Abstract
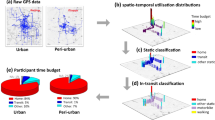
Commonly, population exposure is evaluated by crossing data of atmospheric pollution and population density maps. The former are usually actual measurements or simulated concentrations; depending on the approach or the model resolution, very different patterns may appear both in space and time, so that conclusions can vary significantly. The latter are usually based on residency information, and for many of us, do not reflect the typical wanderings, thus actual exposure. With the rise of portable devices, we are given the unprecedented opportunity to measure pollutant concentrations at a high time rate and to know the exact location of a subject. Moreover, the increase of computational capacities allows one to perform operational runs at spatial and temporal resolutions of about 10 m and 1 h respectively. Furthermore, if the subject writes an activity log, it is also possible to discriminate indoor and outdoor situations. In this ongoing work, we investigate the discrepancy in the evaluation of population exposure when using, on one hand different pollutant concentration maps e.g. yearly, daily or hourly average values, more or less sophisticated and/or refined models, different information related to the population e.g. static or dynamic and on the other hand actual data. Our region of interest for this test case is the city of Liège in Belgium.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Lefebvre, M. Van Poppel, B. Maiheu, S. Janssen, E. Dons, Evaluation of the RIO-IFDM-street canyon model chain. Atmos. Environ. 77, 325–337 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.05.026
A.Y. Watson, R.R. Bates, D. Kennedy (eds.), Assessment of human exposure to air pollution: methods, measurements, and models, in Air Pollution, the Automobile, and Public Health (National Academies Press (US), Washington (DC), 1988), https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK218147/
Disclaimer
All participants involved in the “Personal exposure” part of the OIE project have signed a consent allowing us to use their personal information as well as the measurements they made with our instruments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lenartz, F., Hutsemékers, V., Lefebvre, W. (2020). Trying to Link Personal Exposure Measurement and Population Exposure Modelling: A Test Case in Liège, Belgium. In: Mensink, C., Gong, W., Hakami, A. (eds) Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XXVI. ITM 2018. Springer Proceedings in Complexity. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22055-6_75
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22055-6_75
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-22054-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-22055-6
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)