Abstract
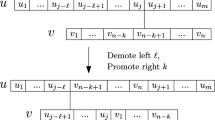
We investigate the issue of stalling in the LogP model. In particular, we introduce a novel quantitative characterization of stalling, referred to as δ-stalling, which intuitively captures the realistic assumption that once the network’s capacity constraint is violated, it takes some time (at most δ) for this information to propagate to the processors involved. We prove a lower bound that shows that LogP under δ-stalling is strictly more powerful than the stall-free version of the model where only strictly stall-free computations are permitted. On the other hand, we show that δ-stalling LogP with δ = L can be simulated with at most logarithmic slowdown by a BSP machine with similar bandwidth and latency values, thus extending the equivalence (up to logarithmic factors) between stall-free LogP and BSP argued in [1] to the more powerful L-stalling LogP.
This research was supported, in part, by the Italian CNR, and by MURST under Project Algorithms for Large Data Sets: Science and Engineering.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Bilardi, K.T. Herley, A. Pietracaprina, G. Pucci and P. Spirakis. BSP vs. LogP. Algorithmica, 24:405–422, 1999.
D.E. Culler, R. Karp, D. Patterson, A. Sahay, K.E. Schauser, E. Santos, R. Subramonian, and T.V. Eicken. LogP: A practical model of parallel computation. Communications of the ACM, 39(11):78–85, November 1996.
M.T. Goodrich. Communication-Efficient Parallel Sorting. In Proc. of the 28th ACM Symp on Theory of Computing, pages 247–256, Philadelphia PA, 1996.
P.D. MacKenzie. Lower bounds for randomized exclusive write PRAMs. Theorey of Computing Systems, 30(6):599–626, 1997.
V. Ramachandran, B. Grayson, and M. Dahlin. Emulations between QSM, BSP and LogP: a framework for general-purpose parallel algorithm design. TR98-22, Dept. of CS, Univ. of Texas at Austin, November 1998. (Summary in Proc. of ACM-SIAM SODA, 1999.)
L.G. Valiant. A bridging model for parallel computation. Communications of the ACM, 33(8):103–111, August 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bilardi, G., Herley, K.T., Pietracaprina, A., Pucci, G. (2000). On stalling in LogP. In: Rolim, J. (eds) Parallel and Distributed Processing. IPDPS 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1800. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45591-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45591-4_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-67442-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45591-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive