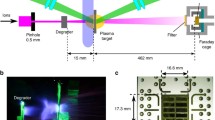
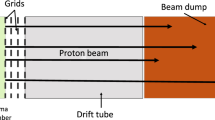
Abstract
Is the ion beam target interaction suitable for ICF targets? This paper answers this fundamental question affirmatively. However, because existing ion accelerators cannot produce fusion-intensity beams, the question is answered on the basis of theory and experiments with low-intensity beams. Therefore, the answer is tentative, and this paper emphasizes theoretical and experimental uncertainties and their effects on predictions of target performance. Conventional single-particle stopping theory, plasma instabilities, and preheat mechanisms are discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olson, C. L., in Proceedings of the Heavy Ion Fusion Workshop, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory/Stanford Linear Accelerator Center report LBL-10301/SLAC-PUB-2575, p. 403 (Sept. 1980).
R. O. Bangerter, J. W.-K. Mark, and A. R. Thiessen, Phys. Lett. 88A, 225 (1982).
R. O. Bangerter, J.W.-K. Mark, and D. J. Meeker, Los Alamos National Laboratory report LA-UR-81–2989 (1981).
D. J. Meeker and R. O. Bangerter, Proceedings of the 4th International Topical Conference on High-Power Electron and Ion-Beam Research and Technology, edited by H. J. Doucet and J. M. Ruzzi, Palaiseau France, June 29-July 3, 1981.
L. Spitzer, Jr., Physics of Fully Ionized Gasses, Chapter 5, Interscience Publishers, New York, (1962).
J. D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Chapter 13, John Wiley and Sons, New York (1975).
D. Mosher, Proceedings of the ERDA Summer Study of Heavy Ions for Inertial Fusion, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory report LBL-5543 (1976).
E. Nardi, E. Peleg and Z. Zinamon, Phys. Fluids 21, 574 (1978).
R. O. Bangerter, Proceedings of the Heavy Ion Fusion Workshop held at Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne National Laboratory Report ANL-79–41, p. 415 (1979).
T. A. Mehlhorn, Journal of Applied Physics 52, 6522 (1981).
Informal Workshop on the Penetration of Charged Particles in Matter Under Extreme Conditions, New York University, Jan. 3–5, 1980, New York University Department of Physics report, Stanley Stern Editor.
K. A. Brueckner, L. Senbetu, N. Metzler, Phys. Rev. B25, 4377 (1982).
F. Bloch, Zeitschrift fuer Physik 81, 363 (1933).
M. D. Brown and C. D. Moak, Phys. Rev. B6, 90 (1972).
D. Bailey, Y. T. Lee, and R. M. More, in Proceedings of the Symposium on Accelerator Aspects of Heavy Ion Fusion, held at Darmstadt, Germany, (March 29-April 2, 1982) Gesellschaft fuer Schwerionenforschung report 82–8.
E. Nardi and Z. Zinamon, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 1251 (1982).
R. M. More and D. Bailey, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Report 84991, p. 200 (1981).
G. Tarlè and M. Solarz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 41, 483 (1978).
H. Geissel, Y. Laichter, W. Schneider, and P. Armbruster, Gesellschaft fuer Schwerionenforschung report 82–2 (Feb. 1982).
L. C. Northcliffe and R. F. Schilling, Nucl. Data A7, 233 (1970).
F. C. Young, D. Mosher, S. J. Stephanakis, Shyke A. Goldstein, and T. A. Mehlhorn, Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 549 (1982).
J. A. Swegle, Comments on Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion 7, 141 (1982) and private communication.
P. F. Ottinger, D. Mosher, and Shyke A. Goldstein, Phys. Fluids 22, 332 (1979).
N. A. Krall and A. W. Trivelpiece, Principles of Plasma Physics, Chapter 9, McGraw-Hill (1973).
Edward P. Lee, Simon Yu, H. L. Buchanan, F. W. Chambers, and Marshall N. Rosenbluth, Phys. Fluids 23, 2095 (1980).
P. F. Ottinger, D. Mosher, and Shyke A. Goldstein, Phys. Fluids 24, 164 (1981).
R. O. Bangerter, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Report UCRL-50021–79, Laser Program Annual Report, p. 3–10 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1984 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bangerter, R.O. (1984). Ion Beam Interactions with ICF Targets. In: Hora, H., Miley, G.H. (eds) Laser Interaction and Related Plasma Phenomena. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7332-6_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7332-6_61
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4615-7334-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-7332-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive