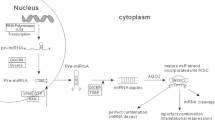
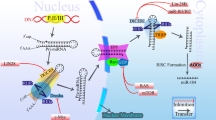
Abstract
Tumor initiation and progression have been widely investigated and ongoing work implicates microRNAs (miRNAs) as central players. miRNAs can control proliferation and differentiation as well as apoptosis, consistent with miRNAs functioning as oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Specific miRNAs have been shown to play roles in the overlapping fields of cancer stem cells and chemoresistance. In this review, we summarize existing data to elucidate the role of miRNAs in tumorigenesis and potential strategies using miRNAs for cancer therapy or as biomarkers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100(1):57–70.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–74.
Pantel K, Brakenhoff RH. Dissecting the metastatic cascade. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(6):448–56.
Perez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond LA, Rowinsky EK, Huberman M, Karp D, Rigas J, Clark GM, Santabarbara P, Bonomi P. Determinants of tumor response and survival with erlotinib in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(16):3238–47.
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414(6859):105–11.
Visvader JE. Cells of origin in cancer. Nature. 2011;469(7330):314–22.
Wu XZ. Origin of cancer stem cells: the role of self-renewal and differentiation. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(2):407–14.
Joseph NM, Mosher JT, Buchstaller J, Snider P, McKeever PE, Lim M, Conway SJ, Parada LF, Zhu Y, Morrison SJ. The loss of Nf1 transiently promotes self-renewal but not tumorigenesis by neural crest stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2008;13(2):129–40.
Fan H, Oro AE, Scott MP, Khavari PA. Induction of basal cell carcinoma features in transgenic human skin expressing Sonic Hedgehog. Nat Med. 1997;3(7):788–92.
Aster JC, Blacklow SC, Pear WS. Notch signalling in T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma and other haematological malignancies. J Pathol. 2011;223(2):262–73.
Hendler FJ, Ozanne BW. Human squamous cell lung cancers express increased epidermal growth factor receptors. J Clin Invest. 1984;74(2):647–51.
Segditsas S, Tomlinson I. Colorectal cancer and genetic alterations in the Wnt pathway. Oncogene. 2006;25(57):7531–7.
Leal JA, Lleonart ME. MicroRNAs and cancer stem cells: Therapeutic approaches and future perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2013;338(1):174–83.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5(7):522–31.
Bartel D. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Bushati N, Cohen SM. microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:175–205.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120(1):15–20.
Lee YS, Dutta A. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu RevPathol. 2009;4:199–227.
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero S, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Blanco D, Montuenga LM, Rossi S, Nicoloso MS, Faller WJ, Gallagher WM, Eccles SA, Croce CM, Esteller M. A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(36):13556–61.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW, Hannon GJ, Hammond SM. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature. 2005;435(7043):828–33.
Ota A, Tagawa H, Karnan S, Tsuzuki S, Karpas A, Kira S, Yoshida Y, Seto M. Identification and characterization of a novel gene, C13orf25, as a target for 13q31-q32 amplification in malignant lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64(9):3087–95.
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Kawahara K, Sekido Y, Takahashi T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005;65(21):9628–32.
Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, Chadburn A, Li Z, Gomez MF, Lund E, Dahlberg JE. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(10):3627–32.
Tam W, Ben-Yehuda D, Hayward WS. bic, a novel gene activated by proviral insertions in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas, is likely to function through its noncoding RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17(3):1490–1502.
Gironella M, Seux M, Xie MJ, Cano C, Tomasini R, Gommeaux J, Garcia S, Nowak J, Yeung ML, Jeang KT, Chaix A, Fazli L, Motoo Y, Wang Q, Rocchi P, Russo A, Gleave M, Dagorn JC, Iovanna JL, Carrier A, Pebusque MJ, Dusetti NJ. Tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 expression is repressed by miR-155, and its restoration inhibits pancreatic tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(41):16170–5.
Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH, He XH, Li Y, Gu H, Liu MF, Wang ED. MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res. 2010;70(8):3119–27.
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A, Zlotorynski E, Yabuta N, De Vita G, Nojima H, Looijenga LH, Agami R. A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 2006;124(6):1169–81.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. The age of high-throughput microRNA profiling. Nat Methods. 2004;1(2):106–7.
Dalmay T, Edwards DR. MicroRNAs and the hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene. 2006;25(46):6170–5.
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(14):6029–33.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(7):2257–61.
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26(19):2799–803.
Liu ZL, Wang H, Liu J, Wang ZX. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) expression promotes growth, metastasis, and chemo- or radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;372(1–2):35–45.
Weinstein IB. Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes–the Achilles heal of cancer. Science. 2002;297(5578):63–4.
Jain M, Arvanitis C, Chu K, Dewey W, Leonhardt E, Trinh M, Sundberg CD, Bishop JM, Felsher DW. Sustained loss of a neoplastic phenotype by brief inactivation of MYC. Science. 2002;297(5578):102–4.
Chin L, Tam A, Pomerantz J, Wong M, Holash J, Bardeesy N, Shen Q, O’Hagan R, Pantginis J, Zhou H, Horner JW 2nd, Cordon-Cardo C, Yancopoulos GD, DePinho RA. Essential role for oncogenic Ras in tumour maintenance. Nature. 1999;400(6743):468–72.
Medina PP, Nolde M, Slack FJ. OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 2010;467(7311):86–90.
Krichevsky AM, Gabriely G. miR-21: a small multi-faceted RNA. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(1):39–53.
Wang P, Zou F, Zhang X, Li H, Dulak A, Tomko RJ Jr., Lazo JS, Wang Z, Zhang L, Yu J. microRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69(20):8157–65.
Zhong Z, Dong Z, Yang L, Gong Z. miR-21 induces cell cycle at S phase and modulates cell proliferation by down-regulating hMSH2 in lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138(10):1781–88.
Reis ST, Pontes-Junior J, Antunes AA, Dall’Oglio MF, Dip N, Passerotti CC, Rossini GA, Morais DR, Nesrallah AJ, Piantino C, Srougi M, Leite KR. miR-21 may acts as an oncomir by targeting RECK, a matrix metalloproteinase regulator, in prostate cancer. BMC Urology. 2012;12:14.
Ciafre SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM, Farace MG. Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;334(4):1351–8.
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S, Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, Kloos RT, Croce CM, de la Chapelle A. The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(52):19075–80.
Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E, Massalini S, Frajese GV, Ciafre SA, Farace MG. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(32):23716–24.
Park JK, Kogure T, Nuovo GJ, Jiang J, He L, Kim JH, Phelps MA, Papenfuss TL, Croce CM, Patel T, Schmittgen TD. miR-221 silencing blocks hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes survival. Cancer Res. 2011;71(24):7608–16.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, Bullrich F, Croce CM. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(24):15524–9.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, Rassenti L, Alder H, Volinia S, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(39):13944–9.
Whiteside TL. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene. 2008;27(45):5904–12.
Musumeci M, Coppola V, Addario A, Patrizii M, Maugeri-Sacca M, Memeo L, Colarossi C, Francescangeli F, Biffoni M, Collura D, Giacobbe A, D’Urso L, Falchi M, Venneri MA, Muto G, De Maria R, Bonci D. Control of tumor and microenvironment cross-talk by miR-15a and miR-16 in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2011;30(41):4231–42.
Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A, Murmann AE, Peter ME. The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17(1):F19–36.
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D, Slack FJ. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell. 2005;120(5):635–47.
Roush S, Slack FJ. The let-7 family of microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18(10):505–16.
Mayr C, Hemann MT, Bartel DP. Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science. 2007;315(5818):1576–9.
Finlay CA, Hinds PW, Levine AJ. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989;57(7):1083–93.
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, Jackson AL, Linsley PS, Chen C, Lowe SW, Cleary MA, Hannon GJ. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature. 2007;447(7148):1130–4.
Di Vinci A, Infusini E, Peveri C, Risio M, Rossini FP, Giaretti W. Deletions at chromosome 1p by fluorescence in situ hybridization are an early event in human colorectal tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology. 1996;111(1):102–7.
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ. miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(36):13421–6.
Bosch-Presegue L, Vaquero A. The dual role of sirtuins in cancer. Genes Cancer. 2011;2(6):648–62.
El-Osta A. DNMT cooperativity–the developing links between methylation, chromatin structure and cancer. Bioessays. 2003;25(11):1071–84.
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z, Zanesi N, Callegari E, Liu S, Alder H, Costinean S, Fernandez-Cymering C, Volinia S, Guler G, Morrison CD, Chan KK, Marcucci G, Calin GA, Huebner K, Croce CM. MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(40):15805–10.
Zhang X, Zhao X, Fiskus W, Lin J, Lwin T, Rao R, Zhang Y, Chan JC, Fu K, Marquez VE, Chen-Kiang S, Moscinski LC, Seto E, Dalton WS, Wright KL, Sotomayor E, Bhalla K, Tao J. Coordinated silencing of MYC-mediated miR-29 by HDAC3 and EZH2 as a therapeutic target of histone modification in aggressive B-Cell lymphomas. Cancer Cell. 2012;22(4):506–23.
Wurdinger T, Tannous BA, Saydam O, Skog J, Grau S, Soutschek J, Weissleder R, Breakefield XO, Krichevsky AM. miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in angiogenic endothelial cells. Cancer Cell. 2008;14(5):382–93.
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh P, Muth D, Teruya-Feldstein J, Reinhardt F, Onder TT, Valastyan S, Westermann F, Speleman F, Vandesompele J, Weinberg RA. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(3):247–56.
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(6):1420–8.
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y, Goodall GJ. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(5):593–601.
Tavazoie SF, Alarcon C, Oskarsson T, Padua D, Wang Q, Bos PD, Gerald WL, Massague J. Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2008;451(7175):147–52.
Png KJ, Halberg N, Yoshida M, Tavazoie SF. A microRNA regulon that mediates endothelial recruitment and metastasis by cancer cells. Nature. 2012;481(7380):190–4.
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324(5930):1029–33.
Gao P, Tchernyshyov I, Chang TC, Lee YS, Kita K, Ochi T, Zeller KI, De Marzo AM, Van Eyk JE, Mendell JT, Dang CV. c-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature. 2009;458(7239):762–5.
Rao X, Di Leva G, Li M, Fang F, Devlin C, Hartman-Frey C, Burow ME, Ivan M, Croce CM, Nephew KP. MicroRNA-221/222 confers breast cancer fulvestrant resistance by regulating multiple signaling pathways. Oncogene. 2011;30(9):1082–97.
Polyak K. Heterogeneity in breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(10):3786–8.
Miller TW, Balko JM, Arteaga CL. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(33):4452–61.
Higgins MJ, Baselga J. Targeted therapies for breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(10):3797–803.
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong C, Huang Y, Hu X, Su F, Lieberman J, Song E. let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell. 2007;131(6):1109–23.
Dontu G, Al-Hajj M, Abdallah WM, Clarke MF, Wicha MS. Stem cells in normal breast development and breast cancer. Cell Prolif. 2003;36(Suppl 1):59–72.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(11):857–66.
Bader AG, Brown D, Stoudemire J, Lammers P. Developing therapeutic microRNAs for cancer. Gene Ther. 2011;18(12):1121–6.
Mo MH, Chen L, Fu Y, Wang W, Fu SW. Cell-free circulating miRNA biomarkers in cancer. J Cancer. 2012;3:432–48.
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, Pulford K, Banham AH, Pezzella F, Boultwood J, Wainscoat JS, Hatton CS, Harris AL. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Brit J Haematol. 2008;141(5):672–5.
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney KJ, Newell J, Kerin MJ. Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 2010;251(3):499–505.
Zhang HL, Yang LF, Zhu Y, Yao XD, Zhang SL, Dai B, Zhu YP, Shen YJ, Shi GH, Ye DW. Serum miRNA-21: elevated levels in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer and potential predictive factor for the efficacy of docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Prostate. 2011;71(3):326–31.
Lin SC, Liu CJ, Lin JA, Chiang WF, Hung PS, Chang KW. miR-24 up-regulation in oral carcinoma: positive association from clinical and in vitro analysis. Oral Oncol. 2010;46(3):204–8.
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W, Du X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(1):118–26.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(5):1046–54.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, Calin GA, Liu CG, Croce CM, Harris CC. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(3):189–98.
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK, Vessella RL, Tammela TL, Visakorpi T. MicroRNA expression profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67(13):6130–5.
Ji J, Shi J, Budhu A, Yu Z, Forgues M, Roessler S, Ambs S, Chen Y, Meltzer PS, Croce CM, Qin LX, Man K, Lo CM, Lee J, Ng IO, Fan J, Tang ZY, Sun HC, Wang XW. MicroRNA expression, survival, and response to interferon in liver cancer. New Engl J Med. 2009;361(15):1437–47.
Trang P, Medina PP, Wiggins JF, Ruffino L, Kelnar K, Omotola M, Homer R, Brown D, Bader AG, Weidhaas JB, Slack FJ. Regression of murine lung tumors by the let-7 microRNA. Oncogene. 2010;29(11):1580–7.
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang HW, Chang TC, Vivekanandan P, Torbenson M, Clark KR, Mendell JR, Mendell JT. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell. 2009;137(6):1005–17.
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Marcusson EG, Teruya-Feldstein J, Bell GW, Weinberg RA. Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(4):341–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Andrews, O., Patton, J. (2014). MicroRNAs in Cancer Progression. In: Singh, S., Rameshwar, P. (eds) MicroRNA in Development and in the Progression of Cancer. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-8065-6_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-8065-6_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4899-8064-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4899-8065-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)