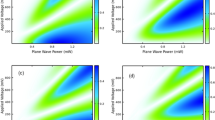
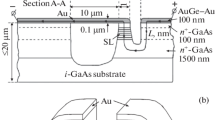
Abstract
Semiconductor superlattice frequency multipliers have emerged as a nonlinear medium able to generate radiation in a wide frequency range. This property facilitates the potential of sources suitable for sensing and spectroscopy applications. In this study, we further investigate the consequences on harmonic generation in a superlattice multiplier after excitation by an input signal oscillating at different frequencies. Here we provide a rigorous description of our theoretical model including a semiclassical Boltzmann approach to nonlinear miniband transport and non-equilibrium Green’s functions calculations treating scattering processes under forward and reverse bias. To fully exploit the features of this radiation source, we focus on the effects of elastic scattering and systematic imperfections in the superlattice structure which lead to asymmetric current flow.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tonouchi M (2007) Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nat Photonics 1:97
Kampfrath T, Tanaka K, Nelson Keith A (2013) Resonant and nonresonant control over matter and light by intense terahertz transients. Nat Photonics 7:680–690
Jepsen PU, Cooke DG, Koch M (2010) Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging-modern techniques and applications. Laser Photon Rev 5:124–166
Pereira MF (2015) TERA-MIR radiation: materials, generation, detection and applications II. Opt Quant Electron 47:815–820
Pereira MF, Shulika O (2014) Terahertz and mid infrared radiation: detection of explosives and CBRN (using terahertz). NATO science for peace and security series-B: physics and biophysics. Springer, Dordrecht
Pereira MF (1995) Analytical solutions for the optical absorption of superlattices. Phys Rev B 52:1978–1983
Apostolakis A, Awodele MK, Alekseev KN, Kusmartsev FV, Balanov AG (2017) Nonlinear dynamics and band transport in a superlattice driven by a plane wave. Phys Rev E 95(6):062203
Wacker A (2002) Semiconductor superlattices: a model system for nonlinear transport. Phys Rep 357:1–111
Pereira MF, Winge D, Wacker A, Zubelli JP, Rodrigues AS, Anfertev V, Vaks V (2017) Theory and measurements of harmonic generation in semiconductor superlattices with applications in the 100 GHz to 1 THz range. Phys Rev B 96:045306
Eisele H, Li L, Linfield EH (2018) High-perfomance GaAs/AlAs superlattice electronic devices in oscillators at frequencies 100-320 GHz. Appl Phys Lett 112:172103
Pereira MF, Anfertev V, Zubelli JP, Vaks V (2017) THz generation by GHz multiplication in superlattices. J Nanophotonics 11:046022
Winnerl S, Schomburg E, Brandl S, Kus O, Renk KF, Wanke M, Allen S, Ignatov A, Ustinov V, Zhukov A, Kopev P (2000) Mup doubling and tripling of terahertz radiation in a GaAs/AlAs superlattice due to frequency modulation of Bloch oscillations. Appl Phys Lett 77:1762
Klappenberger F, Renk KF, Renk P, Rieder B, Koshurinov YI, Pavelev DG (2004) Semiconductor-superlattice frequency multiplier for generation of submillimeter waves. Appl Phys Lett 84:3924
Apostolakis A, Pereira MF (2019) Controlling the harmonic conversion efficiency in semiconductor superlattices by interface roughness design. AIP Adv 9:015022
Apostolakis A, Pereira MF (2019) Numerical studies of superlattice multipliers performance. Quantum Sens Nano Electron Photonics XVI:109262G
Ignatov AA, Dodin EP, Shashkin VI (1991) Transient response theory of semiconductor superlattices: connection with Bloch oscillations. Modern Phys Lett B 05(16):1087–1094
Ignatov AA, Shashkin VI (1983) A simplified approach to nonlinear HF response theory of superlattice materials. Phys Lett A 94A(3–4):169–172
Apostolakis A, Pereira MF (2019) Potential and limits of superlattice multipliers coupled to different input power sources. J Nanophotonics 3:1–11
Pereira MF, Anfertev V, Shevchenko Y, Vaks V (2020) Giant controllable gigahertz to terahertz nonlinearities in superlattices. Sci Rep 10:15950
Wacker A, Jauho AP, Zeuner S, Allen SJ (1997) Sequential tunnelling in doped superlattices: fingerprints of impurity bands and photon-assisted tunnelling. Phys Rev B 56:13268
Keay BJ, Zeuner S, Allen SJ, Maranowski KD, Gossard AC, Bhattacharya U, Rodwell MJW (1995) Dynamic localization, absolute negative conductance, and stimulated, multiphoton emission in sequential resonant tunneling semiconductor superlattices. Phys Rev Lett 75:4102
Holthaus M (1992) Collapse of minibands in far-infrared irradiated superlattices. Phys Rev Lett 69:351
Pereira MF, Koch SW, Chow WW (1991) Many-body effects in the gain spectra quantum-wells. Appl Phys Lett 59:2941–2943
Oriaku CI, Pereira MF (2017) Analytical solutions for semiconductor luminescence including Coulomb with applications to dilute bismides. J Opt Soc Am B 34:321–328
Pereira MF (2018) Analytical expressions for numerical characterization of semiconductors per comparison with luminescence. Materials 11:1–15
Grempel H, Diesel A, Ebeling W, Gutowski J, Schüll K, Jobst B, Hommel D, Pereira MF, Henneberger K (1996) High-density effects, stimulated emission, and electrooptical properties of ZnCdSe/ZnSe single quantum wells and laser diodes. Phys Status Solidi B 194:199
Pereira MF, Binder R, Koch SW (1991) Theory of nonlinear optical absorption in coupled-band quantum wells with many-body effects. Appl Phys Lett 64:279–281
Pereira MF, Henneberger K (1998) Microscopic theory for the optical properties of coulomb-correlated semiconductors. Phys Status Solidi B 206:477–491
Chow WW, Pereira MF, Koch SW (1992) Many-body treatment on the modulation response in a strained quantum well semiconductor laser medium. Appl Phys Lett 61:758
Jin R, Okada K, Khitrova G, Gibbs HM, Pereira MF, Koch SW, Peyghambarian N (1992) Optical nonlinearities in strained-layer InGaAs/GaAs multiple quantum wells. Appl Phys Lett 61:1745
Pereira MF, Henneberger K (1997) Gain mechanisms and lasing in II-VI compounds. Phys Status Solidi B 202:751–762
Pereira MF (2018) Analytical expressions for numerical characterization of semiconductors per comparison with luminescence. Materials 11:2
Pereira MF, Nelander R, Wacker A, Revin DG, Soulby MR, Wilson LR, Cockburn JW, Krysa AB, Roberts JS, Airey RJ (2007) Characterization of intersubband devices combining a nonequilibrium many body theory with transmission with transmission spectroscopy experiments. Sci Mater Electron 18:689
Pereira MF, Tomić S (2011) Intersubband gain without global inversion through dilute nitride band engineering. Appl Phys Lett 98:061101
Pereira MF, Faragai IA (2014) Coupling of THz radiation with intervalence band transitions in microcavities. Opt Express 22:3439
Pereira MF (2011) Microscopic approach for intersubband-based thermophotovoltaic structures in the terahertz and mid-infrared. JOSA B 28:2014–2017
Pereira MF, Schmielau T (2009) Momentum dependent scattering matrix elements in quantum cascade laser transport. Microelectron J 40:869–871
Nelander R, Wacker A, Pereira MF, Revin DG, Soulby MR, Wilson LR, Cockburn JW, Krysa AB, Roberts JS, Airey RJ (2007) Fingerprints of spatial charge transfer in quantum cascade lasers. Appl Phys 102:11314
Pereira MF (2016) The linewidth enhancement factor of intersubband lasers: from a two-level limit to gain without inversion conditions. Appl Phys Lett 109:222102
Schmielau T, Pereira MF (2009) Nonequilibrium many body theory for quantum transport in terahertz quantum cascade lasers. Appl Phys Lett 95:231111
Hyart T, Shorokhov AV, Alekseev KN (2007) Theory of parametric amplification in superlattices. Phys Rev Lett 98:220404
Apostolakis A, Pereira MF (2020) Superlattice nonlinearities for Gigahertz-Terahertz generation in harmonic multi-pliers. Nanophotonics 9(12):3941–3952. https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2020-0155
Pereira MF, Anfertev V, Shevchenko Y, Vaks V (2020) Giant controllable gigahertz to terahertz nonlinearities in superlattices. Sci Rep 10:15950
Rose TP, Di Gennaro E, Abbate G, Andreone A (2011) Isotropic properties of the photonic band gap in quasicrystals with low-index contrast. Phys Rev B 84:125111
Savo S, Di Gennaro E, Andreone A (2009) Superlensing properties of one-dimensional dielectric photonic crystals. Opt Express 17:19848–19856
Di Gennaro E, Morello D, Miletto C, Savo S, Andreone A, Castaldi G, Galdi V, Pierro V (2008) A parametric study of the lensing properties of dodecagonal photonic quasicrystals. Photonics and Nanostruct Fundam Appl 6:60–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Schevchenko, Y., Apostolakis, A., Pereira, M.F. (2021). Recent Advances in Superlattice Frequency Multipliers. In: Pereira, M.F., Apostolakis, A. (eds) Terahertz (THz), Mid Infrared (MIR) and Near Infrared (NIR) Technologies for Protection of Critical Infrastructures Against Explosives and CBRN. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series B: Physics and Biophysics. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-2082-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-2082-1_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-024-2081-4
Online ISBN: 978-94-024-2082-1
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)