Abstract
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a severe and fatal clinical syndrome. C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) is known to be expressed in cancer and stem/progenitor cells. In the present study, PAH was induced in a rat model by 5 weeks of 10% hypoxia and treatment with a single subcutaneous injection of monocrotaline (60 mg/kg) [1] to investigate the involvement of CXCR4 in PAH development [2].
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a severe and fatal clinical syndrome. C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) is known to be expressed in cancer and stem/progenitor cells. In the present study, PAH was induced in a rat model by 5 weeks of 10% hypoxia and treatment with a single subcutaneous injection of monocrotaline (60 mg/kg) [1] to investigate the involvement of CXCR4 in PAH development [2].
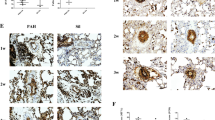
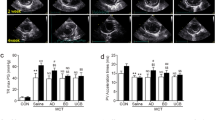
The successful establishment of the PAH model was confirmed by significant differences in the right ventricular systolic pressure, Fulton index, wall thickness, vascular occlusion score determined by immunohistochemical staining, and the expression of inflammatory markers measured by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) between the PAH and control groups We compared the expression of CXCR4 and other stem cell markers in the PAH and control groups. The results of RT-qPCR revealed that the expression of CXCR4, SCF, c-Kit, and CD29 was significantly higher in the PAH group. Immunohistochemical staining also showed that the numbers of CXCR4-, c-Kit-, and CD90-positive cells were significantly higher in the PAH group. We hypothesized that these markers play important roles in chemotaxis, proliferation, and survival of smooth muscle cells or endothelial cells, leading to pulmonary vascular remodeling. Further studies to clarify the role of CXCR4 and stem cells in PAH development may provide additional treatment options, such as CXCR4 inhibitors.
References
Lan B, Hayama E, Kawaguchi N, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of valproic acid in a combined monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia rat model of severe pulmonary hypertension. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0117211.
Zhang T, Kawaguchi N, Hayama E, et al. High expression of CXCR4 and stem cell markers in a monocrotaline and chronic hypoxia-induced rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6):4615–22. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6027.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge Mr. Kenji Yoshihara and Mr. Hiroaki Nagao at Tokyo Women’s Medical University for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Copyright information
© 2020 The Author(s)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, T., Kawaguchi, N., Hayama, E., Furutani, Y., Nakanishi, T. (2020). Involvement of CXCR4 and Stem Cells in a Rat Model of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. In: Nakanishi, T., Baldwin, H., Fineman, J., Yamagishi, H. (eds) Molecular Mechanism of Congenital Heart Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1185-1_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1185-1_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-1184-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-1185-1
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)