Abstract
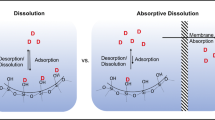
Ordered mesoporous silica (OMS) materials offer much promise as carriers for poorly soluble drugs because of their high porosity, large specific surface area, and uniform pore shape and dimensions. Liquid as well as solid type phases of drugs, confined and stabilized in the pores of OMS, can exhibit special physicochemical properties and enhanced dissolution rates compared to crystalline forms. The ability to design mesopore size precisely provides the formulation scientist with the potential to readily attain and closely control drug release. Absorption enhancement may require stable supersaturation of released drug. If this can be effected (viz. drug precipitation attenuated by suitable formulation adjuvants), systemic absorption can be enhanced. In vivo proof of concept of OMS as a dissolution-enhancing technology has been demonstrated in various animal species. The findings are promising and suggest that adsorption on OMS can successfully enhance and control absorption of poorly soluble drugs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2001) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46:3–26
Monkhouse DC, Lach JL (1972) Use of adsorbents in enhancement of drug dissolution. I. J Pharm Sci 61:1430–1435
Monkhouse DC, Lach JL (1972) Use of adsorbents in enhancement of drug dissolution. II. J Pharm Sci 61:1435–1441
Vallet-Regi M, Ramilla A, del Real RP, Perez-Pariente J (2001) A new property of MCM-41: drug delivery system. Chem Mater 13:308–311
Horcajada P, Rámila A, Pérez-Pariente J, Vallet-Regi M (2004) Influence of pore size of MCM-41 matrices on drug delivery rate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 68:105–109
Doadrio AL, Sousa EMB, Doadrio JC, Pérez Pariente J, Izquierdo-Barba I, Vallet-Regí M (2004) Mesoporous SBA-15 HPLC evaluation for controlled gentamicin drug delivery. J Control Release 97:125–132
Tozuka Y, Oguchi T, Yamamoto K (2003) Adsorption and entrapment of salicylamide molecules into the mesoporous structure of folded sheets mesoporous material (FSM-16). Pharm Res 20:926–930
Charnay C, Bégu S, Tourné-Péteilh C, Nicole L, Lerner DA, Devoisselle JM (2004) Inclusion of ibuprofen in mesoporous templated silica: drug loading and release property. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 57:533–540
Mellaerts R, Aerts CA, Van Humbeeck J, Augustijns P, Van den Mooter G, Martens JA (2007) Enhanced release of itraconazole from ordered mesoporous SBA-15 silica materials. Chem Commun 1375–1377
Mellaerts R, Mols R, Jammaer JAG, Aerts CA, Annaert P, Van Humbeeck J, Van den Mooter G, Augustijns P, Martens JA (2008) Increasing the oral bioavailability of the poorly water soluble drug itraconazole with ordered mesoporous silica. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 69:223–230
Leuner C, Dressman J (2000) Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:47–60
Serajuddin AT (1999) Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J Pharm Sci 88:1058–1066
Alcoutlabi M, McKenna GB (2005) Effects of confinement on material behaviour at the nanometer size scale. J Phys Condens Matter 17:461–524
Alba-Simionesco C, Coasne B, Dosseh G, Dudziak G, Gubbins K, Radhakrishnan R, Sliwinska-Bartkowiak M (2006) Effects of confinement on freezing and melting. J Phys Condens Matter 18:15–68
Kaneko K, Watanabe A, Iiyama T, Radhakrishan R, Gubbins KE (1999) A remarkable elevation of freezing temperature of CCl4 in graphitic micropores. J Phys Chem B 103:7061–7063
Sliwinska-Bartkowiak M, Dudziak G, Sikorski R, Gras R, Radhakrishnan R, Gubbins KE (2001) Melting/freezing behavior of a fluid confined in porous glasses and MCM-41: dielectric spectroscopy and molecular simulation. J Chem Phys 114:950–962
Sliwinska-Bartkowiak M, Dudziak G, Gras R, Sikorski R, Radhakrishnan R, Gubbins KE (2001) Freezing behavior in porous glasses and MCM-41. Colloids Surf A Physicochem 187–188:523–529
Azaïs T, Tourné-Péteilh C, Aussenac F, Baccile N, Coelho C, Devoiselle J, Babonneau F (2006) Solid-state NMR study of ibuprofen confined in MCM-41 material. Chem Mater 18:6382–6390
Mellaerts R, Houthoofd K, Elen K, Chen H, Van Speybroeck M, Van Humbeeck J, Augustijns P, Mullens J, Van den Mooter G, Martens JA (2010) Aging behavior of pharmaceutical formulations of itraconazole on SBA-15 ordered mesoporous silica carrier material. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 130:154–161
Van Speybroeck M, Barillaro V, Thi TD, Mellaerts R, Martens J, Van Humbeeck J, Vermant J, Annaert P, Van den Mooter G, Augustijns P (2009) Ordered mesoporous silica material SBA-15: a broad-spectrum formulation platform for poorly soluble drugs. J Pharm Sci 98:2648–2658
Janssens S, Van den Mooter G (2009) Review: physical chemistry of solid dispersions. J Pharm Pharmacol 61:1571–1586
Babonneau F, Yeung L, Steunou N, Gervais C, Ramila A, Vallet-Regi M (2004) Solid state NMR characterisation of encapsulated molecules in mesoporous silica. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 31:223
Van Speybroeck M, Mols R, Mellaerts R, Thi TD, Martens JA, Van Humbeeck J, Annaert P, Van den Mooter G, Augustijns P (2010) Enhanced absorption of the poorly soluble drug fenofibrate by tuning its release rate from ordered mesoporous silica. Eur J Pharm Sci 41(5):623–30
Andersson J, Rosenholm J, Areva S, Lindén M (2004) Influences of material characteristics on ibuprofen drug loading and release profiles from ordered micro- and mesoporous silica matrices. Chem Mater 16:4160–4167
Qu F, Zhu G, Huang S, Li S, Sun J, Zhang D, Qiu S (2006) Controlled release of Captopril by regulating the pore size and morphology of ordered mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 92:1–9
Grün M, Unger KK, Matsumoto A, Tsutsumi K (1999) Novel pathways for the preparation of mesoporous MCM-41 materials: control of porosity and morphology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 27:207–216
Kosuge K, Sato T, Kikukawa N, Takemori M (2004) Morphological control of rod- and fiberlike SBA-15 type mesoporous silica using water-soluble sodium silicate. Chem Mater 16:899–905
Brouwers J, Brewster ME, Augustijns P (2009) Supersaturating drug delivery systems: the answer to solubility-limited oral bioavailability? J Pharm Sci 98:2549–2572
Song S, Hidajat K, Kawi S (2005) Functionalized SBA-15 materials as carriers for controlled drug delivery: influence of surface properties on matrix-drug interactions. Langmuir 21:9568–9575
Rosenholm JM, Lindén M (2008) Towards establishing structure-activity relationships for mesoporous silica in drug delivery applications. J Control Release 128:157–164
Beck JS, Vartuli JC, Roth WJ, Leonowicz ME, Kresge CT, Schmitt KD, Chu CT, Olson DH, Sheppard EW, McCullen SB, Higgins JB, Schlenker JL (1992) A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J Am Chem Soc 114:10834–10843
Zhao D, Feng J, Huo Q, Melosh N, Fredrickson G, Chmelka B, Stucky G (1998) Triblock copolymer syntheses of mesoporous silica with periodic 50 to 300 angstrom pores. Science 279:548–552
Kresge CT, Leonowicz ME, Roth WJ, Vartuli JC, Beck JS (1992) Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 359:710–712
Galarneau A, Nader M, Guenneau F, DiRenzo F, Gedeon A (2007) Understanding the stability in water of mesoporous SBA-15 and MCM-41. J Phys Chem 111:8268–8277
Van Speybroeck M, Mols R, Mellaerts R, Thi TD, Martens JA, Humbeeck JV, Annaert P, Van den Mooter G, Augustijns P (2010) Combined use of ordered mesoporous silica and precipitation inhibitors for improved oral absorption of the poorly soluble weak base itraconazole. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 75:354–365
Heikkilä T, Salonen J, Tuura J, Kumar N, Salmi T, Murzin DY, Hamdy MS, Mul G, Laitinen L, Kaukonen AM, Hirvonen J, Lehto V (2007) Evaluation of mesoporous TCPSi, MCM-41, SBA-15, and TUD-1 materials as API carriers for oral drug delivery. Drug Deliv 14:337–347
Izquierdo-Barba I, Martinez A, Doadrio AL, Pérez-Pariente J, Vallet-Regí M (2005) Release evaluation of drugs from ordered three-dimensional silica structures. Eur J Pharm Sci 26:365–373
Heikkilä T, Salonen J, Tuura J, Hamdy MS, Mul G, Kumar N, Salmi T, Murzin DY, Laitinen L, Kaukonen AM, Hirvonen J, Lehto V (2007) Mesoporous silica material TUD-1 as a drug delivery system. Int J Pharm 331:133–138
Tozuka Y, Wongmekiat A, Kimura K, Moribe K, Yamamura S, Yamamoto K (2005) Effect of pore size of FSM-16 on the entrapment of flurbiprofen in mesoporous structures. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 53:974–977
Higuchi T (1963) Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J Pharm Sci 52:1145–1149
Korsmeyer RW, Gurny R, Doelker E, Buri P, Peppas NA (1983) Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm 15:25–35
Zurner A, Kirstein J, Doblinger M, Brauchle C, Bein T (2007) Visualizing single-molecule diffusion in mesoporous materials. Nature 450:705–708
Godec A, Gaberscek M, Jamnik J, Merzel F (2009) Nonlinear diffusion in two-dimensional ordered porous media based on a free volume theory. J Chem Phys 131:234106–234112
Mellaerts R, Mols R, Kayaert P, Annaert P, Van Humbeeck J, Van den Mooter G, Martens JA, Augustijns P (2008) Ordered mesoporous silica induces pH-independent supersaturation of the basic low solubility compound itraconazole resulting in enhanced transepithelial transport. Int J Pharm 357:169–179
Mellaerts R, Jammaer JAG, Van Speybroeck M, Chen H, Van Humbeeck J, Augustijns P, Van den Mooter G, Martens JA (2008) Physical state of poorly water soluble therapeutic molecules loaded into SBA-15 ordered mesoporous silica carriers: a case study with itraconazole and ibuprofen. Langmuir 24:8651–8659
Kinoshita M, Baba K, Nagayasu A, Yamabe K, Shimooka T, Takeichi Y, Azuma M, Houchi H, Minakuchi K (2002) Improvement of solubility and oral bioavailability of a poorly water-soluble drug, TAS-301, by its melt-adsorption on a porous calcium silicate. J Pharm Sci 91:362–370
Smirnova I, Mamic J, Arlt W (2003) Adsorption of drugs on silica aerogels. Langmuir 19:8521–8525
Konno T, Kinuno K (1989) Physical and chemical changes of medicinals in mixtures with adsorbents in the solid state. II. Application of reduced pressure treatment for the improvement of dissolution of flufenamic acid. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 37:2481–2484
Bahl D, Hudak J, Bogner RH (2008) Comparison of the ability of various pharmaceutical silicates to amorphize and enhance dissolution of indomethacin upon co-grinding. Pharm Dev Technol 13:255–269
Shen S, Ng WK, Chia L, Dong Y, Tan RBH (2010) Stabilized amorphous state of ibuprofen by co-spray drying with mesoporous SBA-15 to enhance dissolution properties. J Pharm Sci 99:1997–2007
Cassiers K, Linssen T, Mathieu M, Benjelloun M, Schrijnemakers K, Van Der Voort P, Cool P, Vansant EF (2002) A detailed study of thermal, hydrothermal, and mechanical stabilities of a wide range of surfactant assembled mesoporous silicas. Chem Mater 14:2317–2324
Hartmann M, Vinu A (2002) Mechanical stability and porosity analysis of large-pore SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieves by mercury porosimetry and organics adsorption. Langmuir 18:8010–8016
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Flemish Government for financial support from the Industrial Research Fund (IOF). MVS acknowledges the Flemish Institute for the Promotion of Innovation through Science and Technology (IWT-Vlaanderen) for a PhD grant. RM acknowledges the Research Fund-Flanders (FWO- Vlaanderen) for a postdoctoral research fellowship. JAM acknowledges the Flemish Government for long-term structural funding (Methusalem).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Controlled Release Society
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Van Speybroeck, M., Mellaerts, R., Martens, J.A., Annaert, P., Van den Mooter, G., Augustijns, P. (2011). Ordered Mesoporous Silica for the Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs. In: Wilson, C., Crowley, P. (eds) Controlled Release in Oral Drug Delivery. Advances in Delivery Science and Technology. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-1004-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-1004-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-1003-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-1004-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)