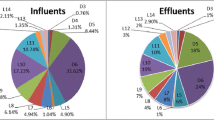
Abstract
Concentration, distribution, fate, removal efficiencies, daily and seasonal variations of volatile methylsiloxanes (VMS) in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) were reviewed in this chapter. Purge-and-trap, headspace, liquid-liquid extraction, liquid-solid extraction, membrane-assisted solvent extraction, and modified QuEChERS methods have been developed to analyze of VMS in samples from WWTPs. The different consumption quantities of commercial products containing siloxanes result in the difference of concentrations and proportion of VMS in the world. Daily fluctuations of VMS concentrations in water usage induce in flow variation to WWTP and VMS show seasonal variation in the WWTPs with different types of processes. In cold seasons, VMS prefer to stay in water phase rather than air or sludge because the air/water and organic carbon/water partition coefficients decrease with temperature. Although most WWTP remove siloxanes efficiently, long-term environmental monitoring of VMS is necessary in certain environments, considering the potential of VMS to bioaccumulate in biota and its toxicity to sensitive aquatic organisms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lofrano G, Brown J (2010) Wastewater management through the ages: a history of mankind. Sci Total Environ 408:5254–5264
Royal Commission on Sewage Disposal Eighth Report (1912) Standards and tests for sewage and sewage effluent discharging to rivers and streams. Cd 6464, London
Tchobanoglous G, Metcalf & Eddy (1991) Wastewater engineering treatment, disposal and reuse. Water resources and environmental engineering, vol 73. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 50–51
Horii Y, Kannan K (2008) Survey of organosilicone compounds, including cyclic and linear siloxanes, in personal-care and household products. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55:701–710
Capela D, Ratola N, Alves A, Homem V (2017) Volatile methylsiloxanes through wastewater treatment plants - a review of levels and implications. Environ Int 102:9–29
Dewil R, Appels L, Baeyens J (2006) Energy use of biogas hampered by the presence of siloxanes. Energy Conver Manage 47:1711–1722
Kaj L, Andersson J, Palm Cousins A, Schmidbauer N, Brorstrom-Lunden E, Cato I (2005) Results from the Swedish national screening programme 2004. Subreport 4: siloxanes. IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute, Stockholm
Wang D-G, Steer H, Tait T, Williams Z, Pacepavicius G, Young T, Ng T, Smyth SA, Kinsman L, Alaee M (2013) Concentrations of cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in biosolid amended soil, influent, effluent, receiving water, and sediment of wastewater treatment plants in Canada. Chemosphere 93:766–773
Carpenter JC, Gerhards R (1997) Methods for the extraction and detection of trace organosilicon materials in environmental samples. In: Chandra G (ed) Organosilicon materials: the handbook of environmental chemistry. Springer, New York, pp 27–51
Varaprath S, Stutts DH, Kozerski GE (2006) A primer on the analytical aspects of silicones at trace levels-challenges and artifacts - a review. Silicon Chem 3:79–102
Wang D-G, Alaee M, Steer H, Tait T, Williams Z, Brimble S, Svoboda L, Barresi E, DeJong M, Schachtschneider J, Kaminski E, Norwood W, Sverko E (2013) Determination of cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in water, sediment, soil, biota, and biosolid using large-volume injection-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 93:741–748
Wang D-G, Solla SRD, Lebeuf M, Bisbicos T, Barrett GC, Alaee M (2017) Determination of linear and cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in blood of turtles, cormorants, and seals from Canada. Sci Total Environ 574:1254–1260
Badjagbo K, Furtos A, Alaee M, Moore S, Sauve S (2009) Direct analysis of volatile methylsiloxanes in gaseous matrixes using atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 81:7288–7293
Badjagbo K, Heroux M, Alaee M, Moore S, Sauve S (2009) Quantitative analysis of volatile methylsiloxanes in waste-to-energy landfill biogases using direct APCI-MS/MS. Environ Sci Technol 44:600–605
US EPA (2003) Method 5053C: purge-and-trap for aqueous samples
Whelan MJ, Sanders D, van Egmond R (2009) Effect of Aldrich humic acid on water-atmosphere transfer of decamethylcyclopentasiloxane. Chemosphere 74:1111–1116
David MD, Fendinger NJ, Hand VC (2000) Determination of Henry’s law constants for organosilicones in actual and simulated wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 34:4554–4559
Varaprath S, Salyers KL, Plotzke KP, Nanavati S (1998) Extraction of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane and its metabolites from biological matrices. Anal Biochem 256:14–22
Dewil R, Appels L, Baeyens J, Buczynska A, Van Vaeck L (2007) The analysis of volatile siloxanes in waste activated sludge. Talanta 74:14–19
Wang DG, Norwood W, Alaee M, Byer JD, Brimble S (2013) Review of recent advances in research on the toxicity, detection, occurrence and fate of cyclic volatile methyl siloxanes in the environment. Chemosphere 93:711–725
Xu L, He X, Zhi L, Zhang C, Zeng T, Cai Y (2016) Chlorinated methylsiloxanes generated in papermaking process and their fate in wastewater treatment processes. Environ Sci Technol 50:12732–12741
Wang D-G, Steer H, Pacepavicius G, Smyth SA, Kinsman L, Alaee M (2013) Seasonal variation and temperature-dependent removal efficiencies of cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in fifteen wastewater treatment plants. Organohalogen Compd 75:1286–1290
Mueller JA, Di Toro DM, Maiello JA (1995) Fate of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (OMCTS) in the atmosphere and in sewage treatment plants as an estimation of aquatic exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1657–1666
Parker WJ, Shi J, Fendinger NJ, Monteith HD, Chandra G (1999) Pilot plant study to assess the fate of two volatile methyl siloxane compounds during municipal wastewater treatment. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:172–181
Zhang Z, Qi H, Ren N, Li Y, Gao D, Kannan K (2011) Survey of cyclic and linear siloxanes in sediment from the Songhua river and in sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants, northeastern China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:204–211
Liu N, Shi Y, Li W, Xu L, Cai Y (2014) Concentrations and distribution of synthetic musks and siloxanes in sewage sludge of wastewater treatment plants in China. Sci Total Environ 476–477:65–72
Wang D-G, Aggarwal M, Tait T, Brimble S, Pacepavicius G, Kinsman L, Theocharides M, Smyth SA, Alaee M (2015) Fate of anthropogenic cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in a wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 72:209–217
Bletsou AA, Asimakopoulos AG, Stasinakis AS, Thomaidis NS, Kannan K (2013) Mass loading and fate of linear and cyclic siloxanes in a wastewater treatment plant in Greece. Environ Sci Technol 47:1824–1832
Schweigkofler M, Niessner R (1999) Determination of siloxanes and VOC in landfill gas and sewage gas by canister sampling and GC-MS/AES analysis. Environ Sci Technol 33:3680–3685
Schweigkofler M, Niessner R (2001) Removal of siloxanes in biogases. J Hazard Mater 83:183–196
Rasi S, Lehtinen J, Rintala J (2010) Determination of organic silicon compounds in biogas from wastewater treatments plants, landfills, and co-digestion plants. Renew Energy 35:2666–2673
Tansel B, Surita SC (2014) Differences in volatile methyl siloxane (VMS) profiles in biogas from landfills and anaerobic digesters and energetics of VMS transformations. Waste Manag 34:2271–2277
Graiver D, Farminer KW, Narayan R (2003) A review of the fate and effects of silicones in the environment. J Polym Environ 11:129–136
Kent D, Fackler P, Hartley D, Hobson J (1996) Interpretation of data from nonstandard studies: the fate of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane in a sediment/water microcosm system. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 11:145–149
Xu S (1999) Fate of cyclic methylsiloxanes in soils. 1. The degradation pathway. Environ Sci Technol 33:603–608
Xu S, Chandra G (1999) Fate of cyclic methylsiloxanes in soils. 2. Rates of degradation and volatilization. Environ Sci Technol 33:4034–4039
Wang D-G, Du J, Pei W, Liu Y, Guo M (2015) Modeling and monitoring cyclic and linear volatile methylsiloxanes in a wastewater treatment plant using constant water level sequencing batch reactors. Sci Total Environ 512–513:472–479
Sanchís J, Martínez E, Ginebreda A, Farré M, Barceló D (2013) Occurrence of linear and cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in wastewater, surface water and sediments from Catalonia. Sci Total Environ 443:530–538
Stevens C, Annelin RB (1997) Ecotoxicity testing challenges of organosilicon materials. In: Chandra G (ed) Organosilicon materials: the handbook of environmental chemistry. Springer, New York, pp 83–103
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wang, DG., Alaee, M. (2018). Fate of Volatile Methylsiloxanes in Wastewater Treatment Plants. In: Homem, V., Ratola, N. (eds) Volatile Methylsiloxanes in the Environment. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, vol 89. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/698_2018_365
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/698_2018_365
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-50134-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-50135-8
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)