Abstract
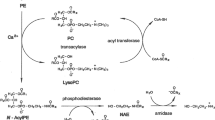
Fatty acid primary amides are potent, bioactive molecules. Oleamide induces physiological sleep1,2, potentiates the action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on rat brain 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors3, and blocks gap junction communication in glial cells4. Erucamide stimulates angiogenesis5, arachidonamide is a tight-binding inhibitor of human synovial phospholipase A2 6, and valpromide (n-propylpentanamide) is used clinically as an antiepileptic7. These studies indicate that the fatty acid primary amides are an exciting new class of mammalian, bioactive lipid. The biosynthetic pathway leading to the formation of the fatty acid primary amides is not understood and is information critical to the understanding and control of diseases related to their production.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.A. Lerner, G. Siuzdak, O. Prospero-Garcia, S.J. Hendriksen, D.L. Boger, and B.F. Cravatt, Cerebrodiene: a brain lipid isolated from sleep-deprived cats, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sei USA 91:9505 (1994).
B.F. Cravatt, O. Prospero-Garcia, G. Siuzdak, N.B. Gilula, S.J. Henriksen, D.L. Boger, and R.A. Lerner, Chemical characterization of a family of brain lipids that induce sleep, Science 268:1506 (1995).
J.F. Hiudobro-Toro and R.A. Harris, Brain lipids that induce sleep are novel modulators of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 8078 (1996).
X. Guan, B.F. Cravatt, G.R. Ehring, J.E. Hall, D.L. Boger, R.A. Lerner, and N.B. Gilula, The sleep-inducing lipid oleamide deconvolutes gap junction communication and calcium wave transmission in glial ells, J. Cell Biol. 139:1785 (1997).
K. Wakamatsu, T. Masaki, F. Itoh, K. Kondo, and K. Sudo, Isolation of fatty acid amide as an angiogenic principle from bovine mesentery, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168:423 (1990).
M.K. Jain, F. Ghomashchi, B.-Z. Yu, T. Bayburt, D. Murphy, D. Houck, J. Brownell, J.C. Reid, J.E. Solowiej, S.-M. Wong, U. Mocek, R. Jarrell, M. Sasser, and M.H. Gelb, Fatty acid amides: scooting mode-based discovery of tight-binding inhibitors of secreted phospholipase A2, J. Med. Chem. 35:3584 (1992).
M. Bialer, Clinical pharmacology of valpromide, Clin. Pharmacokin. 20:114 (1991).
R.E. Mains, B.A. Eipper, C.C. Glembotski, and R.M. Dores, Strategies for the biosynthesis of bioactive peptides, Trends Neurosci. 6:229 (1983).
S.P. Smeekens, S.J. Chan, and D.F. Steiner, The biosynthesis and processing of neuroendocrine peptides, Prog. Brain Res. 92:235 (1992).
A.F. Bradbury, M.D.A. Finnie, and D.G. Smyth, Mechanism of C-terminal amide formation by pituitary enzymes, Nature 298:686 (1982).
B.A. Eipper, R.E. Mains, and C.C. Glembotski, Identification in pituitary tissue of a peptide α-amidation activity that acts on glycine-extended peptides and requires molecular oxygen, copper, and ascorbic acid, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:5144 (1983).
D.J. Merkler, K.A. Merkler, W. Stern, and F.F. Fleming, Fatty acid amide biosynthesis: a possible new role for peptidylglycine α-amidating enzyme and acyl-coenzyme A:glycine N-acyltransferase, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 330:430 (1996).
D. Schachter, and J.V. Taggart, Glycine N-acylase: purification and properities, J. Biol. Chem. 208:263 (1954).
N. Gregersen, S. KØlvraa, and P.B. Mortensen, Acyl-CoA:glycine N-acyltransferase: in vitro studies on the glycine conjugations of straight-and branched-chain acyl-CoA esters in human liver, Biochem. Med. Metabol. Biol. 35:210 (1986).
K. Asaoka, Enzymes that metabolize acyl-coenzyme A in the monkey — their distribution, properties, and roles in an alternative pathway for the excretion of nitrogen, Int. J. Biochem. 23:429 (1991).
G.S. Wand, R.L. Ney, S. Baylin, B. Eipper, and R.E. Mains, Characterization of a peptide α-amidation activity in human plasma and tissues, Metabolism 34:1044 (1985).
C. de Sousa, R.A. Chalmers, T.E. Stacey, B.M. Tracey, C.M. Weaver, and D. Bradley, The response to L-carnitine and glycine therapy in isovaleric acidaemia, Eur. J. Pediatr. 144:451 (1986).
Z. Gregus, T. Fekete, F. Varga, and C.D. Klaassen, Availability of glycine and coenzyme A limits glycine conjugation in vivo, Drug Metab. Dispos. 20:234 (1992).
A.H. Bertelsen, G.A. Beaudry, E.A. Galella, B.N. Jones, M.L. Ray, and N.M. Mehta, Cloning and characterization of two alternatively spliced rat α-amidating cDNAs from rat medullary thyroid carcinoma, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 279:87 (1990).
D.A. Miller, K.U. Sayad, R. Kulathila, G.A. Beaudry, DJ. Merkler, and A.H. Bertelsen, Characterization of a bifunctional peptidylglycine α-amidating enzyme expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 298:380 (1992).
B.N. Jones, P.P. Tamburini, A.P. Consalvo, S.D. Young, S.J. Lovato, J.P. Gilligan, A.Y. Jeng, and L.P. Wennogle, A fluorometric assay for peptidyl α-amidation activity using high-performance liquid chromatography, Anal. Biochem. 168:272 (1988).
A.G. Katopodis, and S.W. May, Novel substrates and inhibitors of peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase, Biochemistry 29:4541 (1990).
S.D. Young and P.P. Tamburini, Enzymatic peptidyl α-amidation proceeds through formation of an α-hydroxyglycine intermediate, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111:1933 (1989).
A.G. Katopodis, D. Ping, and S.W. May, A novel enzyme from bovine neurointermediate pituitary catalyzes dealkylation of α-hydroxyglycine derivatives, thereby functioning sequentially with peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase in peptide amidation, Biochemistry 29:6115 (1990).
P.T. Ozand and G.G. Gascon, Organic acidurias: a review, J. Child Neurol. 6:288 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Merkler, K.A. et al. (1999). A Pathway for the Biosynthesis of Fatty Acid Amides. In: Honn, K.V., Marnett, L.J., Nigam, S., Dennis, E.A. (eds) Eicosanoids and Other Bioactive Lipids in Cancer, Inflammation, and Radiation Injury, 4. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 469. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4793-8_76
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4793-8_76
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-7171-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-4793-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive