Abstract
Background
Significant limb length discrepancy (LLD) after total hip arthroplasty (THA) is associated with limb, unremitting pain, neurological complications, and recurrent dislocations and has been a major cause of patient dissatisfaction and litigation against operating surgeon. The authors present a prospective study involving a double-stitch technique to prevent postoperative LLD after THA.
Materials and Methods
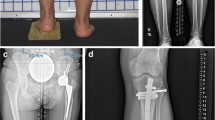
Fifty patients undergoing primary THA over a period of 2 years were included in the study and were divided into two groups of 25 each. In Group I, double-stitch technique was used for intraoperative adjustment of preoperative radiological LLD, whereas in Group II, palpation and comparison of level of patella was used for assessment of LLD. Postoperative LLD and hip outcome scores were obtained and compared.
Results
Postoperative radiological LLD (mean ± standard deviation) was 2.72 ± 2.07 mm (range −5 mm to +6 mm) in Group I and +4.28 ± 7.2 mm (range −15 mm to +12 mm) in Group II. Nine patients in Group I and 2 patients in Group II had no true clinical leg lengths discrepancy postoperatively. Postoperative radiological LLD within 5 mm could be achieved in 24 patients in Group I and in 9 patients in Group II.
Conclusion
The study indicates that double-stitch technique is a simple and effective method in reducing postoperative LLD following THA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark CR, Huddleston HD, Schoch EP 3rd, Thomas BJ. Leg-length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2006;14:38–45.
Desai AS, Dramis A, Board TN. Leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty: A review of literature. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2013;6:336–41.
Knutson GA. Anatomic and functional leg-length inequality: A review and recommendation for clinical decision-making. Part I, anatomic leg-length inequality: Prevalence, magnitude, effects and clinical significance. Chiropr Osteopat 2005;13:11.
McWilliams AB, Grainger AJ, O’Connor PJ, Redmond AC, Stewart TD, Stone MH, et al. A review of symptomatic leg length inequality following total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int 2013;23:6–14.
Harris Hip Score – Orthopaedic Scores. Available from: http://www.orthopaedicscore.com/scorepages/harris_hip_score.html. [Last accessed on 2017 Oct 09].
Nilsdotter A, Bremander A. Measures of hip function and symptoms: Harris hip score (HHS), hip disability and osteoarthritis outcome score (HOOS), oxford hip score (OHS), lequesne index of severity for osteoarthritis of the hip (LISOH), and American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS) hip and knee questionnaire. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2011;63 Suppl 11:S200–7.
Woolson ST, Hartford JM, Sawyer A. Results of a method of leg-length equalization for patients undergoing primary total hip replacement. J Arthroplasty 1999;14:159–64.
Gurney B. Leg length discrepancy. Gait Posture 2002;15:195–206.
Petis S, Howard JL, Lanting BL, Vasarhelyi EM. Surgical approach in primary total hip arthroplasty: Anatomy, technique and clinical outcomes. Can J Surg 2015;58:128–39.
Rice IS, Stowell RL, Viswanath PC, Cortina GJ. Three intraoperative methods to determine limb-length discrepancy in THA. Orthopedics 2014;37:e488–95.
Ranawat CS, Rao RR, Rodriguez JA, Bhende HS. Correction of limb-length inequality during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2001;16:715–20.
González Della Valle A, Slullitel G, Piccaluga F, Salvati EA. The precision and usefulness of preoperative planning for cemented and hybrid primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2005;20:51–8.
Jasty M, Webster W, Harris W. Management of limb length inequality during total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1996;333:165–71.
Woolson ST, Harris WH. A method of intraoperative limb length measurement in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1985;194:207–10.
Barbier O, Ollat D, Versier G. Interest of an intraoperative limb-length and offset measurement device in total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2012;98:398–404.
Naito M, Ogata K, Asayama I. Intraoperative limb length measurement in total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop 1999;23:31–3.
Papadopoulos DV, Koulouvaris P, Aggelidakis GC, Tsantes AG, Lykissas MG, Mavrodontidis A, et al. Intraoperative measurement of limb lengthening during total hip arthroplasty. Indian J Orthop 2017;51:162–7.
Halai M, Gupta S, Gilmour A, Bharadwaj R, Khan A, Holt G, et al. The exeter technique can lead to a lower incidence of leg-length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J 2015;97-B:154–9.
Hofmann AA, Bolognesi M, Lahav A, Kurtin S. Minimizing leg-length inequality in total hip arthroplasty: Use of preoperative templating and an intraoperative x-ray. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2008;37:18–23.
Knight JL, Atwater RD. Preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Quantitating its utility and precision. J Arthroplasty 1992;7 Suppl:403–9.
McGee HM, Scott JH. A simple method of obtaining equal leg length in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1985;194;269–70.
Shiramizu K, Naito M, Shitama T, Nakamura Y, Shitama H. L-shaped caliper for limb length measurement during total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004;86:966–9.
Sarin VK, Pratt WR, Bradley GW. Accurate femur repositioning is critical during intraoperative total hip arthroplasty length and offset assessment. J Arthroplasty 2005;20:887–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R., Pathak, P., Singh, R. et al. Double-Stitch Technique: A Simple and Effective Method to Minimize Limb Length Discrepancy after Total Hip Arthroplasty. JOIO 53, 169–173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4103/ortho.IJOrtho_188_18
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/ortho.IJOrtho_188_18