Abstract
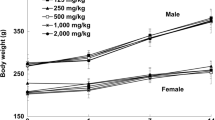
Thymus vulgaris L. is widely used as an ingredient in cooking and in herbal medicine. However, there is little information about its toxicity. The present study was performed to evaluate the acute and repeated 28-day oral dose toxicity of thyme essential oil in rats. For the acute toxicity test, two groups of three rats were used. The rats received a single dose of essential oil: 300 or 2,000 mg/kg of body weight (bw). The rats were observed individually during the first four hours, and then daily until day 14. For the toxicity test with repeated doses, four groups of 10 rats were used. Doses of 100, 250, and 500 mg/kg/day were tested for 28 days. At the end of the experiment, blood was collected and the animals were sacrificed. Histopathological examination showed that in the lungs of rats given the 2,000 mg/kg bw dose, polymorph nuclear infiltrates, hemosiderin macrophages, and interstitial space thickening were present. In the repeated dose study, all rats survived the 28-day treatment period and apparently showed no signs of toxicity. The hematological and biochemical parameters were not altered. The histopathological study of the organs showed severe changes in the lung, with the dose of 500 mg/kg/day; in the other organs, no alterations were observed or the changes were slight. The body weight was only altered in male rats given the 500 mg/kg dose. The relative weight of the organs did not show any significant changes. Our studies revealed that the essential oil of Thymus vulgaris has moderate oral toxicity according to the results of the acute test, whereas the results of the 28-day oral toxicity test suggest that the no-observed-adverse effect level (NOAEL) is greater than 250 mg/kg/day.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Brack, A. (1999) Encyclopedic Dictionary of Useful Plants of Peru, Center for Andean Regional Studies “Bartolomé de las Casas”/United Nations program for development, Cuzco, p. 500.
Al-Bayati, F.A. (2008) Synergistic antibacterial activity between Thymus vulgaris and Pimpinellaanisum essential oils and methanol extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol., 116, 403–406.
Mohsenzadeh, M. (2007) Evaluation of antibacterial activity of selected Iranian essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli in nutrient broth medium. Pak. J. Biol. Sci., 10, 3693–3697.
Zu, Y., Yu, H., Liang, L., Fu, Y., Efferth, T., Liu, X. and Wu, N. (2010) Activities of ten essential oils towards Propionibacterium acnes and PC-3, A-549 and MCF-7 cancer cells. Molecules, 15, 3200–3210.
Rojas, J., Ruiz, J., Almonacid, R., Ortiz, J., Palomino, M., Huaroto, L., Collahua, E., Chavez, R. and Anampa, A. (2016) Antibacterial activities of essential oils from three medicinal plants in combination with EDTA against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Br. Microbiol. Res. J., 17, 1–10.
Radaelli, M., Parraga da Silva, D., Weidlich, L., Hoehne, L., Flach, A. and Alves da Costa, L.A. (2016) Antimicrobial activities of six essential oils commonly used as condiments in Brazil against Clostridium perfringens. Braz. J. Microbiol., 47, 424–430.
Puškárová, A., Bučková, M., Kraková, L., Pangallo, D. and Kozics, K. (2017) The antibacterial and antifungal activity of six essential oils and their cyto/genotoxicity to human HEL 12469 cells. Nature, 7, 1–11.
Soković, M., Glamoclija, J., Cirić, A., Kataranovski, D., Marin, P.D., Vukojević, J. and Brkić, D. (2008) Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Thymus vulgaris L. and thymol on experimentally induced dermatomycoses. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 34, 1388–1393.
Rojas, J., Ortiz, J., Jauregui, J., Ruiz, J. and Almonacid, R. (2015) Essential oil of Thymus vulgaris L. (thyme), its combination with EDTA against Candida albicans and formulation of a cream. An. Fac. Med., 76, 235–240.
Flores, F.C., Beck, R.C. and Da Silva, C. (2016) Essential oils for treatment for onychomycosis: a mini review. Mycopathologia, 181, 9–15.
Al-Shahrani, M.H., Mahfoud, M., Anvarbatcha, R., Athar, T. and Al Asmari, A. (2017) Evaluation of antifungal activity and cytotoxicity of Thymus vulgaris essential oil. Pharmacogn. Commn., 7, 34–40.
Pensel, P.E., Maggiore, M.A., Gende, L.B., Eguaras, M.J., Denegri, M.G. and Elissondo, M.C. (2014) Efficacy of essential oils of Thymus vulgaris and Origanum vulgare on Echinococcus granulosus. Interdisc. Persp. Infect. Dis., 2014, 693289.
Rojas, J., Palacios, O. and Palomino, M. (2015) Chemical composition and anti-Trypanosoma cruzi effect of Thymus vulgaris L. (Thyme) essential oil and its main component, thymol, in mice. Am. J. Pharm.Pharmacol., 2, 21–27.
Grespan, R., Aguiar, R.P., Giubilei, F.N., Fuso, R.R., Damião, M.J., Silva, E.L., Mikcha, J.G., Hernandes, L., Bersani Amado, C. and Cuman, R.K. (2014) Hepatoprotective effect of pretreatment with Thymus vulgaris essential oil in experimental model of acetaminophen-induced injury. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med., 2014, 954136.
Sammi, S.R., Trivedi, S., Rath, S.K., Nagar, A., Tandon, S., Kalra, A. and Pandey, R. (2017) 1-Methyl-4-propan-2-ylbenzene from Thymus vulgaris attenuates cholinergic dysfunction. Mol. Neurobiol., 54, 5468–5481.
Kim, M.J., Lee, M.J., Lee, Y.-H., Park, S.H., Kim, D., Park, C.B., Kang, J.S. and Kang, J.-K. (2017) Subchronic oral toxicity study of Acanthopanax divaricatus var. albeofructus in rats. Toxicol. Res., 33, 15–23.
Park, S.-J., Lim, K.-H., Noh, J.-H., Jeong, E.J., Kim, Y.-S., Han, B.-C., Lee, S.-H. and Moon, K.-S. (2013) Subacute oral toxicity study of Korean red ginseng extract in spraguedawley rats. Toxicol. Res., 29, 285–292.
Tisserand, R. and Young, R. (2013) Toxicity in Essential Oil Safety (2nd edition), Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier, New York, pp. 23–38.
Lahlou, M. (2004) Methods to study the phytochemistry and bioactivity of essential oils. J. Phytother. Res., 18, 435–448.
National Research Council (2011) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (8th edition), The National Academies Press, Washington.
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (2001) Acute Oral Toxicity-Acute Toxic Class Method. Guideline 423.
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (2008) Repeated Dose 28-Day Oral Toxicity Study in Rodents, Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals, Test Guideline 407.
Belvisi, M.G., Dubuis, E. and Birrell, M.A. (2011) Transient receptor potential A1 channels: insights into cough and airway inflammatory disease. Chest, 140, 1040–1047.
Tisserand, R. and Young, R. (2013) Essential oil safety in The Respiratory System (2nd edition). Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier, New York, pp. 99–110.
Lee, S.P., Buber, M.T., Yang, Q., Cerne, R., Cortés, R.Y. and Sprous, D.G. (2008) Thymol and related alkyl phenols activate the hTRPA1 channel. Br. J. Pharmacol., 153, 1739–1749.
Xu, Z.H., Wang, C., Fujita, T., Jiang, C.Y. and Kumamoto, E. (2015) Action of thymol on spontaneous excitatory transmission in adult rat spinal substantia gelatinosa neurons. Neurosci. Lett., 606, 94–99.
Jukic, M., Politeo, O., Maksimovic, M., Milos, M. and Milos, M.L. (2007) In vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibitory properties of thymol, carvacrol and their derivatives thymoquinone and thymohydroquinone. Phytother. Res., 21, 259–261.
Tisserand, R. and Young, R. (2013) Essential oil safety in The Nervous System (2nd edition). Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier, New York, pp. 131–146.
Priestley, C.M., Williamson, E.M., Wafford, K.A. and Sattelle, D.B. (2003) Thymol, a constituent of thyme essential oil, is a positive allosteric modulator of human GABAA receptors and a homo-oligomeric GABA receptor from Drosophila melanogaster. Br. J. Pharmacol., 140, 1363–1372.
Lagarto, A., Tillán, J., Bueno, V., Chávez, I., Guerra, I. and Vega, Y. (2005) Acute oral and subchronic toxicity in rats of a lyophilized aqueous extract of Ocimumtenuiflorum L. Rev. Toxicol., 22, 175–179.
Maisanaba, S., Prieto, A., Puerto, M., Gutiérrez-Praena, D., Demir, E. and Marcos, R. (2015) In vitro genotoxicity testing of carvacrol and thymol using the micronucleus and mouse lymphoma assays. Mutat. Res., 784, 37–44.
Buyukleyla, M. and Rencuzogullari, E. (2009) The effects of thymol on sister chromatid exchange, chromosome aberration and micronucleus in human lymphocytes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 72, 943–947.
Aydın, S., Başaran, A. and Başaran, N. (2005) The effects of thyme volatiles on the induction of DNA damage by the heterocyclic amine IQ and mitomycin C. Mutat. Res., 581, 43–53.
Ündeğer, Ü., Başaran, A., Degen, G.H. and Başaran, N. (2009) Antioxidant activities of major thyme ingredients and lack of (oxidative) DNA damage in V79 Chinese hamster lung fibroblast cells at low levels of carvacrol and thymol. Food Chem. Toxicol., 47, 2037–2043.
Lana-Ruiz-Cabello, M., Maisanaba, S., Puerto, M., Prieto, A.I., Pichardo, S., Jos, A. and Camean A.M. (2014) Evaluation of the mutagenicity and genotoxic potential of carvacrol and thymol using the Ames Salmonella test and alkaline, Endo IIIand FPG-modified comet assays with the human cell line Caco-2. Food Chem. Toxicol., 72, 122–128.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Rights and permissions
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Rojas-Armas, J., Arroyo-Acevedo, J., Ortiz-Sánchez, M. et al. Acute and Repeated 28-Day Oral Dose Toxicity Studies of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil in Rats. Toxicol Res. 35, 225–232 (2019). https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2019.35.3.225
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2019.35.3.225



