Abstract
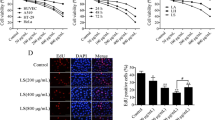
α-Curcumene is one of the physiologically active components of Curcuma zedoaria, which is believed to perform anti-tumor activities, the mechanisms of which are poorly understood. In the present study, we investigated the mechanism of the apoptotic effect of α-curcumene on the growth of human overian cancer, SiHa cells. Upon treatment with α-curcumene, cell viability of SiHa cells was inhibited > 73% for 48 h incubation. α-Curcumene treatment showed a characteristic nucleosomal DNA fragmentation pattern and the percentage of sub-diploid cells was increased in a concentration-dependent manner, hallmark features of apoptosis. Mitochondrial cytochrome c activation and an in vitro caspase-3 activity assay demonstrated that the activation of caspases accompanies the apoptotic effect of α-curcumene, which mediates cell death. These results suggest that the apoptotic effect of α-curcumene on SiHa cells may converge caspase-3 activation through the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Lobo, R., Prabhu, K.S. and Shirwaikar, A. (2009) Curcuma zedoaria Rosc, (white turmeric): a review of its chemical, pharmacological and ethnomedicinal properties. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 61, 13–21.
Moon, C.K., Park, K.S., Lee, S.H. and Yoon, Y.P. (1985) Antitumor activities of several phytopolysaccharides. Arch. Pham. Res., 8, 42–44.
Kim, K.I., Kim, J.W., Hong, B.S., Shin, D.H., Cho, H.Y., Kim, H.K. and Yang, H.C. (2000) Antitumor, genotoxicity and anticlastogenic activities of polysaccharide from Curcuma zedoaria. Mol. Cells, 10, 392–398.
Syu, W.J., Shen, C.C., Don, M.J., Ou, J.C., Lee, G.H. and Sun, C.M. (1998) Cytotoxicity of curcuminoids and some novel compounds from Curcuma doaria. J. Nat. Prod., 61, 1531–1534.
Lay, E.Y., Chyau, C.C., Mau, J.L., Chen, C.C., Lai, Y.J., Shih, C.F. and Lin, L.L. (2004) Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of the essential oil of Curcuma zedoaria. Am. J. Chin. Med., 32, 281–290.
Lu, J.J., Dang, Y.Y., Huang, M., Xu, W.S., Chen, X.P. and Wang, Y.T. (2012) Anti-cancer properties of terpenoids isolated from Rhizoma Curcumaea review. J. Ethnopharmacol., 143, 406–411.
Syed Abdul Rahman, S.N., Abdul Wahab, N. and Abd Malek, S.N. (2013) In vitro orphological assessment of apoptosis induced by antiproliferative constituents from the rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria. Evidence Based Complement Alternat. Med., 2013, 257108.
Lakshmi, S., Padmaja, G. and Remani, P. (2011) Antitumour effects of isocurcu-menol isolated from Curcuma zedoaria rhizomes on human and murine cancer cells. Int. J. Med. Chem., 253, 962–967.
Chen, W., Lu, Y., Gao, M., Wu, J., Wang, A. and Shi, R. (2011) Anti-angiogenesis effect of essential oil from Curcuma zedoaria in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol., 133, 220–226.
Ashkenazi, A. (2008) Directing cancer cells to self-destruct with pro-apoptotic receptor agonists. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 7, 1001–1012.
Elmore, S. (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol., 35, 495–516.
Li, P., Nijhawan, D., Budihardjo, I., Srinivasula, S.M., Ahmad, M., Alnemri, E.S. and Wang, X. (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell, 91, 479–489.
Liu, X., Kim, C.N., Yang, J., Jemmerson, R. and Wang, X. (1996) Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extract: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell, 86, 147–157.
Kim, M.G., Kim, J.S., Hong, J.K., Ji, M.J. and Lee, Y.K. (2003) Cytotoxic activity of the extracts from Curcuma zedoaria. Toxicol. Res., 19, 293–296.
Hong, C.H., Kim, Y.L. and Lee, S.K. (2001) Sesquiterpenoids from the rhizome of Curcuma zedoaria. Arch. Pharm. Res., 24, 424–426.
Simonsen, H.T., Andersen, A., Bremner, P., Heinrich, M., Wagner Smitt, U. and Jaroszewski, J.W. (2004) Antifungal constituents of Melicope borbonica. Phytother. Res., 18, 542–545.
Ji, M.G., Choi, J., Lee, J. and Lee, Y. (2004) Induction of apoptosis by ar-turmerone on various cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Med., 14, 253–256.
Mohammad, A.M., Yazdanparast, R. and Sanati, M.H. (2005) The cytotoxic and anti-proliferative effects of 30hydrogenkwadaphin in K562 and Jurkat cells is reduced by guanosine. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 38, 391–398.
Bhalla, R.C., Toth, K.F., Bhatty, R.A., Thompson, L.P. and Sharma, R.V. (1997) Estrogen reduces proliferation and agonist-induced calcium increase in coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol., 272, H1996–2003.
Finucanne, D.M., Bossy-Wetzel, E., Waterhouse, N.J., Cotter, T.G. and Green, D.R. (1999) Bax-induced caspase activation and apoptosis via cytochrome c release from mitochondria is inhibitable by Bcl-XL. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 2225–2233.
Steller, H. (1995) Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science, 267, 1445–1449.
Kluck, R.M., Bossy-Wetzel, E., Green, D.R. and Newmeyer, D.D. (1997) The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria : a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science, 275, 1132–1136.
Kroemer, G., Dallaporta, B. and Resche-Rigon, M. (1998) The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol., 60, 619–642.
Zamzami, N., Brenner, C., Marzo, I., Susin, S.A. and Kroemer, G. (1998) Subcellular and submitochondrial mode of action of Bcl-2 like oncoproteins. Oncogene, 16, 2265–2282.
Hsu, Y.T., Wolter, K.G. and Youle, R.J. (1997) Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-X(L) during apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 94, 3668–3672.
Rossé, T., Olivier, R., Monney, L., Rager, M., Conus, S., Fellay, I., Jansen, B. and Borner, C. (1998) Bcl-2 prolongs cell survival after Bax-induced release of cytochrome c. Nature, 391, 496–499.
Thornberry, N.A, Bull, H.G., Calaycay, J.R., Chapman, K.T., Howard, A.D., Kostura, M.J., Miller, D.K., Molineaux, S.M., Weidner, J.R., Aunius, J., Elliston, K.O., Ayala, J.M., Casano, F.J., Chin, J., Ding, G.J.F., Egger, L.A., Gaffney, E.P., Limjuco, G., Palyha, O.C., Raju, S.M., Rolando, A.M., Paul Salley, J., Yamin, T.T., Lee, T.D., Shively, J.E., Maccross, M., Mumford, R.A., Schmidt, J.A. and Tocci, M.J. (1992) A novel heterodimeric cysteine protease is required for interleukin-1 beta processing in monocytes. Nature, 356, 768–774.
Yuan, J., Shaham, S., Ledoux, S., Ellis, H.M. and Horvitz, H.R. (1993) The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell, 75, 641–652.
Decaudin, D., Marzo, I., Brenner, C. and Kroemer, G. (1998) Mitochondria in chemotherapy-induced apoptosis: a prospective novel target of cancer therapy. Int. J. Oncol., 12, 141–152.
Earnshaw, W.C., Martins, L.M. and Kaufmann, S.H. (1999) Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates and functions during apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 68, 383–424.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, Y., Lee, Y. Cytotoxic Activity from Curcuma zedoaria Through Mitochondrial Activation on Ovarian Cancer Cells. Toxicol Res. 29, 257–261 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2013.29.4.257
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2013.29.4.257