Abstract
Background
Osteoporosis is a major health problem in the elderly worldwide.
Aim
The aim of the present study was to evaluate and compare the effect of low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field therapy (LFPEMFT) versus low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on bone mineral density (BMD) in osteoporotic elderly.
Patients and methods
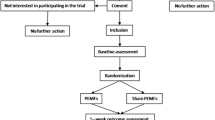
A total of 60 participants with primary osteoporosis, aged 55–65 years, were randomly allocated into three groups: the LFPEMFT group (group I; n=20), the LLLT group (group II; n=20), and the control group (group III; n=20). Each treatment regimen was applied for 30 min, three times weekly for 3 months on the lumbar region. BMD was evaluated using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.
Results
There were significant increases in BMD in groups I and II, whereas there was a nonsignificant increase in group III (P<0.001, 0.001, and 0.14 for groups I, II, and III, respectively). Between groups, there were significant differences in BMD but in favor of group I (P<0.001). The mean values and percentages of change in BMD were −1.94±0.76 and 39.48%, −2.63±0.49 and 16.79%, and −3.19±0.54 and 0.79% in groups I, II, and III, respectively.
Conclusion
LFPEMFT and LLLT are useful therapeutic procedures to increase BMD in osteoporotic elderly. Furthermore, LFPEMFT is more effective than LLLT in increasing BMD in the elderly with primary osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanis JA, McCloskey EV, Johansson H, Cooper C, Rizzoli R, Reginster JY. European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 2013; 24:23–57.
Riggs BL, Melton LJ. Evidence for two distinct syndromes of involutional osteoporosis. Am J Med 1983; 75:899–901.
Cummings SR, Melton LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet 2002; 359:1761–1767.
Liu H, Yang L, He H, Zhou J, Liu Y, Wang C, et al. The hemorheological safety of pulsed electromagnetic fields in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis in southwest China: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2013; 55:285–295.
Cooper C, Compion G, Melton LJ. Hip fractures in the elderly: a worldwide projection. Osteoporos Int 1992; 2:285–289.
Nikander-Sievänen H, Heinonen A, Daly RM, Uusi-Rasi K, Kannus P. Targeted exercise against osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis for optimizing bone strength throughout life. BMC Med 2010; 8:47–23.
Ringe J, Faber H, Farahm P, Dorst A. Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis: results of a 1-year study. Rheumatol Int 2006; 26:427–443.
Rizzoli R, Reginster JY, Boonen S, Breart G, Diez-Perez A, Felsenberg D, et al. Adverse reactions and drug-drug interactions in the management of women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int 2011; 89:91–104.
Riggs BL, Melton LJ. The worldwide problem of osteoporosis: insights afforded by epidemiology. Bone 1995; 17:505S–511S.
Bassett CA. Fundamental and practical aspects of therapeutic uses of pulsed electromagnetic fields. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 1989; 17:451–459.
Garland DE, Adkins RH, Matsuno NN, Stewart CA. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields on osteoporosis at the knee in individuals with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 1999; 22:239–245.
Jing D, Shen G, Huang J, Xie K, Cai J, Xu Q, et al. Circadian rhythm affects the preventive role of pulsed electromagnetic fields on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Bone 2010; 46:487–495.
Boeriu S. The effects of low-level laser therapy on osseointegration of dental implants. Act Medica Marisiensis 2010; 56:3–6.
Khadra M, Lyngstadaas SP, Haanaes HR, Mustafa K. Effect of laser therapy on attachment, proliferation, and differentiation of human osteoblast-like cells cultured on titanium implant material. Biomaterials 2005; 26:3503–3509.
Saracino S, Mozzati M, Martinasso G, Pol R, Canuto RA. Muzio GSuper-pulsed laser irradiation increases osteoblast activity via modulation of bone morphogenetic factors. Lasers Surg Med 2009; 41:298–304.
Glazer PA, Heilman MR, Lotz JC, Bradford DS. Use of electromagnetic fields in a spinal fusion. Spine 1997; 20:2351–2356.
Gossling HR, Bernstein RA, Abbott J. Treatment of ununited tibial fractures: a comparison of surgery and pulsed electromagnetic fields. Orthopedics 1992; 15:711–719.
Yamada S, Guenther HL, Fleisch H. The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone cell metabolism and calvaria resorption in vitro, and on calcium metabolism in the live rat. Int Orthop 1985; 9:129–134.
Riggs BL, Melton LJ. Involutional osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 1986; 314:1676–1686.
Sert C, Mustafa D, Düz MZ, Akşen F, Kaya A. The preventive effect on bone loss of 50 Hz, 1-mT electromagnetic field in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Metab 2002; 20:345–349.
Tsai MT, Chang WH, Chang K, Hou RJ, Wu TW. Pulsed electromagnetic fields affect osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in bone tissue engineering. Bioelectromag 2007; 28:519–528.
Chang WH, Chen LT, Sun JS, Lin FH. Effect of pulse-burst electromagnetic field stimulation on osteoblast cell activities. Bioelectromag 2004; 25:457–465.
Darendeliler M, Darendeliler A, Sinclair P. Effects of static magnetic and pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone healing. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg 2005; 12:43–53.
Richard H, Thomas M, Nurdan O. Electromagnetic effects –from cell biology to medicine. Prog Histochem Cytochem 2008; 43:177–186.
Icaro-Cornaglia A, Casasco M, Riva F, Farina A, Fassina L, Visai L, Casasco A. Stimulation of osteoblast growth by an electromagnetic field in a model of bone-like construct. Eur J Histochem 2006; 50:199–204.
Selvam R, Ganesan K, Narayana Raju KV, Gangadharan AC, Manohar BM, Puvanakrishnan R. Low frequency and low intensity pulsed electromagnetic field exerts its anti-inflammatory effect through restoration of plasma membrane calcium ATPase activity. Life Sci 2007; 80:2403–2410.
Goodwin T. Physiologic and molecular genetic effects of time-varying electromagnetic fields on human neuronal cells. NASA/TP-2003-212054. Houston, TX, United States: Lyndon B Johnson Space Center; 2003.
Byerly D, Sognier M, Arndt D, Ngo P, Phan C, Byerly K, Weinstein R. Pulsed electromagnetic fields –a countermeasure for bone loss and muscle atrophy. Space Life Sciences. NASA/TP-2003-212054. Houston, TX, United States: Biennial Research and Technology, NASA Johnson Space Center; 2003.
Pires-Oliveira DA, Oliveira RF, Amadei SU, Pacheco-Soares C, Rocha RF. Laser 904nm action on bone repair in rats with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 2010; 21:2109–2114.
Dörtbudak O, Haas R, Mailath-Pokorny G. Biostimulation of bone marrow cells with a diode soft laser. Clin Oral Impl Res 2000; 11:540–545.
Diniz JS, Nicolau RA, de Melo-Ocarino N, do Carmo-Magalhaes F, de Oliveira-Pereira RD, Serakides R. Effect of low-power gallium aluminum-asenium laser therapy (830 nm) in combination with bisphosphonate treatment on osteopenic bone structure: an experimental animal study. Lasers Med Sci 2009; 24:347–352.
Saad A, El Yamany M, Abbas O, Yehia M. Possible role of low-level laser therapy on bone turnover in ovariectomized rats. Endocr Regul 2010; 44:155–163.
Patrocínio-Silva TL, de Souza AM, Goulart RL, Pegorari CF, Oliveira JR, Fernandes K, et al. The effects of low-level laser irradiation on bone tissue in diabetic rats. Lasers Med Sci 2014; 29:1357–1364.
Petri AD, Teixeira LN, Crippa GE, Beloti MM, de Oliveira PT, Rosa AL. Effects of low-level laser therapy on human osteoblastic cells grown on titanium. Braz Dent J 2010; 21:491–498.
Bashardoust-Tajali S, Macdermid JC, Houghton P, Grewal R. Effects of low power laser irradiation on bone healing in animals: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 2010; 4:5–11.
Garavello-Freitas I, Baranauskas V, Joazeiro P. Low-power laser irradiation improves histomorphometrical parameters and bone matrix organization during tibia wound healing in rats. J Photochem Photobiol 2003; 70:81–89.
Zati A, Valent A. Laserterapia in medicina. In: Terapia Fisica: Nuove Tecnologie in Medicina Riabilitativa. Edizioni Minerva Medica 2006; 162–185
Monici M, Cialdai F, Fusi F, Romano G, Pratesi R. Effects of pulsed Nd: YAG laser at molecular and cellular level. A study on the basis of Hilterapia. Proceeding of the International Meeting on Hilterapia; Venice; 2008.
Bossini P, Rennó A, Ribeiro D, Fangel R, Peitl O, Zanotto E, Parizotto N. Biosilicate and low-level laser therapy improve bone repair in osteoporotic rats. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2011; 5:229–237.
Bossini P, Rennó A, Ribeiro D, Fangel R, Ribeiro A, Lahoz-Mde A, Parizotto N. Low-level laser therapy (830nm) improves bone repair in osteoporotic rats: similar outcomes at two different dosages. Exp Gerontol 2012; 47:136–142.
Renno A, McDoneell P, Parizotto N, Laakso E. The effects of laser irradiation on osteoblast and osteosarcoma cell proliferation on differentiation in vitro. Photomed Laser Surg 2007; 25:275–280.
Parenti SI, Panseri S, Gracco A, Sandri M, Tampieri A, Bonetti GA. Effect of low-level laser irradiation on osteoblast-like cells cultured on porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds. Ann Ist Super Sanità 2013; 49:255–260.
Stein A, Benayahu D, Maltz L, Oron U. Low-level laser irradiation promotes proliferation and differentiation of human osteoblasts in vitro. Photomed Laser Surg 2005; 23:161–166.
Liu X, Lyon R, Meier H, Thometz J, Haworth S. Effect of lower-level laser therapy on rabbit tibial fracture. Photomed Laser Surg 2007; 25:487–494.
Coombe AR, Ho CT, Darendeliler MA, Hunter N, Philips JR, Chapple CC. The effects of low-level laser irradiation on osteoblastic cells. Clin Orthod Res 2001; 4:3–14.
Pires-Oliveira DA, de Oliveira RF, Zangaro RA, Soares CP. Evaluation of low-level laser therapy of osteoblastic cells. Photomed Laser Surg 2008; 26:401–404.
Renno AC, de-Moura FM, dos-Santos NS, Tirico RP, Bossini PS, Parizotto NA. Effects of 830 nm laser, light on preventing bone loss after ovariectomy. Photomed Laser Surg 2006; 24:642–645.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work noncommercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelaal, A.A.M., Taha, M.M., Amin, D.I. et al. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic therapy versus low-level laser therapy on bone mineral density in the elderly with primary osteoporosis: a randomized, controlled trial. Bull Fac Phys Ther 22, 34–39 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4103/bfpt.bfpt_58_16
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/bfpt.bfpt_58_16