Abstract
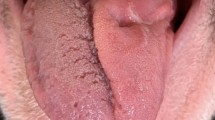
Reporting a rare scenario of hypoglossal nerve palsy in craniovertebral tuberculosis. Two patients presented in outpatient department with chief complaints of pain in neck, restricted neck movements, gait changes, difficulty in speech and weakness in all the extremities. On the basis of clinicoradiological correlation, the patients were diagnosedwithtuberculosis of C1–C2 spine. They were started on antituberculosis therapy Category 1. The patients improved clinically and there was no worsening of symptoms, but they noticed tongue deviation and hypotrophy on one side of the tongue. C1–C2 tuberculosis along with cranial nerve palsy, especially hypoglossal nerve is one of the rarest presentations. Hypoglossal nerve arises from the medulla, exits through hypoglossal canal in the base of the skull and traverses neck to supply tongue musculature. Prevertebral fascia extends from superior mediastinum to base of the skull. Abscess in this area can cause either actual compression of the hypoglossal canal or C1 and base of the skull dissociation which can lead to compression of the canal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehrotra A, Das KK, Nair AP, Kumar R, Srivastava AK, Sahu RN, et al. Pediatric cranio-vertebral junction tuberculosis: Management and outcome. Childs NervSyst 2013;29:809–14.
Chaudhary K, Potdar P, Bapat M, Mathod A, Laheri V. Structural odontoid lesions in craniovertebral tuberculosis: A review of 15 cases. Spine 2012;37:836–43.
Dhammi IK, Singh S, Jain AK. Hemiplegic/monoplegic presentation of cervical spine (C1–C2) tuberculosis. Eur Spine J 2001;10:540–4.
Fang D, Leong JC, Fang HS. Tuberculosis of the upper cervical spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1983;65:47–50.
Jain AK, Kumar S, Tuli SM. Tuberculosis of spine (C1 to D4). Spinal Cord 1999;37:362–9.
Karapurkar AP. Tuberculosis atlantoaxial disease including dislocation. Vimhans J 1988;89–98.
Lifeso R. Atlanto-axial tuberculosis in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1987;69:183–7.
Tuli SM. Tuberculosis of the craniovertebral region. ClinOrthopRelat Res 1974;104:209–12.
Greenberg HS, Deck MD, Vikram B, Chu FC, Posner JB. Metastasis to the base of the skull: Clinical findings in 43 patients. Neurology 1981;31:530–7.
Keane JR. Twelfth-nerve palsy. Analysis of 100 cases. Arch Neurol 1996;53:561–6.
Neera C, Yogesh P, Vinod P, Khwaja GA. Occipital condyle syndrome in a young male: A rare presentation of cranio-vertebral tuberculosis. J ClinDiagn Res 2014;8:MD01–3.
Wilson JD, Braunwald E, Isselbacher KJ. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 12th ed., Vol. 2. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1991. p. 1988, 1989.
Lifeso RM, Weaver P, Harder EH. Tuberculous spondylitis in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1985;67:1405–13.
Jutte PC, Van Loenhout-Rooyackers JH. Routine surgery in addition to chemotherapy for treating spinal tuberculosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;1:CD004532. Review. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;5:CD004532.
Tuli SM. Treatment of neurological complications in tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1969;51:680–92.
Hodgson AR, Francis E. Anterior spine fusion for the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg 1960;42:295–310.
Tuli SM. Results of treatment of spinal tuberculosis by “middle-path” regime. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1975;57:13–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, R., Bhayana, H., Dhammi, I.K. et al. Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy as a Rare Complication of C1–C2 Pott’s Spine. JOIO 53, 204–207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4103/ortho.IJOrtho_600_17
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/ortho.IJOrtho_600_17