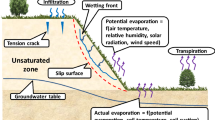
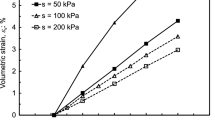
Abstract
Fundamental challenges in unsaturated soil mechanics have been identified in four major areas: quantifying internal stress state, developing a new paradigm for soil classification, developing new computational and theoretical constructs for unsaturated soil behavior, and tackling emerging problems in geotechnical engineering practice from the perspective of unsaturated soil mechanics. This chapter addresses each of these needs by critically reviewing some of the history in each area and summarizing recent research advances as current understanding of unsaturated soil behavior continues to evolve.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agus, S.S., Schanz, T., Fredlund, D.G.: Measurements of suction versus water content for bentonite–sand mixtures. Can. Geotech. J. 47(5), 583–594 (2010)
Akin, I.D., Likos, W.J.: Specific surface area of clay using water vapor and EGME sorption methods. Geotech. Test. J. 37(6), 1–12 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20140064
Akin, I.D., Likos, W.J.: Water vapor sorption of polymer-modified bentonites. Geo-Chicago 2016, 508–517 (2016)
Allen, M.P., Tildesley, D.J.: Computer simulation of liquids. Oxford University Press (1989)
Alonso, E.E., Gens, A., Josa, A.: A constitutive model for partially saturated soils. Geotechnique 40(3), 405–430 (1990)
Amarasinghe, P.M., Anandarajah, A.: Influence of fabric variable s on clay–water–air capillary meniscus. Can. Geotech. J. 48(7), 987–995 (2011)
Amarasinghe, P.M., Anandarajah, A., Ghosh, P.: Molecular dynamic study of capillary forces on clay particles. Appl. Clay Sci. 88, 170–177 (2014)
Anandarajah, A., Amarasinghe, P.M.: Microstructural investigation of soil suction and hysteresis of fine-grained soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 138(1), 38–46 (2011)
Anderson, D.M., Tice, A.R.: Predicting unfrozen water contents in frozen soils from surface area measurements. Highway Research Record 393, (1972)
Andrade, J.E., Borja, R.I.: Modeling deformation banding in dense and loose fluid-saturated sands. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 43(5), 361–383 (2007)
Baker, R., Frydman, S.: Unsaturated soil mechanics: critical review of physical foundations. Eng. Geol. 106(1), 26–39 (2009)
Berendsen, H., Grigera, J., Straatsma, T.: The missing term in effective pair potentials. J. Phys. Chem. 91(24), 6269–6271 (1987)
Berend, et al.: Mechanism of adsorption and desorption of water vapor by homoionic montmorillonites. Clays Clay Miner. 43(3), 324–336 (1995)
Bishop, A.W.: The principle of effective stress. Teknisk ukeblad 106(39), 859–863 (1959)
Borja, R.I.: Bifurcation of elastoplastic solids to shear band mode at finite strain. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 191(46), 5287–5314 (2002)
Borja, R.I.: Cam-clay plasticity. Part V: a mathematical framework for three-phase deformation and strain localization analyses of partially saturated porous media. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193(48), 5301–5338 (2004)
Borja, R.I., Song, X., Rechenmacher, A.L., Abedi, S., Wu, W.: Shear band in sand with spatially varying density. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 61(1), 219–234 (2013)
Borja, R.I., Song, X., Wu, W.: Critical state plasticity. part vii: triggering a shear band in variably saturated porous media. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 261, 66–82 (2013)
Borja, R., Song, X.: Strain localization in porous materials with spatially varying density and degree of saturation. Comput. Methods Recent Adv. Geomech. p. 13 (2014)
Briaud, J.-L., Chen, H.-C., Govindasamy, A., Storesund, R.: Levee erosion by overtopping in New Orleans during the Katrina Hurricane. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 134(5), 618–632 (2008)
Brooks, B.R., Bruccoleri, R.E., Olafson, B.D., States, D.J., Swaminathan, S.A., Karplus, M.: CHARMm: a program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 4(2), 187–217 (1983)
Burns, S.E., Culligan, P.J., Lu, N., Santamarina, J.C., Wayllace, A.: NSF workshop on geotechnical fundamentals. Geo-Strata Geo Inst. ASCE 21(2), 62–63 (2017)
Callari, C., Armero, F., Abati, A.: Strong discontinuities in partially saturated poroplastic solids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(23), 1513–1535 (2010)
Carrier, B., Vandamme, M., Pellenq, R.J.-M., Van Damme, H.: Elastic properties of swelling clay particles at finite temperature upon hydration. J. Phys. Chem. C 118(17), 8933–8943 (2014)
Cases, J., Berend, I., Besson, G., Francois, M., Uriot, J., Thomas, F., Poirier, J.: Mechanism of adsorption and desorption of water vapor by homoionic montmorillonite. 1. The sodium-exchanged form, Langmuir 8(11), 2730–2739 (1992)
Cerato, A.B.: Influence of specific surface area on geotechnical characteristics of fine-grained soils, Unpublished M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Massachusetts (2001)
Cerato, A., Lutenegger, A.: Determination of surface area of fine-grained soils by the Ethylene Glycol Monoethyl Ether (EGME) method. Geotech. Test. J. 25(3) 315–321. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ11087J. ISSN: 0149-6115 (2002)
Cerato, A.B., Lutenegger, A.J.: Activity, relative activity and specific surface area of fine-grained soils. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, vol. 16, Balkema (2005)
Chen, F.H.: Foundations on expansive soils, vol. 12. Elsevier (1988)
Chen, S., Doolen, G.D.: Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30(1), 329–364 (1998)
Chen, Y.-H., Anderson, A.: Methodology for estimating embankment damage caused by flood overtopping. Transport. Res. Rec. 1151 (1987)
Chittoori, B., Puppala, A.J.: Quantitative estimation of clay mineralogy in fine-grained soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 137(11), 997–1008 (2011)
Chuoke, R., Van Meurs, P., van der Poel, C. et al.: The instability of slow, immiscible, viscous liquid-liquid displacements in permeable media (1959)
Churchman, G., Burke, C.: Properties of sub soils in relation to various measures of surface area and water content. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 42(3), 463–478 (1991)
Civan, F., Rai, C.S., Sondergeld, C.H., et al.: Determining shale permeability to gas by simultaneous analysis of various pressure tests. SPE J. 17(03), 717–726 (2012)
Clarkson, C., Bustin, R.: The effect of pore structure and gas pressure upon the transport properties of coal: a laboratory and modeling study. 1. isotherms and pore volume distributions. Fuel 78(11), 1333–1344 (1999)
Collis-George, N.: The hydration and dehydration of Na-montmorillonite (belle fourche). Eur. J. Soil Sci. 6(1), 99–110 (1955)
Cui, X., Bustin, A., Bustin, R.M.: Measurements of gas permeability and diffusivity of tight reservoir rocks: different approaches and their applications. Geofluids 9(3), 208–223 (2009)
Cygan, R.T., Liang, J.-J., Kalinichev, A.G.: Molecular models of hydroxide, oxyhydroxide, and clay phases and the development of a general force field. J. Phys. Chem. B 108(4), 1255–1266 (2004)
Dasog, G., Acton, D., Mermut, A., JONG, E.D.: Shrink-swell potential and cracking in clay soils of Saskatchewan. Can. J. Soil Sci. 68(2), 251–260 (1988)
De Borst, R., Sluys, L., Mühlhaus, H.-B., Pamin, J.: Fundamental issues in finite element analyses of localization of deformation. Eng. Comput. 10(2), 99–121 (1993)
Dong, Y., Lu, N.: Measurement of suction-stress characteristic curve under drying and wetting conditions. Geotech. Test. J. 40(1), (2017)
Dos Santos, M., DeCastro, E.: Soil erosion in roads. In: 6th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering 1, 116–118 (1965)
Ebrahimi, D., Pellenq, R.J.-M., Whittle, A.J.: Nanoscale elastic properties of montmorillonite upon water adsorption. Langmuir 28(49), 16855–16863 (2012)
Ehlers, W., Graf, T., Ammann, M.: Deformation and localization analysis of partially saturated soil. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193(27), 2885–2910 (2004)
Eliassi, M., Glass, R.J.: On the porous-continuum modeling of gravity-driven fingers in unsaturated materials: extension of standard theory with a hold-back-pile-up effect. Water Resour. Res. 38(11) (2002)
Farrar, D., Coleman, J.: The correlation of surface area with other properties of nineteen British clay soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 18(1), 118–124 (1967)
Finno, R.J., Harris, W.W., Mooney, M.A., Viggiani, G.: Strain localization and undrained steady state of sand. J. Geotech. Eng. 122(6), 462–473 (1996)
Fredlund, D.G., Morgenstern, N.R.: Stress state variables for unsaturated soils. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. 15(3), 313–321 (1977)
Fredlund, D.G., Rahardjo, H.: Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils. Wiley, New York (1993)
Garcia, M.: Sedimentation engineering: processes, measurements, modeling, and practice. American Society of Civil Engineers (2008)
Gessler, J.: Beginning and Ceasing of sediment motion, Chap. 7 River Mechanics. In: Shen, H.W. (ed.) Water Resources Publication, Littleton, Co. (1971)
Gray, W.G., Miller, C.T.: Introduction to the thermodynamically constrained averaging theory for porous medium systems. Springer (2014)
Held, R.J., Illangasekare, T.H.: Fingering of dense nonaqueous phase liquids in porous media: 1. experimental investigation. Water Resour. Res. 31(5), 1213–1222 (1995)
Hill, S., et al.: Channeling in packed columns. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1(6), 247–253 (1952)
Hillel, D.: Environmental soil physics: fundamentals, applications, and environmental considerations. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA (1998)
Hoehn, A., Scovazzo, P., Stodieck, L.S., Clawson, J., Kalinowski, W., Rakow, A., Simmons, D., Heyenga, A.G., Kliss, M.H.: Microgravity root zone hydration systems, Technical report, SAE Technical Paper (2000)
Holtz, W.G., Gibbs, H.J.: Engineering properties of expansive clays. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 121(1), 641–663 (1956)
Homsy, G.M.: Viscous fingering in porous media. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 19(1), 271–311 (1987)
Iwata, S., Tabuchi, T., Warkentin, B.P., et al.: Soil-water interactions—mechanisms and applications. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, NY (1988)
Jang, J., Santamarina, J.C.: Fines classification based on sensitivity to pore-fluid chemistry. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 142(4), 06015018 (2016)
Javadpour, F., Fisher, D., Unsworth, M. et al.: Nanoscale gas flow in shale gas sediments. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 46(10), (2007)
Johnson, L.D.: Evaluation of laboratory suction tests for prediction of heave in foundation soils, Department of Defense, Department of the Army, Corps of Engineers, Waterways Experiment Station, Soils and Pavements Laboratory (1977)
Jury, W.A., Wang, Z., Tuli, A.: A conceptual model of unstable flow in unsaturated soil during redistribution. Vadose Zone J. 2(1), 61–67 (2003)
Keren, R., Shainberg, I.: Water vapor isotherms and heat of immersion of Na/Ca-montmorillonite systems: I, homoionic clay. Clays Clay Miner. 23(3), 193–200 (1975)
Khalili, N., Geiser, F., Blight, G.: Effective stress in unsaturated soils: review with new evidence. Int. J. Geomech. 4(2), 115–126 (2004)
Khalili, N., Khabbaz, M.: A unique relationship of chi for the determination of the shear strength of unsaturated soils. Geotechnique 48(5), 681–687 (1998)
Khorshidi, M., Lu, N.: Intrinsic relation between soil water retention and cation exchange capacity. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 143(4), 04016119 (2016)
Knight, R., Chapman, A., Knoll, M.: Numerical modeling of microscopic fluid distribution in porous media. J. Appl. Phys. 68(3), 994–1001 (1990)
Kramer, H.: Sand mixtures and sand movement in fluvial models. ASCE Trans. 100 (1935)
Laird, D.A.: Influence of layer charge on swelling of smectites. Appl. Clay Sci. 34(1), 74–87 (2006)
Langbein, D., Grossbach, R., Heide, W.: Parabolic flight experiments on fluid surfaces and wetting. Appl. Microgravity Technol. 2, 198–211 (1990)
Lawson, W.D.: A survey of geotechnical practice for expansive soils in Texas. Unsaturated Soils 2006, 304–314 (2006)
Lazari, M., Sanavia, L., Schrefler, B.: Local and non-local elasto-viscoplasticity in strain localization analysis of multiphase geomaterials. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 39(14), 1570–1592 (2015)
Lebeau, M., Konrad, J.-M.: A new capillary and thin film flow model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 46(12) (2010)
Likos, W.J.: Measurement of crystalline swelling in expansive clay. Geotech. Test. J. 27(6), 540–546 (2004)
Likos, W.J.: Effective stress in unsaturated soil: accounting for surface tension and interfacial area. Vadose Zone J. 13(5) (2014)
Likos, W.J., Lu, N.: Water vapor sorption behavior of smectite-kaolinite mixtures. Clays Clay Miner. 50(5), 553–561 (2002)
Likos, W.J., Lu, N.: Automated humidity system for measuring total suction characteristics of clay. Geotech. Test. J. 26(2), 178–189 (2003)
Likos, W.J., Lu, N.: Pore-scale analysis of bulk volume change from crystalline interlayer swelling in Na+- and Ca2+-smectite. Clays Clay Miner. 54(4), 515–528 (2006)
Likos, W.J., Lu, N., Wenszel, W.: Performance of a dynamic dew point method for moisture isotherms of clays. Geotech. Test. J. 34(4), 373–382 (2011)
Likos, W.J., Wayllace, A.: Porosity evolution of free and confined bentonites during interlayer hydration. Clays Clay Miner. 58(3), 399–414 (2010)
Lin, B.: A comprehensive investigation on microscale properties and macroscopic behavior of natural expansive soils, Thesis, The University of Oklahoma (2012)
Lin, B., Cerato, A.B.: Prediction of expansive soil swelling based on four micro-scale properties. Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 71(1), 71–78 (2012)
Liu, S., Harpalani, S.: A new theoretical approach to model sorption-induced coal shrinkage or swelling. AAPG Bulletin 97(7), 1033–1049 (2013)
Liu, S., Harpalani, S.: Compressibility of sorptive porous media: Part I—background and theory. AAPG Bulletin 98(9), 1761–1772 (2014)
Liu, S., Harpalani, S.: Compressibility of sorptive porous media: Part II–experimental study on coal. AAPG Bulletin 98(9), 1773–1788 (2014)
Liu, W.K., Karpov, E.G., Park, H.S.: Nano Mechanics and Materials: Theory, Multiscale Methods and Applications. Wiley & Sons (2006)
Low, P.F.: The swelling of clay: I. montmorillonites. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44(4), 667–676 (1980)
Lu, N.: Generalized soil water retention equation for adsorption and capillarity. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 142(10), 04016051 (2016)
Lu, N., Dong, Y.: Correlation between soil-shrinkage curve and water-retention characteristics. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 143(9), 04017054 (2017)
Lu, N., Dong, Y.: Vapor condensation technique for measuring stress-strain relation of unsaturated soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 143(6), 02817002 (2017)
Lu, N., Godt, J.W., Wu, D.T.: A closed-form equation for effective stress in unsaturated soil. Water Resour. Res. 46(5) (2010)
Lu, N., Kaya, M.: A drying cake method for measuring suction-stress characteristic curve, soil–water-retention curve, and hydraulic conductivity function. Geotech. Test. J. 36(1), 1–19 (2013)
Lu, N., Kaya, M., Godt, J.W.: Interrelations among the soil-water retention, hydraulic conductivity, and suction-stress characteristic curves. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 140(5), 04014007 (2014)
Lu, N., Khorshidi, M.: Mechanisms for soil-water retention and hysteresis at high suction range. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 141(8), 04015032 (2015)
Lu, N., Kim, T.-H., Sture, S., Likos, W.J.: Tensile strength of unsaturated sand. J. Eng. Mech. 135(12), 1410–1419 (2009)
Lu, N., Likos, W.J.: Unsaturated Soil Mechanics. Wiley (2004)
Lu, N., Likos, W.J.: Suction stress characteristic curve for un-saturated soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 132(2), 131–142 (2006)
Lu, N., Zeidman, B.D., Lusk, M.T., Willson, C.S., Wu, D.T.: A Monte Carlo paradigm for capillarity in porous media. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37(23) (2010)
McKeen, R.: A model for predicting expansive soil behavior: proceedings of the 7th international conference on expansive soils, Dallas, TX American Society of Civil Engineers Geotechnical Division, pp. 1–6 (1992)
McKeen, R.G., Nielsen, J.P.: Characterization of expansive soils for airport pavement design. Technical report, University of New Mexico, Eric H Wang Civil Engineering Research Facility (1978)
Merry, S.M., Kavazanjian Jr., E., Fritz, W.U.: Reconnaissance of the July 10, 2000, Payatas Landfill failure. J. Performance Constr. Facil. 19(2), 100–107 (2005)
Mitchell, J.: Fundamentals of Soil Behavior. Wiley and Sons Inc., New York (1993)
Mitchell, J.K., Soga, K., et al.: Fundamentals of Soil Behavior, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New Jersey (2005)
Monje, O., Stutte, G., Wang, H., Kelly, C.: Nds water pressures affect growth rate by changing leaf area, not single leaf photosynthesis, Technical report, SAE Technical Paper (2001)
Mooney, R., Keenan, A., Wood, L.: Adsorption of water vapor by montmorillonite. II. Effect of exchangeable ions and lattice swelling as measured by x-ray diffraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74(6) 1371–1374 (1952)
Morgenstern, N., Balasubramonian, B.: Effects of pore fluid on the swelling of clay-shale, pp. 190–205. Expansive Soils, ASCE (1980)
Muhunthan, B.: Liquid limit and surface area of clays. Chem. Clays Clay Min. 6, 237–274 (1991)
Nelson, J., Miller, D.J.: Expansive soils: problems and practice in foundation and pavement engineering. Wiley & Sons Inc., New Jersey (1997)
Newman, A.: The interaction of water with clay mineral surfaces. Chem. Clays Clay Min. 6, 237–274 (1987)
Nieber, J.L., Dautov, R.Z., Egorov, A.G., Sheshukov, A.Y., et al.: Dynamic capillary pressure mechanism for instability in gravity-driven flows; review and extension to very dry conditions. Transp. Porous Media 58(1–2), 147–172 (2005)
Nixon, J.: Discrete ice lens theory for frost heave in soils. Can. Geotech. J. 28(6), 843–859 (1991)
Norrish, K.: The swelling of montmorillonite. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 18, 120–134 (1954)
Or, D., Tuller, M.: Liquid retention and interfacial area in variably saturated porous media: upscaling from single-pore to sample-scale model. Water Resour. Res. 35(12), 3591–3605 (1999)
Peric, D., Zhao, G., Khalili, N.: Strain localization in unsaturated elastic-plastic materials subjected to plane strain compression. J. Eng. Mech. 140(7), 0401405 (2014)
Petersen, L.W., Moldrup, P., Jacobsen, O.H., Rolston, D.: Relations between specific surface area and soil physical and chemical properties. Soil Sci. 161(1), 9–21 (1996)
Pillalamarry, M., Harpalani, S., Liu, S.: Gas diffusion behavior of coal and its impact on production from coalbed methane reservoirs. Int. J. Coal Geol. 86(4), 342–348 (2011)
Reddi, L.N., Xiao, M., Steinberg, S.L.: Discontinuous pore fluid distribution under microgravity-kc-135 flight investigations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 69(3), 593–598 (2005)
Rethore, J., De Borst, R., Abellan, M.-A.: A two-scale model for fluid flow in an unsaturated porous medium with cohesive cracks. Comput. Mech. 42(2), 227–238 (2008)
Revil, A., Lu, N.: Unified water isotherms for clayey porous materials. Water Resour. Res. 49(9), 5685–5699 (2013)
Rexer, T.F., Benham, M.J., Aplin, A.C., Thomas, K.M.: Methane adsorption on shale under simulated geological temperature and pressure conditions. Energy Fuels 27(6), 3099–3109 (2013)
Rieke, R.D.: The role of specific surface area and related index properties in the frost susceptibility of soils. Thesis, Oregon State University (1982)
Romero, E., Simms, P.H.: Microstructure investigation in unsaturated soils: a review with special attention to contribution of mercury intrusion porosimetry and environmental scanning electron microscopy. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 26(6), 705–727 (2008)
Ross, G.: Relationships of specific surface area and clay content to shrink-swell potential of soils having different clay mineralogical compositions. Can. J. Soil Sci. 58(2), 159–166 (1978)
Rudnicki, J.W., Rice, J.: Conditions for the localization of deformation in pressure-sensitive dilatant materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 23(6), 371–394 (1975)
Saffman, P.G., Taylor, G.: The penetration of a fluid into a porous medium or hele-shaw cell containing a more viscous liquid. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, vol. 245, The Royal Society, pp. 312–329 (1958)
Santamarina, J.C., Klein, A., Fam, M.A.: Soils and waves: particulate materials behavior, characterization and process monitoring. J. Soils Sediments 1(2), 130 (2001)
Schiava, R., Etse, G.: Constitutive modeling and discontinuous bifurcation assessment in unsaturated soils. J. Appl. Mech. 73(6), 1039–1044 (2006)
Seed, H.B., Woodward, R.J., Lundgren, R.: Prediction of swelling potential for compacted clays. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 128(1), 1443–1477 (1962)
Shields, A.: Application of similarity principles and turbulence research to bed-load movement. California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA (1936). (translated from German)
Simons, D.B., Richardson, E.V.: Resistance to flow in alluvial channels. US Government Printing Office (1966)
Song, X.: Strain localization in unsaturated porous media, Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University (2014)
Song, X.: Transient bifurcation condition of partially saturated porous media at finite strain. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 41(1), 135–156 (2017)
Song, X.: A physical based multi-scale computational framework for triphasic geomaterials. In: White paper and presentation, NSF Workshop on Geotechnical Fundamentals in The Face of New World Challenges, National Science Foundation (2016)
Song, X., Borja, R.I.: Finite deformation and fluid flow in unsaturated soils with random heterogeneity. Vadose Zone J. 13(5), 1 (2014)
Song, X., Borja, R.I.: Mathematical framework for unsaturated flow in the finite deformation range. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 97(9), 658–682 (2014)
Song, X., Borja, R. I., Wu, W.: Triggering a shear band in variably saturated porous materials. In: Poromechanics V: Proceedings of the Fifth Biot Conference on Poromechanics, pp. 367–370 (2013)
Song, X., Idinger, G., Borja, R.I., Wu, W.: Finite element simulation of strain localization in unsaturated soils. Unsaturated Soils: Research and Applications, pp. 189–195 (2012)
Song, X., Wang, K., Ye, M.: Localized failure in unsaturated soils under non-isothermal conditions. Acta Geotechnica, pp. 1–13 (2017)
Song, X., Ye, M., Wang, K.: Strain localization in a solid-water-air system with random heterogeneity via stabilized mixed finite elements. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 112, 1926 (2017)
Song, X., Zhang, K., Wang, M.: Molecular dynamics modeling of a partially saturated clay-water system at finite temperature. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech., In submission (2017)
Sposito, G., et al.: The thermodynamics of soil solutions. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1981)
Stutte, G., Monje, O., Anderson, S.: Wheat (triticum aesativum l. cv. usu apogee) growth onboard the international space station (ISS): Germination and early development. Proc. Plant Growth Regul. Soc. Am. 30, 66–71 (2003)
Sudibandriyo, M., Pan, Z., Fitzgerald, J.E., Robinson, R.L., Gasem, K.A.: Adsorption of methane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and their binary mixtures on dry activated carbon at 318.2 K and pressures up to 13.6 MPa. Langmuir 19(13), 5323–5331 (2003)
Taylor, G.: The instability of liquid surfaces when accelerated in a direction perpendicular to their planes, I. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, vol. 201, The Royal Society, pp. 192–196 (1950)
Teich-McGoldrick, S.L., Greathouse, J.A., Cygan, R.T.: Molecular dynamics simulations of structural and mechanical properties of muscovite: Pressure and temperature effects. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(28), 15099–15107 (2012)
Thoman, R.W., Niezgoda, S.L.: Determining erodibility, critical shear stress, and allowable discharge estimates for cohesive channels: case study in the powder river basin of Wyoming. J. Hydraul. Eng. 134(12), 1677–1687 (2008)
Tison, L.: Studies of the critical tractive force of entrainment of bed materials. Proceedings: Minnesota International Hydraulics Conference, Minneapolis, MN (1953)
Tuller, M., Or, D., Dudley, L.M.: Adsorption and capillary condensation in porous media: Liquid retention and interfacial configurations in angular pores. Water Resour. Res. 35(7), 1949–1964 (1999)
Van Olphen, H.: Thermodynamics of interlayer adsorption of water in clays. J. Colloid Sci. 20(8), 822–837 (1965)
Van Olphen, H.: Clay colloid chemistry (reprinted edition) (1991)
Vanoni, V.A.: Sedimentation engineering, ASCE manuals and reports on engineering practice No. 54, American Society of Civil Engineers, New York, NY (1975)
Vardoulakis, I.: Deformation of water-saturated sand: II. Effect of pore water flow and shear banding. Geotechnique 46(3), 457–472 (1996)
Wang, S., Elsworth, D., Liu, J.: A mechanistic model for permeability evolution in fractured sorbing media. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 117(B6) (2012)
Wang, Y., Liu, S.: Estimation of pressure-dependent diffusive permeability of coal using methane diffusion coefficient: laboratory measurements and modeling. Energy Fuels 30(11), 8968–8976 (2016)
Wang, Z., Feyen, J., Elrick, D.E.: Prediction of fingering in porous media. Water Resour. Res. 34(9), 2183–2190 (1998)
Wang, Z., Tuli, A., Jury, W.A.: Unstable flow during redistribution in homogeneous soil. Vadose Zone J. 2(1), 52–60 (2003)
Weinan, E.: Principles of Multiscale Modeling. Cambridge University Press (2011)
White, C.: The equilibrium of grains on the bed of a stream. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, pp. 322–338 (1940)
Wynn, T.M., Mostaghimi, S., Alphin, E.F. et al.: The effects of vegetation on stream bank erosion. In: 2004 ASAE Annual Meeting, American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, p. 1 (2004)
Xiao, M., Reddi, L.N., Syeinberg, S.L.: Variation of water retention characteristics due to particle rearrangement under zero gravity. Int. J. Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)1532-3641. 9, 4(179) (2009)
Yong, R.: Soil suction and soil-water potentials in swelling clays in engineered clay barriers. Eng. Geol. 54(1), 3–13 (1999)
Zeidman, B.D., Lu, N., Wu, D.: Coarse-grained Monte Carlo simulation of the distribution and capillarity of multiple fluids in porous media, Pore Scale Phenomena: Frontiers in Energy and Environment. In: J. Poate, T. Illangasekare, H. Kazemi, and R. Kee (Eds.) (World Scientific, Singapore, 2015) pp. 263–278 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Likos, W.J., Song, X., Xiao, M., Cerato, A., Lu, N. (2019). Fundamental Challenges in Unsaturated Soil Mechanics. In: Lu, N., Mitchell, J. (eds) Geotechnical Fundamentals for Addressing New World Challenges. Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06249-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06249-1_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-06248-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-06249-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)