Abstract
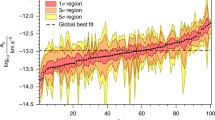
We describe a self-interacting dark matter (SIDM) model that can explain the diverse rotation curves of spiral galaxies while maintaining the success of the cold dark matter model on large scales. The explanation is economical in that it only requires one parameter, the self-interaction cross section, which is common to all galaxies. The existence of this solution is demonstrated through fits to a diverse set of 135 rotation curves from the SPARC sample. Despite the apparent diversity, the model exhibits a tight correlation between the accelerations due to the dark and luminous matter. The inferred stellar mass-to-light ratios, halo masses, and halo concentrations are consistent with independent expectations from astrophysics and cosmology.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Feng, M. Kaplinghat, H. Tu, H.B. Yu, JCAP 0907, 004 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1475-7516/2009/07/004
M.R. Buckley, P.J. Fox, Phys. Rev. D 81, 083522 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.81.083522
A. Loeb, N. Weiner, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 171302 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.171302
A.H.G. Peter, M. Rocha, J.S. Bullock, M. Kaplinghat, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 430, 105 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/sts535
J. Zavala, M. Vogelsberger, M.G. Walker, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. Lett. 431, L20 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnrasl/sls053
S. Tulin, H.B. Yu, K.M. Zurek, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(11), 111301 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.111301
K.A. Oman et al., Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 452(4), 3650 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stv1504
D.N. Spergel, P.J. Steinhardt, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 3760 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.3760
C. Firmani, E. D’Onghia, V. Avila-Reese, G. Chincarini, X. Hernandez, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 315, L29 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-8711.2000.03555.x
M. Vogelsberger, J. Zavala, A. Loeb, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 423, 3740 (2012)
M. Rocha, A.H.G. Peter, J.S. Bullock, M. Kaplinghat, S. Garrison-Kimmel, J. Onorbe, L.A. Moustakas, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 430, 81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/sts514
S. Tulin, H.B. Yu, Phys. Rep. 730, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2017.11.004
O.D. Elbert, J.S. Bullock, S. Garrison-Kimmel, M. Rocha, J. Oñorbe, A.H.G. Peter, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc.453(1), 29 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stv1470
M. Kaplinghat, R.E. Keeley, T. Linden, H.B. Yu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 021302 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.021302
M. Kaplinghat, S. Tulin, H.B. Yu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 116(4), 041302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.041302
A. Kamada, M. Kaplinghat, A.B. Pace, H.B. Yu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 119(11), 111102 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.111102
F. Lelli, S.S. McGaugh, J.M. Schombert, Astron. J. 152, 157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3847/0004-6256/152/6/157
S. McGaugh, F. Lelli, J. Schombert, Phys. Rev. Lett. 117(20), 201101 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.201101
A.A. Dutton, A.V. Maccio, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 441(4), 3359 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stu742
F. Governato, A. Zolotov, A. Pontzen, C. Christensen, S.H. Oh, A.M. Brooks, T. Quinn, S. Shen, J. Wadsley, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 422, 1231 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.20696.x
F.C. van den Bosch, J.J. Dalcanton, Astrophys. J. 534, 146 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1086/308750
M. Kaplinghat, M.S. Turner, Astrophys. J. 569, L19 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1086/340578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kaplinghat, M. (2019). Why I Think That Dark Matter Has Large Self-interactions. In: Essig, R., Feng, J., Zurek, K. (eds) Illuminating Dark Matter. Astrophysics and Space Science Proceedings, vol 56. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31593-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31593-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-31592-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-31593-1
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)