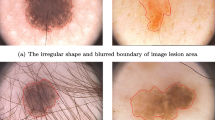
Abstract
Automatic segmentation of skin lesion in dermatoscope images is important for clinic diagnosis and assessment of melanoma. However, due to the large variations of scale, shape and appearance of the lesion area, accurate and automatic segmentation of skin lesion is faced with great challenges. In this paper, we first introduce the pyramid attention module for global multi-scale features aggregation. The module selectively integrates different multi-scale features associated with lesion by optimizing the features of each scale and suppressing the irrelevant noise. Based on this module, we propose an automatic framework for skin lesion segmentation. In addition, the widely used loss function based on dice coefficient is independent of the relative size of the segmented target, which leads to the insufficient attention of the network to small-scale samples. Therefore, we propose a new loss function based on scale-attention to effectively balance the weight of attention of the network to samples with different scales and improve the segmentation accuracy of small-scale samples. The robustness of the proposed method was evaluated on two public databases: ISIC 2017 and 2018 for skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection challenge and it could prove that the proposed method could considerably improve the performance of skin lesion segmentation and achieve the state-of-the-art results on ISIC 2017.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kardynal, A., Olszewska, M.: Modern non-invasive diagnostic techniques in the detection of early cutaneous melanoma. J. Dermatol. Case Rep. 8(1), 1–8 (2014)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Wang, H., Gu, R., Li, Z.: Automated segmentation of intervertebral disc using fully dilated separable deep neural networks. In: CSI, pp. 66–76 (2018)
Sarker, M.M.K., et al.: SLSDeep: skin lesion segmentation based on dilated residual and pyramid pooling networks. In: Frangi, A., Schnabel, J., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11071, pp. 21–29. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00934-2_3
Mirikharaji, Z., Hamarneh, G.: Star shape prior in fully convolutional networks for skin lesion segmentation. In: Frangi, A., Schnabel, J., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11073, pp. 737–745. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00937-3_84
Farabet, C., Couprie, C., Najman, L., LeCun, Y.: Learning hierarchical features for scene labeling. IEEE Trans. PAMI 35(8), 1915–1929 (2013)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: CVPR, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Milletari, F., Navab, N., Ahmadi, S.A.: V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 3DV, pp. 565–571 (2016)
Wu, Y., He, K.: Group normalization. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11217, pp. 3–19. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_1
Roy, A.G., Navab, N., Wachinger, C.: Concurrent spatial and channel ‘squeeze & excitation’ in fully convolutional networks. In: Frangi, A., Schnabel, J., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2018. LNCS, vol. 11070, pp. 421–429. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00928-1_48
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Yuan, Y.: Automatic skin lesion segmentation with fully convolutional-deconvolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.08494 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, H., Wang, G., Sheng, Z., Zhang, S. (2019). Automated Segmentation of Skin Lesion Based on Pyramid Attention Network. In: Suk, HI., Liu, M., Yan, P., Lian, C. (eds) Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. MLMI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11861. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32692-0_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32692-0_50
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-32691-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-32692-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)