Abstract
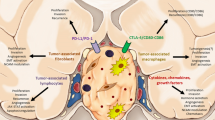
Parathyroid tumors are the second most common endocrine neoplasia, and it is almost always associated with hypersecretion of the parathormone (PTH), involved in calcium homeostasis, causing primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT). Parathyroid neoplasia has a stromal component particularly represented in atypical adenomatous and carcinomatous lesions. Recently, data about the features and the function of the parathyroid tumor microenvironment (TME) have been accumulated. Parathyroid TME includes heterogeneous cells: endothelial cells, myofibroblasts, lymphocytes and macrophages, and mesenchymal stem cells have been identified, each of them presenting a phenotype consistent with tumor-associated cells. Parathyroid tumors overexpress proangiogenic molecules including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A), fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), and angiopoietins that promote both recruitment and proliferation of endothelial cell precursors, thus resulting in a microvessel density higher than that detected in normal parathyroid glands. Moreover, parathyroid tumor endocrine cells operate multifaceted interactions with stromal cells, partly mediated by the CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway, while, at present, the immune landscape of parathyroid tumors has just begun to be investigated. Studies about TME in parathyroid adenomas provide an example of the role of TME in benign tumors, whose molecular mechanisms and functions comprehension are limited.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamoud KA, Kukuruzinska MA (2018) Emerging insights into Wnt/β-catenin signaling in head and neck cancer. J Dent Res 97:665–673. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034518771923
Bilezikian JP (2018) Primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103:3993–4004. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2018-01225
Salcuni AS, Cetani F, Guarnieri V, Nicastro V, Romagnoli E, de Martino D et al (2018) Parathyroid carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 32:877–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2018.11.002
Cetani F, Pardi E, Marcocci C (2019a) Parathyroid carcinoma. Front Horm Res 51:63–76. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491039
Cetani F, Marcocci C, Torregrossa L, Pardi E (2019b. pii: ERC-19-0135.R2) Atypical parathyroid adenomas: challenging lesions in the differential diagnosis of endocrine tumors. Endocr Relat Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-19-0135
Christakis I, Bussaidy N, Clarke C, Kwatampora LJ, Warneke CL, Silva AM, Williams MD, Grubbs EG, Lee JE, Perrier ND (2016) Differentiating atypical parathyroid neoplasm from parathyroid cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 23:2889–2897. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5248-6
Chen H, Senda T, Emura S, Kubo K (2013) An update on the structure of the parathyroid gland. Open Anat J 3:1–9
DeLellis R, Larsson C, Arnold A, Lloy R, Bilezikian J, Mete O, Eng C (2017) Tumors of the parathyroid glands. In: Lloyd R, Osamura R, Kloppel G, Rosai J (eds) WHO Classification of tumors of endocrine organs, 4th edn. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 145–159
Duan K, Gomez Hernandez K, Mete O (2015) Clinicopathological correlates of hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Pathol 68:771–787. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2015-203186
Yuan Y (2016) Spatial heterogeneity in the tumor microenvironment. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med:6. pii:a026583. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a026583
Goradel NH, Asghari MH, Moloudizargari M, Negahdari B, Haghi-Aminjan H, Abdollahi M (2017) Melatonin as an angiogenesis inhibitor to combat cancer: mechanistic evidence. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 335:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.09.022
Carter WB, Uy K, Ward MD, Hoying JB (2000) Parathyroid-induced angiogenesis is VEGF-dependent. Surgery 128:458–464. https://doi.org/10.1067/msy.2000.107102
Ander SJ, Blomkvist LM, Mölne JC, Johansson KJ, Smeds SP (1997) Growth and function of human parathyroid tissue transplanted to athymic mice. J Endocrinol Invest 20:640–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03348025
Garcia de la Torre N, Buley I, Wass JA, Jackson DG, Turner HE (2004) Angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in parathyroid proliferative lesions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2890–2896. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2003-031651
Viacava P, Bocci G, Fanelli G, Cetani F, Marcocci C, Bevilacqua G, Naccarato AG (2006) Microvessel density in human normal and neoplastic parathyroids. Endocr Pathol 17:175–181
Segiet OA, Michalski M, Brzozowa-Zasada M, Piecuch A, Żaba M, Helewski K, Gabriel A, Wojnicz R (2015) Angiogenesis in primary hyperparathyroidism. Ann Diagn Pathol 19:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.01.002
Zaruba MM, Huber BC, Brunner S, Deindl E, David R, Fischer R et al (2008) Parathyroid hormone treatment after myocardial infarction promotes cardiac repair by enhanced neovascularization and cell survival. Cardiovasc Res 77:722–731. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvm080
Huber BC, Brunner S, Segeth A, Nathan P, Fischer R, Zaruba MM et al (2011) Parathyroid hormone is a DPP-IV inhibitor and increases SDF-1-driven homing of CXCR4(+) stem cells into the ischaemic heart. Cardiovasc Res 90:529–537. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvr014
Grabmaier U, Brandl L, Kreiner J, Negele T, Huber BC, Rimmbach C et al (2014) Increased numbers of bone marrow-derived cells in parathyroid adenoma. Eur J Clin Invest 44:833–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.12302
Corbetta S, Belicchi M, Pisati F, Meregalli M, Eller-Vainicher C, Vicentini L et al (2009) Expression of parathyroid-specific genes in vascular endothelial progenitors of normal and tumoral parathyroid glands. Am J Pathol 175:1200–1207. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2009.080979
Shi Y, Hogue J, Dixit D, Koh J, Olson JA (2014) Functional and genetic studies of isolated cells from parathyroid tumors reveal the complex pathogenesis of parathyroid neoplasia. Proc Nat Am Soc USA 111:3092–3097. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1319742111
Haglund F, Hallström BM, Nilsson IL, Höög A, Juhlin CC, Larsson C (2017) Inflammatory infiltrates in parathyroid tumors. Eur J Endocrinol 177:445–453. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-17-0277
Najafi M, Goradel NH, Farhood B, Salehi E, Solhjoo S, Toolee H, Kharazinejad E, Mortezaee K (2019) Tumor microenvironment: Interactions and therapy. J Cell Physiol 234:5700–5721. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27425
Kato T, Noma K, Ohara T, Kashima H, Katsura Y, Sato H et al (2018) Cancer-associated fibroblasts affect intratumoral CD8+ and FoxP3+ T cells via interleukin 6 in the tumor microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res 24:4820–4833. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0205
Silva-Figueroa A, Villalobos P, Williams MD, Bassett RL, Clarke CN, Lee JE et al (2018) Characterizing parathyroid carcinomas and atypical neoplasms based on the expression of programmed death-ligand 1 expression and the presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and macrophages. Surgery 164:960–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2018.06.013
Franklin RA, Li MO (2014) The ontogeny of tumor-associated macrophages: a new understanding of cancer-elicited inflammation. Oncoimmunology 3:e955346. https://doi.org/10.4161/21624011.2014.955346
Pan B, Wang A, Pang J, Zhang Y, Cui M, Sun J, Liang Z (2019) Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in parathyroid tumors. Endocr Connect 8:887–897. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-19-0163
Bu L, Baba H, Yoshida N, Miyake K, Yasuda T, Uchihara T, Tan P, Ishimoto T (2019) Biological heterogeneity and versatility of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 38:4887–4901. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0765-y
Kidd S, Spaeth E, Watson K, Burks J, Lu H, Klopp A et al (2012) Origins of the tumor microenvironment: quantitative assessment of adipose-derived and bone marrow derived stroma. PLoS One 7:e30563
Verdelli C, Avagliano L, Creo P, Guarnieri V, Scillitani A, Vicentini L et al (2015) Tumour-associated fibroblasts contribute to neoangiogenesis in human parathyroid neoplasia. Endocr Relat Cancer 22:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-14-0161
Burger JA, Stewart DJ, Wald O, Peled A (2011) Potential of CXCR4 antagonists for the treatment of metastatic lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 11:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1586/era.11.11
De Clercq E (2019) Mozobil® (Plerixafor, AMD3100), 10 years after its approval by the US Food and Drug Administration. Antivir Chem Chemother 27:2040206619829382. https://doi.org/10.1177/2040206619829382
Duda DG, Kozin SV, Kirkpatrick ND, Xu L, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2011) CXCL12 (SDF1a)–CXCR4/CXCR7 pathway inhibition: an emerging sensitizer for anticancer therapies? Clin Cancer Res 17:2074–2080. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2636
Shih YR, Kuo TK, Yang AH, Lee OK, Lee CH (2009) Isolation and characterization of stem cells from the human parathyroid gland. Cell Prolif 42:461–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2184.2009.00614.x
Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Pober JS, Sessa WC (2007) Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ Res 100:1164–1173. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000265065.26744.17
Goradel NH, Mohammadi N, Haghi-Aminjan H, Farhood B, Negahdari B, Sahebkar A (2019) Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by microRNAs: State of the art. J Cell Physiol 234:1099–1110. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27051
Corbetta S, Vaira V, Guarnieri V, Scillitani A, Eller-Vainicher C, Ferrero S et al (2010) Differential expression of microRNAs in human parathyroid carcinomas compared with normal parathyroid tissue. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1677/ERC-09-0134
Hu Y, Zhang X, Cui M, Su Z, Wang M, Liao Q, Zhao Y (2018) Verification of candidate microRNA markers for parathyroid carcinoma. Endocrine 60:246–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1551-2
Rahbari R, Holloway AK, He M, Khanafshar E, Clark OH, Kebebew E (2011) Identification of differentially expressed microRNA in parathyroid tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 18:1158–1165. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1359-7
Vaira V, Elli F, Forno I, Guarnieri V, Verdelli C, Ferrero S, Scillitani A, Vicentini L, Cetani F, Mantovani G, Spada A, Bosari S, Corbetta S (2012) The microRNA cluster C19MC is deregulated in parathyroid tumours. J Mol Endocrinol 49:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-11-0189
Verdelli C, Forno I, Morotti A, Creo P, Guarnieri V, Scillitani A, Cetani F, Vicentini L, Balza G, Beretta E, Ferrero S, Vaira V, Corbetta S (2018) The aberrantly expressed miR-372 partly impairs sensitivity to apoptosis in parathyroid tumor cells. Endocr Relat Cancer 25:761–771. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-17-0204
Qin A, Wen Z, Zhou Y, Li Y, Li Y, Luo J et al (2013) MicroRNA-126 regulates the induction and function of CD4(+) Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells through PI3K/AKT pathway. J Cell Mol Med 17:252–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12003
Verghese ET, Drury R, Green CA, Holliday DL, Lu X, Nash C et al (2013) MiR-26b is down-regulated in carcinoma-associated fibroblasts from ER-positive breast cancers leading to enhanced cell migration and invasion. J Pathol 231:388–399. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4248
Suzuki HI, Katsura A, Matsuyama H, Miyazono K (2015) MicroRNA regulons in tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 34:3085–3094. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.254
Hwang S, Jeong JJ, Kim SH, Chung YJ, Song SY, Lee YJ, Rhee Y (2018) Differential expression of miRNA199b-5p as a novel biomarker for sporadic and hereditary parathyroid tumors. Sci Rep 8:12016. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30484-9
Kalluri R (2016) The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 16:582–598. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.73
Li P, Gong Z, Shultz LD, Ren G (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells: From regeneration to cancer. Pharmacol Ther 200:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.04.005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Verdelli, C., Vaira, V., Corbetta, S. (2020). Parathyroid Tumor Microenvironment. In: Birbrair, A. (eds) Tumor Microenvironments in Organs. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1226. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36214-0_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36214-0_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36213-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36214-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)