Abstract
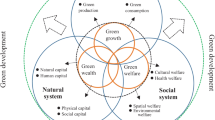
Green development demands the balance between the protection of resources and the environment and the development of the society and the economy. The Green Development Index (GDI) and an evaluation index system were constructed from the perspective of ecological civilization with the method of entire-array-polygon evaluation for the Qin-Ba Mountain area in China. Results show that the overall GDI of the Qin-Ba Mountain area, being 0.184, was below standard level; whereas its resource and environmental indices were higher than socio-economic indices. There are also large regional variations in GDI and different indices. The results provide important references for the green development of cities and towns in this area. Innovative ways of alleviating poverty, developing the economy, and restructuring the industries, on the basis of safeguarding ecological security are needed for green development.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
English
Ahmed, E. M. (2012). Green TFP intensity impact on sustainable East Asian productivity growth. Economic Analysis and Policy, 42(1), 67–78.
Boulding, K. (1971). The economics of the coming spaceship earth. In Global ecology: Readings toward a rational strategy for man (pp. 180–187). New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich.
Hall, C. R., Hodge, A. W., & Haydu, J. J. (2006). The economic impact of the green industry in the United States. Hort Technology, 16(2), 345–353.
Jarvis, A., Varma, A., & Ram, J. (2011). Assessing green jobs potential in developing countries: A practitioner’s guide. Geneva: International Labour Office.
OECD. (2011). Towards green growth: Monitoring progress OECD indicator. Paris: OECD.
Pearce, D., & Turner, R. K. (1990). Economics of natural resources and the environment. New York: Harvester Wheatsheaf.
Pearce, D., Markandya, A., & Barbier, E. (1989). Blueprint 1: For a green economy. London: Routledge.
UK Parliament Department of Trade Industry. (2003). Our Energy Future – Creating a Low Carbon Economy, CM 5761.
UNEP. (2011). Towards a green economy pathways to sustainable development and poverty eradication. Nairobi: UNEP.
Workforce Information Council. (2009). Measurement and analysis of employment in green economy. WIC Greenjobs study group final report.
Chinese
Cai, Y. Y., & Luo, C. (2015). Jiang han pingyuan gengdi ziyuan shengtai anquan zhuangkuang ji kongjian jiju geju [Ecological security condition of cultivated land resources and spatial agglomeration pattern in Jianghan plain]. Huazhong nongye daxue xuebao (shehui kexue ban), 5, 110–120.
Chang, J. W., & Wang, K. Y. (2018). Lun lvse fazhan zhishu tixi de wanshan [Analysis of improvement of green development index system]. Huanjing baohu, 46(07), 36–38.
Department of Urban Social and Economic Surveys, National Bureau of Statistics of People’s Republic of China. (2011). Zhongguo chengshi tongji nianjian [China City statistical yearbook]. Beijing: zhongguo tongji chubanshe.
Gong, Y. B., Zhang, J. G., & Liang, X. C. (2011). Jiyu quanpailie dongbianxing zonghe tushi fa de shuizhi pingjia [Water quality assessment of east route-based on entire-array-polygon evaluation method]. Zhongguo renkou·ziyuan yu huanjing, 21(09), 26–31.
Guo, S. F., & Ma, Y. H. (2017). Ziyuan xing quyu kechixu fazhan nengli cedu yanjiu [Comprehensive evaluation for sustainable development capacity of resource-based region]. Zhongguo renkou·ziyuan yu huanjing, 27(07), 72–79.
Guo, Y. J., Mi, W. B., & Zhao, Y. (2015). Ningxia xianyu lvse fazhan shuiping kongjian fenyi ji yingxiang yinsu [Spatial variation and relevant influence factors of green development levels among the counties in ningxia]. Jingji dili, 35(03), 10, 47–53.
He, T. X., Miao, F., & Wei, X. (2011). Chengshi shengtai wenming zonghe pingjia zhibiao tixi de goujian [Construction of indictors system for evaluation of urban ecological civilization]. Jingji dili, 31(11), 121, 139–142.
He, J. L., Ma, Z. H., & Zhu, X. A. (2012). Qinba shanqu tuigeng huanlin shengtai xiaoyi waixian yu jingji xiaoyi neiyin zhuangkuang diaocha [Ecological and economic benefits of grain-to-green program in Qin-Ba mountainous area]. Shuitu baochi tongbao, 32(04), 257–260, 266.
Hu, A. G., & Zhou, S. J. (2014). Lvse fazhan -gongneng jieding -jizhi fenxi yu fazhan zhanlue [Green development: Functional definition, mechanism analysis and development strategy]. Zhongguo renkou • ziyuan yu huanjing, 24(01), 16–22.
Lai, Z. L., & Cha, X. C. (2007). Shannan qinba shanqu renkou chengzaili yanjiu [Study on population carrying capacity in Qin-Ba mountainous areas of southern Shanxi Province]. Ganhan qu ziyuan yu huanjing, 21(07), 8–11.
Li, L., & Chu, Z. S. (2015). Woguo quyu chanye lvse fazhan zhishu pingjia ji dongtai bijiao [Evaluation and dynamic comparison of regional industrial green development index in China]. Jingji wenti tansuo, 36(01), 68–75.
Li, S. B., & Su, B. T. (2012). Shengtai pinmin dui guojia shengtai baohu zhengce rentong du yanjiu—yi qinba shanqu wei li [Investigation on the recognition of the eco-poor to the national ecological protection policy—The qingling-mountain area for example]. Kexue jingji shehui, 30(01), 7–12, 17.
Liang, Z. X. (2002). Lishi shiqi qinba shanqu ziran huanjing de bianqian [The changes of the natural environment in the Qin-Ba mountains in historical period]. Zhongguo lishi dili luncong, 17(03), 40–48.
Liu, J. Y., Deng, Z. X., Liu, W. D., Li, Y. H., Kruk, R., Thompson, D., Wang, P., & Bai, X. M. (2013). Zhongguo xibu lvse fazhan gainian kuangjia [Conceptual framework of green development in western China]. Zhongguo renkou • ziyuan yu huanjing, 23(10), 3–9.
Liu, M. C., Su, N., Lun, F., Cao, Y., Li, W. H., & Ming, Q. W. (2014). Quyu shengtai wenming jianshe shuiping zonghe pinggu zhibiao [An integrated indicator on regional ecological civilization construction]. Shengtai xuebao, 34(01), 103–110.
Liu, K., Du, W. X., Liu, G. C., & Zhang, Y. G. (2015). Dalian shi kechixu fazhan shuiping cedu [Dalian’s sustainable development level measurement]. Chengshi wenti, 04, 45–51.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. (2011). Zhongguo chengshi jianshe tongji nianjian [China urban construction statistical yearbook]. Beijing: zhongguo tongji chubanshe.
National Bureau of Statistics of People’s Republic of China. (2011). Zhongguo tongji nianjian [China statistical yearbook]. Beijing: zhongguo tongji chubanshe.
Ren, Z. Y., & Li, J. (2004). Qinba shanqu zhibei guding CO2 shifang O2 shengtai jiazhi ceping [The values of CO2 fixation and O2 release by vegetation ecosystem in Qinling-Daba Mountains of Shaanxi Province]. Dili yanjiu, 23(06), 53–59.
School of Economics and Management & Beijing Normal University, Southwestern University of Finance and Economics Development Institute, et al. (2010). 2010 nian zhongguo lvse fazhan zhishu baogao—quyu bijiao [China green development index report—Regional comparison]. Beijing: kexue chubanshe.
The State Council Leading Group of Poverty Alleviation and Development. (2012). Qinba shan pianqu quyu fazhan yu fupin gongjian guihua [QBMA development and poverty alleviation plan]. Beijing: guojia fazhan yu gaige weiyuanhui.
Wang, Y. (2010). Shishi lvse fazhan zhuanbian jingji fazhan fangshi [Transforming economic development pattern through implementing green development]. Zhongguo kexueyuan yuankan, 25(02), 5–10.
Wang, B., & Huang, R. J. (2014). Zhongguo quyu lvse fazhan xiaolv yu lvse quanyaosu shengchan lv :2000–2010—jiyu canshu gongtong bianjie de shizheng yanjiu [Regional green development efficiency and green total productivity growth in China: 2000–2010—Base on parametric metafrontier analysis]. Chan jing pinglun, 5(01), 16–35.
Wang, F., & Xie, J. (2015). Zhongguo fensheng lvse quanyaosu shengchan lv zengzhang lv yanjiu [Research on provincial green total factor productivity growth rate in China]. Zhongguo renkou kexue, 35(02), 53–62+127.
Wang, C., Liu, S. L., Dong, S. K., Deng, L., Li, J. P., Yang, Y. J., & Yang, H. J. (2011). Liaoning sheng yingkou shengtai shi kechixu fazhan pingjia yanjiu [Index system and evaluation method of eco-city sustainable development of Yingkou City in Liaoning Province, China]. Zhongguo renkou • ziyuan yu huanjing, 21(S2), 82–86.
Wu, Q., Wang, R. S., Li, H. Q., & Xu, X. B. (2005). Shengtai chengshi zhibiao tixi yu pingjia fangfa [The indices and the evaluation method of eco-city]. Shengtai xuebao, 35(08), 2090–2095.
Yue, S. J., Zou, Y. L., & Hu, Y. Y. (2015). Chanye jiju dui zhongguo chengshi lvse fazhan xiaolv de yingxiang [The combined effects of industrial agglomeration on the efficiency of urban green development]. Chengshi wenti, 243(10), 51–56.
Zhang, H., Luo, C., Cheng, J. H., & Wang, H. T. (2016a). Hubei sheng lvse fazhan shuiping cedu ji qi kongjian guanxi [The level of green development and its spatial relationship in Hubei Province]. Jingji dili, 36(09), 158–165.
Zhang, L. L., Zheng, X. Q., Yuan, Z. Y., & Cui, H. N. (2016b). Jiyu quan pailie duobianxing zonghe tushi fa de tangshan shi tudi liyong duogongneng xing pingjia [Assessment on multi-functionality of land use based on the entire-array-polygon indictor method in Tangshan]. Zhongguo tudi kexue, 30(06), 23–32.
Zhao, J. Z. (2013). Guanyu shengtai wenming jianshe yu pingjia de lilun sikao [Theoretical considerations on ecological civilization development and assessment]. Shengtai xuebao, 33(15), 35–38.
Zhao, J. Z., Liang, X. Y., & Zhang, X. Y. (1999). Kechixu fazhan gainian de xitong fenxi [System analysis on the definition of sustainable development]. Shengtai xuebao, 23(10), 3–9.
Zhen, L., Du, B. Z., Liu, J. Y., Sun, D. C., & Zhang, Q. (2013). Guoji jingyan dui zhongguo xibu di qu lv se fa zhan de qi shi: zheng ce ji shi jian the international experience of green development and implications to western China: An overall review of policy and practice. Zhongguo renkou • ziyuan yu huanjing, 23(10), 10–18.
Zheng, H. N. (2013). Zhongguo lvse fazhan xitong moxing goujian yu pingjia yanjiu [Study on the construction and evaluation of china’s green development system model]. Dalian: Dalian ligong daxue.
Zhou, Z. X., Ren, Z. Y., & Li, J. S. (2006). Qinba shanqu zhibei turang baochi shengtai jiazhi yanjiu [Study on the ecological value of soil conservation of vegetation in the qinling-daba mountains]. Ganhan qu yanjiu, 23(01), 146–150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Si, L. (2020). Evaluating Green Development Index in Ecologically Fragile Areas of China. In: Huang, Y. (eds) Chinese Cities in the 21st Century. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34780-2_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34780-2_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-34779-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-34780-2
eBook Packages: Social SciencesSocial Sciences (R0)