang X, Xu S, Zhou S, Xu W, Leary M, Choong P, Qian M, Brandt M, Xie YM (2016) Topological design and additive manufacturing of porous metals for bone scaffolds and orthopaedic implants: a review. Biomaterials 83:127–141
Palka K, Pokrowiecki R (2018) Porous titanium implants: a review. Adv Eng Mater 20(5):1700648
Alabort E, Barba D, Reed RC (2019) Design of metallic bone by additive manufacturing. Scr Mater, 164:110–114
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (1999) Cellular solids: structure and properties. Cambridge university press
Neugebauer R, Müller B, Gebauer M, Töppel T (2011) Additive manufacturing boosts efficiency of heat transfer components. Assembly Autom 31(4):344–347
Al-Ketan O, Rowshan R, Al-Rub RKA (2018) Topology-mechanical property relationship of 3D printed strut, skeletal, and sheet based periodic metallic cellular materials. Addit Manufact 19:167–183
Saha K, Acharya S, Nakamata C (2013) Heat transfer enhancement and thermal performance of lattice structures for internal cooling of airfoil trailing edges. J Therm Sci Eng Appl 5(1):11001
Yan C, Hao L, Hussein A, Young P. Ti–6Al–4V triply periodic minimal surface structures for bone implants fabricated via selective laser melting. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 51:61–73
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to OxMet Technologies Ltd for funding this research. The authors are grateful to Renishaw plc and Lucy Grainger who assisted with build preparation and manufacturing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Barba, D., Alabort, C., Reed, R.C., Alabort, E. (2020). On the Size Effects in Additively Manufactured Titanium and the Implications in AM Components. In: TMS 2020 149th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36296-6_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36296-6_42
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36295-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36296-6
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)