Abstract
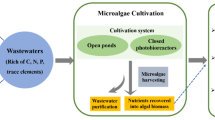
Microalgae are a sustainable source of high value-added bioproducts that can be used for a variety of purposes, such as energy, food, and raw materials. However, the costs incurred to microalgae production are still very high, which prevents its large-scale application from being economically viable. One widely discussed solution in recent years is the association of microalgae cultivation with wastewater treatment, in order to reduce costs related to its cultivation. In this process, the microalgae uptake nutrients (e.g., carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus) and other substances from the wastewater, generating a treated wastewater effluent and a microalgal biomass with high economic value. After the cultivation process, the generated biomass has to be recovered from the wastewater. Harvesting is also a bottleneck process because it represents about 20–60% of the total production costs. Since there is no universal method applied to microalgae recovery, different harvesting methods have been investigated, mainly including centrifugation, filtration, flotation, and sedimentation. Thus, choosing the appropriated harvesting method is crucial for a cost-effective microalgae production. In this context, this chapter presents an overview of the microalgae production, integrated with the wastewater treatment, and the potential harvesting methods. In addition, the challenges to apply the system in Brazil are also discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coppens J, Grunert O, Van Den Hende S, Vanhoutte I, Boon N, Haesaert G, De Gelder L (2016) The use of microalgae as a high-value organic slow-release fertilizer results in tomatoes with increased carotenoid and sugar levels. J Appl Phycol 28:2367–2377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0775-2
Slade R, Bauen A (2013) Micro-algae cultivation for biofuels: cost, energy balance, environmental impacts and future prospects. Biomass Bioenergy 53:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.12.019
WWAP (2017) The United Nations World Water Development report 2017. Wastewater: the untapped resource, Paris
Von Sperling M (2014) Introdução à qualidade das águas e ao tratamento de esgotos.4th edn. Editora UFMG, Belo Horizonte. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150922234
Dodds WK, Bouska WW, Eitzmann JL, Pilger TJ, Pitts KL, Riley AJ, Schloesser JT, Thornbrugh DJ (2009) Eutrophication of U. S. freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environ Sci Technol 43:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801217q
Caporgno MP, Taleb A, Olkiewicz M, Font J, Pruvost J, Legrand J, Bengoa C (2015) Microalgae cultivation in urban wastewater: nutrient removal and biomass production for biodiesel and methane. Algal Res 10:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.05.011
Fernandes TV, Suárez-Muñoz M, Trebuch LM, Verbraak PJ, Van de Waal DB (2017) Toward an ecologically optimized N:P recovery from wastewater by microalgae. Front Microbiol 8:1742. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01742
Foladori P, Petrini S, Andreottola G (2018) Evolution of real municipal wastewater treatment in photobioreactors and microalgae-bacteria consortia using real-time parameters. Chem Eng J 345:507–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.178
Mennaa FZ, Arbib Z, Perales JA (2019) Urban wastewater photobiotreatment with microalgae in a continuously operated photobioreactor: growth, nutrient removal kinetics and biomass coagulation–flocculation. Environ Technol 40:342–355. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1393011
Fernandes TV, Shrestha R, Sui Y, Papini G, Zeeman G, Vet LEM, Wijffels RH, Lamers P (2015) Closing domestic nutrient cycles using microalgae. Environ Sci Technol 49:12450–12456. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02858
de Souza Leite L, Matsumoto T, Albertin LL (2018) Mathematical modeling of thermal drying of facultative pond sludge. J Environ Eng 144:04018079. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001427
de Souza WG (2012) Pós-secagem natural de lodos de estações de tratamento de Água e esgoto sanitários. Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo
Wang L, Liu J, Zhao Q, Wei W, Sun Y (2016) Comparative study of wastewater treatment and nutrient recycle via activated sludge, microalgae and combination systems. Bioresour Technol 211:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.048
Molina Grima E, Belarbi EH, Acién Fernández FG, Robles Medina A, Chisti Y (2003) Recovery of microalgal biomass and metabolites: process options and economics. Biotechnol Adv 20:491–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-9750(02)00050-2
De Francisci D, Su Y, Iital A, Angelidaki I (2018) Evaluation of microalgae production coupled with wastewater treatment. Environ Technol 39:581–592. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1308441
de Souza Leite L, Hoffmann MT, Daniel LA (2019) Microalgae cultivation for municipal and piggery wastewater treatment in Brazil. J Water Process Eng 31:100821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100821
Choi HJ, Lee SM (2015) Effect of the N/P ratio on biomass productivity and nutrient removal from municipal wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38:761–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1317-z
Norvill ZN, Shilton A, Guieysse B (2016) Emerging contaminant degradation and removal in algal wastewater treatment ponds: identifying the research gaps. J Hazard Mater 313:291–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.085
Heimann K, Huerlimann R (2015) Microalgal classification: major classes and genera of commercial microalgal species. In: Handbook of marine microalgae. Biotechnology advances, pp 25–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800776-1.00003-0
Acreman J (1994) Algae and cyanobacteria: isolation, culture and long-term maintenance. J Ind Microbiol 13:193–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01584008
Krienitz L, Huss VAR, Bock C (2015) Chlorella: 125 years of the green survivalist. Trends Plant Sci 20:67–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.11.005
Posten C, Chen SF (2016) Microalgae biotechnology. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(73)80708-2
Randrianarison G, Ashraf MA (2017) Microalgae: a potential plant for energy production. Geol Ecol Landscapes 1:104–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2017.1332853
Markou G, Nerantzis E (2013) Microalgae for high-value compounds and biofuels production: a review with focus on cultivation under stress conditions. Biotechnol Adv 31:1532–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.07.011
Liang M-H, Wang L, Wang Q, Zhu J, Jiang J-G (2018) High-value bioproducts from microalgae: strategies and progress. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1455030
Brennan L, Owende P (2010) Biofuels from microalgae – a review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:557–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2009.10.009
Singh B, Bauddh K, Bux F (2015) Algae and environmental sustainability. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2641-3
Kadir WNA, Lam MK, Uemura Y, Lim JW, Lee KT (2018) Harvesting and pre-treatment of microalgae cultivated in wastewater for biodiesel production: a review. Energ Conver Manage 171:1416–1429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.06.074
Rahman A, Miller CD (2017) Microalgae as a source of bioplastics. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63784-0.00006-0
Chen CY, Zhao XQ, Yen HW, Ho SH, Cheng CL, Lee DJ, Bai FW, Chang JS (2013) Microalgae-based carbohydrates for biofuel production. Biochem Eng J 78:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.03.006
Gong M, Bassi A (2016) Carotenoids from microalgae: a review of recent developments. Biotechnol Adv 34:1396–1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.10.005
Brasil B dos SAF, de Siqueira FG, Salum TFC, Zanette CM, Spier MR (2017) Microalgae and cyanobacteria as enzyme biofactories. Algal Res 25:76–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.04.035
Roux JM, Lamotte H, Achard JL (2017) An overview of microalgae lipid extraction in a biorefinery framework. Energy Procedia 112:680–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1137
Sathasivam R, Radhakrishnan R, Hashem A, Abd Allah EF (2019) Microalgae metabolites: a rich source for food and medicine, Saudi. J Biol Sci 26:709–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.11.003
Koyande AK, Chew KW, Rambabu K, Tao Y, Chu D-T, Show P-L (2019) Microalgae: a potential alternative to health supplementation for humans. Food Sci Human Wellness 8:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2019.03.001
Razzak SA, Hossain MM, Lucky RA, Bassi AS, De Lasa H (2013) Integrated CO2 capture, wastewater treatment and biofuel production by microalgae culturing – a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 27:622–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.05.063
Singh RN, Sharma S (2012) Development of suitable photobioreactor for algae production – a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:2347–2353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.01.026
Jia H, Yuan Q (2016) Removal of nitrogen from wastewater using microalgae and microalgae-bacteria consortia, cogent. Environ Sci 2:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311843.2016.1275089
Eixler S, Karsten U, Selig U (2006) Phosphorus storage in Chlorella vulgaris (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) cells and its dependence on phosphate supply. Phycologia 45:53–60. https://doi.org/10.2216/04-79.1
Geider RJ, La Roche J (2002) Redfield revisited: variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical basis. Eur J Phycol 37:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0967026201003456
Pahazri NF, Mohamed R, Al-gheethi AA, Mohd AH (2016) Production and harvesting of microalgae biomass from wastewater: a critical review, environ. Technol Rev 5:39–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2016.1207713
Raven JA, Cockell CS, De La Rocha CL (2008) The evolution of inorganic carbon concentrating mechanisms in photosynthesis. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 363:2641–2650. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0020
de Godos I, Blanco S, García-Encina PA, Becares E, Muñoz R (2009) Long-term operation of high rate algal ponds for the bioremediation of piggery wastewaters at high loading rates. Bioresour Technol 100:4332–4339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.04.016
Vadlamani A, Viamajala S, Pendyala B, Varanasi S (2017) Cultivation of microalgae at extreme alkaline pH conditions: a novel approach for biofuel production. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:7284–7294. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b01534
Zhang Q, Wang T, Hong Y (2014) Investigation of initial pH effects on growth of an oleaginous microalgae Chlorella sp. HQ for lipid production and nutrient uptake. Water Sci Technol 70:712–719. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2014.285
Singh SP, Singh P (2015) Effect of temperature and light on the growth of algae species: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 50:431–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.05.024
Cuaresma M, Janssen M, Vílchez C, Wijffels RH (2009) Productivity of Chlorella sorokiniana in a short light-path (SLP) panel photobioreactor under high irradiance. Biotechnol Bioeng 104:352–359. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22394
Cazzaniga S, Osto LD, Szaub J, Scibilia L, Ballottari M, Purton S, Bassi R (2014) Domestication of the green alga Chlorella sorokiniana: reduction of antenna size improves light-use efficiency in a photobioreactor. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-014-0157-z
Kessler E (1985) Upper limits of temperature for growth in Chlorella (Chlorophyceae). Plant Syst Evol 151:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02418020
Franco MC, Buffing MF, Janssen M, Lobato CV, Wijffels RH (2012) Performance of Chlorella sorokiniana under simulated extreme winter conditions. J Appl Phycol 24:693–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9687-y
Edmundson SJ, Huesemann MH (2015) The dark side of algae cultivation: characterizing night biomass loss in three photosynthetic algae, Chlorella sorokiniana, Nannochloropsis salina and Picochlorum sp. Algal Res 12:470–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.10.012
Janssen MGJ (2002) Cultivation of microalgae: effect of light/dark cycles on biomass yield. Wageningen University
Khoeyi ZA, Seyfabadi J, Ramezanpour Z (2012) Effect of light intensity and photoperiod on biomass and fatty acid composition of the microalgae, Chlorella vulgaris. Aquac Int 20:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-011-9440-1
Krzemińska I, Nawrocka A, Piasecka A, Jagielski P, Tys J (2015) Cultivation of Chlorella protothecoides in photobioreactors: the combined impact of photoperiod and CO2 concentration. Eng Life Sci 15:533–541. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201400174
Kothari R, Prasad R, Kumar V, Singh DP (2013) Production of biodiesel from microalgae Chlamydomonas polypyrenoideum grown on dairy industry wastewater. Bioresour Technol 144:499–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.116
Solovchenko A, Pogosyan S, Chivkunova O, Selyakh I, Semenova L, Voronova E, Scherbakov P, Konyukhov I, Chekanov K, Kirpichnikov M, Lobakova E (2014) Phycoremediation of alcohol distillery wastewater with a novel Chlorella sorokiniana strain cultivated in a photobioreactor monitored on-line via chlorophyll fluorescence. Algal Res 6:234–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2014.01.002
Yu Z, Song M, Pei H, Han F, Jiang L, Hou Q (2017) The growth characteristics and biodiesel production of ten algae strains cultivated in anaerobically digested effluent from kitchen waste. Algal Res 24:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.04.010
Hu X, Meneses YE, Stratton J, Wang B (2019) Acclimation of consortium of micro-algae help removal of organic pollutants from meat processing wastewater. J Clean Prod 214:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.255
AlMomani FA, Örmeci B (2016) Performance of Chlorella vulgaris, Neochloris oleoabundans, and mixed indigenous microalgae for treatment of primary effluent, secondary effluent and centrate. Ecol Eng 95:280–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.038
Guiry MD (2012) How many species of algae are there? J Phycol 48:1057–1063. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2012.01222.x
Hong J, Kim O, Kim H, Jo S, Cho H, Yoon H (2016) Mass cultivation from a Korean raceway pond system of indigenous microalgae as potential biofuel feedstock. Oil Gas Res 2:1–6. https://doi.org/10.4172/2472-0518.1000108
Kim S, Lee Y (2013) Effects of pH and aeration rates on removal of organic matter and nutrients using mixotrophic microalgae. J Korean Soc Water Wastewater 27:69–76. https://doi.org/10.11001/jksww.2013.27.1.69
Mattos ER, Singh M, Cabrera ML, Das KC (2012) Effects of inoculum physiological stage on the growth characteristics of Chlorella sorokiniana cultivated under different CO2 concentrations. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168:519–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9793-6
Posadas E, Morales M, Gomez C, Acién FG, Muñoz R (2015) Influence of pH and CO2 source on the performance of microalgae-based secondary domestic wastewater treatment in outdoors pilot raceways. Chem Eng J 265:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.059
Shchegolkova N, Shurshin K, Pogosyan S, Voronova E, Matorin D, Karyakin D (2018) Microalgae cultivation for wastewater treatment and biogas production at Moscow wastewater treatment plant. Water Sci Technol 78:1–12. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.088
Mohd Udaiyappan AF, Abu Hasan H, Takriff MS, Sheikh Abdullah SR (2017) A review of the potentials, challenges and current status of microalgae biomass applications in industrial wastewater treatment. J Water Process Eng 20:8–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.09.006
Ansa EDO, Lubberding HJ, Gijzen HJ (2012) The effect of algal biomass on the removal of faecal coliform from domestic wastewater. Appl Water Sci 2:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-011-0025-y
Slompo NDM, Quartaroli L, Fernandes TV, da Silva GHR, Daniel LA (2020) Nutrient and pathogen removal from anaerobically treated black water by microalgae. J Environ Manage 268:2–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110693
Cavet JS, Borrelly GPM, Robinson NJ (2003) Zn, Cu and Co in cyanobacteria: selective control of metal availability. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:165–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00050-0
Zhang L, Lee YW, Jahng D (2012) Ammonia stripping for enhanced biomethanization of piggery wastewater. J Hazard Mater 199–200:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.049
Marcilhac C, Sialve B, Pourcher AM, Ziebal C, Bernet N, Béline F (2014) Digestate color and light intensity affect nutrient removal and competition phenomena in a microalgal-bacterial ecosystem. Water Res 64:278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.012
Kuo CM, Chen TY, Lin TH, Kao CY, Lai JT, Chang JS, Lin CS (2015) Cultivation of Chlorella sp. GD using piggery wastewater for biomass and lipid production. Bioresour Technol 194:326–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.026
Gao F, Peng YY, Li C, Yang GJ, Deng YB, Xue B, Guo YM (2018) Simultaneous nutrient removal and biomass/lipid production by Chlorella sp. in seafood processing wastewater. Sci Total Environ 640–641:943–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.380
Zhang L, Cheng J, Pei H, Pan J, Jiang L, Hou Q (2018) Cultivation of microalgae using anaerobically digested effluent from kitchen waste as a nutrient source for biodiesel production. Renew Energy 115:276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.08.034
Wang M, Yang Y, Chen Z, Chen Y, Wen Y, Chen B (2016) Removal of nutrients from undiluted anaerobically treated piggery wastewater by improved microalgae. Bioresour Technol 222:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.09.128
Metcalf E, Eddy H (2003) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse.4th edn. McGraw-Hill, Boston
Von Sperling M, Freire VH, Chernicharo CAL (2001) Performance evaluation of a UASB-activated sludge system treating municipal wastewater. Water Sci Technol 43:323–328. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2001.0698
Girard JM, Roy ML, Ben Hafsa M, Gagnon J, Faucheux N, Heitz M, Tremblay R, Deschênes JS (2014) Mixotrophic cultivation of green microalgae Scenedesmus obliquus on cheese whey permeate for biodiesel production. Algal Res 5:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2014.03.002
Delgadillo-Mirquez L, Lopes F, Taidi B, Pareau D (2016) Nitrogen and phosphate removal from wastewater with a mixed microalgae and bacteria culture. Biotechnol Rep 11:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2016.04.003
Santana H, Cereijo CR, Teles VC, Nascimento RC, Fernandes MS, Brunale P, Campanha RC, Soares IP, Silva FCP, Sabaini PS, Siqueira FG, Brasil BSAF (2017) Microalgae cultivation in sugarcane vinasse: selection, growth and biochemical characterization. Bioresour Technol 228:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.075
Fasaei F, Bitter JH, Slegers PM, van Boxtel AJB (2018) Techno-economic evaluation of microalgae harvesting and dewatering systems. Algal Res 31:347–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.11.038
Sukenik A, Shelef G (1984) Algal autoflocculation – verification and proposed mechanism. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:4–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260260206
Chys M, Demeestere K, Nopens I, Audenaert WTM, Van Hulle SWH (2018) Municipal wastewater effluent characterization and variability analysis in view of an ozone dose control strategy during tertiary treatment: the status in Belgium. Sci Total Environ 625:1198–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.032
Beuckels A, Depraetere O, Vandamme D, Foubert I, Smolders E, Muylaert K (2013) Influence of organic matter on flocculation of Chlorella vulgaris by calcium phosphate precipitation. Biomass Bioenergy 54:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.03.027
de Souza Leite L, Daniel LA, Pivokonsky M, Novotna K, Branyikova I, Branyik T (2019) Interference of model wastewater components with flocculation of Chlorella sorokiniana induced by calcium phosphate precipitates. Bioresour Technol 286:121352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121352
Vandamme D, Beuckels A, Vadelius E, Depraetere O, Noppe W, Dutta A, Foubert I, Laurens L, Muylaert K (2016) Inhibition of alkaline flocculation by algal organic matter for Chlorella vulgaris. Water Res 88:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.032
Deconinck N, Muylaert K, Ivens W, Vandamme D (2018) Innovative harvesting processes for microalgae biomass production: a perspective from patent literature. Algal Res 31:469–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.01.016
Kurniawati HA, Ismadji S, Liu JC (2014) Microalgae harvesting by flotation using natural saponin and chitosan. Bioresour Technol 166:429–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.079
Pérez L, Luis Salgueiro J, Maceiras R, Cancela Á, Sánchez Á (2017) An effective method for harvesting of marine microalgae: pH induced flocculation. Biomass Bioenergy 97:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.12.010
Rakesh S, Saxena S, Dhar DW, Prasamna R, Saxena KA (2014) Comparative evaluation of inorganic and organic amendments for their flocculation efficiency of selected microalgae. J Appl Phycol 26:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0114-4
Ummalyma SB, Mathew AK, Pandey A, Sukumaran RK (2016) Harvesting of microalgal biomass: efficient method for flocculation through pH modulation. Bioresour Technol 213:216–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.114
Vandamme D, Foubert I, Fraeye I, Meesschaert B, Muylaert K (2012) Flocculation of Chlorella vulgaris induced by high pH: role of magnesium and calcium and practical implications. Bioresour Technol 105:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.105
Wu Z, Zhu Y, Huang W, Zhang C, Li T, Zhang Y, Li A (2012) Evaluation of flocculation induced by pH increase for harvesting microalgae and reuse of flocculated medium. Bioresour Technol 110:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.101
Heasman M, Diemar J, Connor WO, Sushames T, Foulkes L (2000) Development of extended shelf life microalgae concentrate diets harvested by centrifugation for bivalve molluscs – a summary. Aquacult Res 31:637–659. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2109.2000.318492.x
Dassey AJ, Theegala CS (2013) Harvesting economics and strategies using centrifugation for cost effective separation of microalgae cells for biodiesel applications. Bioresour Technol 128:241–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.061
Nagy E (2019) Membrane materials, structures, and modules. In: Nagy E (ed) Basic equations mass transport through a membrane layer2nd edn, Elsevier, pp 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-813722-2.00002-9
Sharma KK, Garg S, Li Y, Malekizadeh A, Schenk PM (2013) Critical analysis of current microalgae dewatering techniques. Biofuels 4:397–407. https://doi.org/10.4155/bfs.13.25
Milledge JJ, Heaven S (2013) A review of the harvesting of micro-algae for biofuel production. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 12:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-012-9301-z
Rios SD, Clavero E, Salvadó J, Farriol X, Torras C (2011) Dynamic microfiltration in microalgae harvesting for biodiesel production. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:2455–2460. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101070q
Sun X, Wang C, Tong Y, Wang W, Wei J (2013) A comparative study of microfiltration and ultrafiltration for algae harvesting. Algal Res 2:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2013.08.004
Ahmad AL, Mat Yasin NH, Derek CJC, Lim JK (2012) Crossflow microfiltration of microalgae biomass for biofuel production. Desalination 302:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.06.026
Laamanen CA, Ross GM, Scott JA (2016) Flotation harvesting of microalgae. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 58:75–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.293
Edzwald JK (1993) Algae, bubbles, coagulants, and dissolved air flotation. Water Sci Technol 27:67–81. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1993.0207
Rubio J, Souza ML, Smith RW (2002) Overview of flotation as a wastewater treatment technique. Miner Eng 15:139–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-6875(01)00216-3
Edzwald JK (2010) Dissolved air flotation and me. Water Res 44:2077–2106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.12.040
Ndikubwimana T, Chang J, Xiao Z, Shao W, Zeng X, Ng I, Lu Y (2016) Flotation: a promising microalgae harvesting and dewatering technology for biofuels production. Biotechnol J 11:315–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201500175
Shi W, Zhu L, Chen Q, Lu J, Pan G, Hu L, Yi Q (2017) Synergy of flocculation and flotation for microalgae harvesting using aluminium electrolysis. Bioresour Technol 233:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.084
de Souza Leite L, Hoffmann MT, Daniel LA (2019) Coagulation and dissolved air flotation as a harvesting method for microalgae cultivated in wastewater. J Water Process Eng 32:100947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100947
Besson A, Guiraud P (2013) High-pH-induced flocculation-flotation of the hypersaline microalga Dunaliella salina. Bioresour Technol 147:464–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.053
de Souza Leite L, dos Santos PR, Daniel LA (2020) Microalgae harvesting from wastewater by pH modulation and flotation: assessing and optimizing operational parameters. J Environ Manage 254:109825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109825
Kwon H, Lu M, Lee EY, Lee J (2014) Harvesting of microalgae using flocculation combined with dissolved air flotation. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 19:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0433-y
Wiley PE, Brenneman KJ, Jacobson AE (2009) Improved algal harvesting using suspended air flotation. Water Environ Res 81:702–708. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143009x407474
Zhang X, Hewson JC, Amendola P, Reynoso M, Sommerfeld M, Chen Y, Hu Q (2014) Critical evaluation and modeling of algal harvesting using dissolved air flotation. Biotechnol Bioeng 111:2477–2485. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25300
Marchioretto MM, Reali MAP (2001) Ozonation followed by coagulation/flocculation and flotation as post-treatment of the effluent from an anaerobic baffled reactor treating domestic sewage. Water Sci Technol Technol 43:99–106. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2001.0474%0A
Santos PR, Daniel LA (2017) Dissolved air flotation as a potential treatment process to remove Giardia cysts from anaerobically treated sewage. Environ Technol 38:2392–2399. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1262461
Lei X, Chen Y, Shao Z, Chen Z, Li Y, Zhu H, Zhang J, Zheng W, Zheng T (2015) Effective harvesting of the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris via flocculation – flotation with bioflocculant. Bioresour Technol 198:922–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.095
Zhang D, Yu Y, Li C, Chai C, Liu L (2015) Factors affecting microalgae harvesting efficiencies using electrocoagulation-flotation for lipid extraction. RSC Adv 5:5795–5800. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra09983d
Feng Q, Chen M, Wang W (2016) Study on the harvest of oleaginous microalgae Chlorella sp. by photosynthetic hydrogen mediated auto-flotation for biodiesel production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:16772–16777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.07.142
Branyikova I, Filipenska M, Urbanova K, Ruzicka MC, Pivokonsky M, Branyik T (2018) Physicochemical approach to alkaline flocculation of Chlorella vulgaris induced by calcium phosphate precipitates. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 166:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.03.007
Vandamme D, Foubert I, Muylaert K (2013) Flocculation as a low-cost method for harvesting microalgae for bulk biomass production. Trends Biotechnol 31:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.12.005
Salim S, Kosterink NR, Tchetkoua Wacka ND, Vermuë MH, Wijffels RH (2014) Mechanism behind autoflocculation of unicellular green microalgae Ettlia texensis. J Biotechnol 174:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.01.026
Ummalyma SB, Gnansounou E, Sukumaran RK, Sindhu R, Pandey A, Sahoo D (2017) Bioflocculation: an alternative strategy for harvesting of microalgae – an overview. Bioresour Technol 242:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.097
Cole AJ, Neveux N, Whelan A, Morton J, Vis M, de Nys R, Paul NA (2016) Adding value to the treatment of municipal wastewater through the intensive production of freshwater macroalgae. Algal Res 20:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.09.026
Instituto Trata Brasil, Dados de esgoto no Brasil (2020) http://www.tratabrasil.org.br/saneamento/principais-estatisticas/no-brasil/esgoto
Ganeshkumar V, Subashchandrabose SR, Dharmarajan R, Venkateswarlu K, Naidu R, Megharaj M (2018) Use of mixed wastewaters from piggery and winery for nutrient removal and lipid production by Chlorella sp. MM3. Bioresour Technol 256:254–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.025
Kunz A, Steinmetz RLR, Ramme MA, Coldebella A (2009) Effect of storage time on swine manure solid separation efficiency by screening. Bioresour Technol 100:1815–1818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.09.022
Associação Brasileira de proteina animal (2018) Annual Report, São Paulo
Franchino M, Tigini V, Varese GC, Mussat Sartor R, Bona F (2016) Microalgae treatment removes nutrients and reduces ecotoxicity of diluted piggery digestate. Sci Total Environ 569–570:40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.100
Sánchez E, Borja R, Travieso L, Martín A, Colmenarejo MF (2005) Effect of organic loading rate on the stability, operational parameters and performance of a secondary upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor treating piggery waste. Bioresour Technol 96:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.04.003
de Souza Leite L, Daniel LA (2020) Optimization of microalgae harvesting by sedimentation induced by high pH. Water Sci Technol:1–10. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Leite, L.d.S., Daniel, L.A. (2022). Microalgae Production Integrated with the Wastewater Treatment: A Management Approach. In: Nasr, M., Negm, A.M. (eds) Cost-efficient Wastewater Treatment Technologies. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, vol 117. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/698_2022_862
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/698_2022_862
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-12917-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-12918-6
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)