Abstract
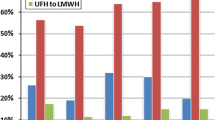
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is one of the most common preventable cause of morbidity and mortality after trauma. Though most of the western countries have their guidelines for thromboprophylaxis in these patients, India still does not have these. The increasing detection of VTE among Indian population, lack of awareness, underestimation of the risk, and fear of bleeding complications after chemical prophylaxis have made deep vein thrombosis (DVT) a serious problem, hence a standard guideline for thromboprophylaxis after trauma is essential. The present review article discusses the incidence of DVT and role of thromboprophylaxis in Indian patients who have sustained major orthopedic trauma. A thorough search of ‘PubMed’ and ‘Google Scholar’ revealed 10 studies regarding venous thromboembolism in Indian patients after major orthopedic trauma surgery (hip or proximal femur fracture and spine injury). Most of these studies have evaluated venous thromboembolism in patients of arthroplasty and trauma. The incidence, risk factors, diagnosis and management of VTE in the subgroup of trauma patients (1049 patients) were separately evaluated after segregating them from the arthroplasty patients. Except two studies, which were based on spinal injury, all other studies recommended screening/ thromboprophylaxis in posttraumatic conditions in the Indian population. Color Doppler was used as common diagnostic or screening tool in most of the studies (eight studies, 722 patients). The incidence of VTE among thromboprophylaxis-receiving group was found to be 8% (10/125), whereas it was much higher (14.49%, 40/276) in patients not receiving any form of prophylaxis. Indian patients have defnite risk of venous thromboembolism after major orthopedic trauma (except spinal injury), and thromboprophylaxis either by chemical or mechanical methods seems to be justifed in them.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geerts WH, Code KI, Jay RM, Chen E, Szalai JP. A prospective study of venous thromboembolism after major trauma. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1601–6.
Morgan SJ, Jeray KJ, Laura SP. Attitude of Orthopedic trauma surgeons regarding current controversies in management of pelvic and acetabular fracture. J Orthop Trauma 2001;15:526–32.
Todi SK, Sinha S, Chakraborthy A, Sarkar A, Gupta S, Das T, et al. Utilisation of deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis in medical/surgical intensive care units. Indian J Crit Care Med 2003;7:103–5.
Leizorovicz A, TurpieAG, Cohen AT, Pellois A, Diebolt P, Darmon JY. Epidemiology of post-operative venous thromboembolismm in Asian countries. Int J Angiol 2004;13:101–8.
Lee AD, Stephen E, Agarwal S, Premkumar P. Venous thrombo-embolism in India. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2009;37:482–5.
Kakkar N, Vasishta RK. Pulmonary embolism in medical patients: An autopsy-based study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2008;14:159–67.
Dhillon KS, Askander A, Doraisamy S. Postoperative deep-vein thrombosis in Asian patients is not a rarity. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1996;78:427–30.
Piovella F, Wang CJ, Lu H, Lee K, Lee LH, Lee WC, et al. Deep venous thrombosis rates after major Orthopedic surgeries in Asia. An epidemiological study based on postoperative screening with centrally adjusted bilateral Venography. J Thromb Haemostat 2005;3:2664–70.
Wang CJ, Wang JW, Weng LH, Haung CC, Yu PC. Clinical significance of muscular deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. Chang Gung Med J 2007;30:41–5.
Shead GV, Narayanan R. Incidence of postoperative venous thromboembolism in south India. Br J Surg 1980;67:813–4.
Sharma H, Maini L, Agrawal N, Upadhyay A, Vishwanath J, Dhaon BK. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis in patients with fractures around hip joint: A prospective study. Indian J Orthop 2002;36:5.
Agarwala S, Wadhwani R, Modhe JM, Bhagwat AS. Screening for deep venous thrombosis in postoperative orthopaedic patients: Comparison of color Doppler sonography and contrast venography. Indian J Orthop 2002;36:4.
Agarwala S, Bhagwat A, Modhe J, Dastur FD, Patil S. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis in Indian patients: A prospective study in 104 patients. Indian J Orthop 2003;37:2.
Agarwala S, Bhagwat AS, Modhe J. Deep vein thrombosis in Indian patients undergoing major lower limb surgery. Indian J Orthop 2003;65:159–62.
Agarwala S, Bhagwat AS, Wadhwani R. Pre and postoperative DVT in Indian patients- Efficacy of LMWH as a prophylaxis agent. Indian J Orthop 2005;39:55–8.
Leizorovicz A, Turpie AG, Cohen AT, Wong L, Yoo MC, Dans A; SMART Study Group. Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in Asian patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery without thromboprophylaxis. The SMART Study. J Thromb Haemost 2005;3:28–34.
Maini PS, Talwar N, Nijhawan VK, Dhawan M. Results of cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty for fracture of the femoral neck-10 year study. Indian J Orthop 2006;40:154–6.
Nandi PL, Li WS, Leung R, Chan J, Chan HT. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in chinese population. Hong Kong Med J 1998;4:305–10.
Sudo A, Sano T, Horikawa T, Yamakawa T, Shi D, Uchida A. The incidence of deep vein thrombosis after hip and knee arthroplasties in Japanese patients: A prospective study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2003;11:174–7.
Jain V, Dhal AK, Dhaon BK. Deep vein thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty in Indian patients with and without Enoxaparin. J Orth Surg 2004;12:173–7.
Mavalankar AP, Majmundar D, Sudha R. Routine chemoprophylaxis for DVT in Indian patients. Indian J Orthop 2007;41:188–91.
Wells PS, Lensing AW, Davidson BL, Prins MH, Hirsh J. Accuracy of ultrasound for the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis in asymptomatic patients after Orthopedic surgery: A meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 1995;122:47–53.
Agarwal NK, Mathur N. Deep vein thrombosis in acute spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2009:47;769–72
Bhan S, Dhaon BK, Gulati Y, Aggarwal S. Deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis - a multicentric study. Indian J Orthop 2004;38:178–82.
Saraf SK, Rana RJ, Sharma OP. Venous thromboembolism in acute spinal cord injury patients. Indian J Orthop 2007;41:194–7.
Bagaria V, Modi N, Panghate A, Vaidya S. Incidence and risk factors for development of venous thromboembolism in Indian patients undergoing major orthopaedic surgery: Results of a prospective study. Postgrad Med J 2006;82:136–9.
Rajagopalan N. Thromboprophylaxis by daletaparin sodium in elective major orthopaedic surgery. Indian J Orthop 2003;37:94–97.
Virchow R (translated by Chance F)(translator). Cellular Pathology. New York: Dewitt; 1860.
Geerts WH, Pieno GF, Heit JA, Bergquist D. The seventh ACCP conference on anti thrombotic and thrombolytic therapy. Chest 2004;126:338–400.
Montgomery KD, Geerts WH, Potter HG, David L, Helfet DL. Practical management of venous thromboembolism following pelvic fracture. Orthop Clin North Am 1997;28:397–404.
Miller RS, Weatherford DA, Stein D, Crane MM, Stein M. Antithrombin III and trauma patients: Factors that determine low levels. J Trauma 1994;37:442–5.
Napolitano LM, Garlapati VS, Heard SO, Silva WE, Cutler BS, O’Neill AM, et al. Asymptomatic deep venous thrombosis in the trauma patient: Is an aggressive screening protocol justified? J Trauma 1995;39:651–7.
Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, Heit JA, Samama CM, Lassen MR, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest 2008;133:381S-453.
Singh AP, Sigh AP, Mahajan S. Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis following soft tissue trauma. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2009;43:376–8.
Montgomery KD, Potter HG, Helfet DL. Magnetic resonance Venography to evaluate the deep venous system of the pelvis in patients who have an acetabular fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77:1639–49.
Stannard JP, Riley RS, McClenney MD, Lopez-Ben RR, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. Mechanical prophylaxis against deep-vein thrombosis after pelvic and acetabular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2001;83:1047–51.
Knudson MM, Collins JA, Goodman SD, McCrory DW. Thromboembolism following multiple trauma. J Trauma 1992;32:2–11.
Brathwaite CE, OMalley KF, Ross SE, Pappas P, Alexander J, Spence RK. Continuous pulse oxymetry and the diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism in critically ill trauma patients. J Trauma 1992;33:528–30.
Lensing AW, Prandoni P, Brandjes D. Detection of deep vein thrombosis by real-time B-mode ultrasonography. N Engl J Med 1989;320:342–5.
Carpenter JP, Holland GA, Baum RA, Owen RS. Magnetic resonance Venography for detection of venous thrombosis, comparison with contrast venography and duplex ultrasonography. J Vasc Surg 1993;18:734–41.
Parakh R, Kakkar VV, Kakkar AK. Managemnt of venous thromboembolism. J Assoc Physicians India 2007;55:49–70.
Parakh R, Somaya A, Todi SK, Iyengar SS. Consensus development recommendations for the Role of LMWHs in prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism: An Indian Perspective. J Assoc Physicians India 2007;55:5–30.
Dutta TK, venugopal V. Venous thromboembolism: The intricacies. J Postgrad Med 2009;55:55–64.
Nagi ON, Dhillon MS, Katariya S, Mayeeb SM. Deep vein thrombosis after major surgery-evaluation by compression ultrasonography. ArchJ Orthop 1999;33:200–3.
Moser KM, Lemoine Jr. Is embolic risk conditioned by location of deep venous thrombosis? Ann Intern Med 1981;91:439–44.
Geerts WH, Code KI, Jay R, Montgomery KD. A comparison of low dose heparin with low moleculr weight heparin in prophylaxis against venous thromboembolismm after major trauma. N Eng J Med 1996;335:701–7.
Montgomery KD, Geerts WH, Code KI. Thromboembolic complications in patients with pelvic trauma. Clin Orthop 1996;329:68–87.
Kim YH, Kim JS. Incidence and natural history of deep-vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2002;84:566–70.
Kim YH, Oh SH, Kim JS. Incidence and natural history of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty. A prospective and randomised clinical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2003;85:661–5.
Haas SB, Tribus CB, Insall JN, Becker MW, Windsor RE. The significance of calf thrombi after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1992;74:799–802.
Stein PD, Kayali F, Olson RE, Milford CE. Pulmonary thromboembolism in Asians/Pacific islanders in the United States: Analysis of data from the National Hospital Discharge Survey and the United States Bureau of the Census. Am J Med 2004;116:435–42.
Dennis JW, Menawat S, Von Thron J, Fallon WF Jr, Vinsant GO, Laneve LM, et al. Efficacy of deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis in trauma patients and identification of high-risk groups. J Trauma 1993;35:132–8.
Burns GA, Cohn SM, Frumento RJ, Degutis LC, Hammers L. Prospective ultrasound evaluation of venous thrombosisin high-risk trauma patients. J Trauma 1993;35:405–8.
Comerota AJ, Katz ML, White JV. Why does prophylaxis with external pneumatic compression for deep vein thrombosis fail? Am J Surg 1992;164:265–8.
Brathwaite CE, Mure AJ, O’Malley KF, Spence RK, Ross SE. Complications of anticoagulation for pulmonary embolism in low risk trauma patients. Chest 1993;104:718–20.
Ruiz AJ, Hill SL, Berry RE. Heparin, deep venous thrombosis and trauma patients. Am J Surg 1991;162:159–62.
Steel N, Dodenhoff RM, Ward AJ. Thromboprophylaxis in pelvic and acetabular trauma surgeries. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2005;87:209–12.
Hirsh J. Heparin and low moleculr weight heparin. The seventh ACCP conference on anti Thrombotic and thrombolytic therapy. Chest 2004;126:1885–2035.
Lensing AW, Davidson BL, Prins MH. Treatment of deep venous thrombosis with low moleculr weight heparin: A meta-analysis. Arch Int Med 1995;155–601.
Levine M, Gent M, Hirsh J, Leclerc J, Anderson D, Weitz J, et al. A comparison of low molecular-weight heparin administered primarily at home with heparin administered in the hospital for proximal deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med 1996;334:677–81.
Kearon C, Kahn SR, Agnelli G, Goldhaber S, Raskob GE, Comerota AJ; American College of Chest Physicians. Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest 2008;133(6 Suppl):454S–545.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, R.K., Tripathy, S.K. & Singh, A.K. Is routine thromboprophylaxis justified among Indian patients sustaining major orthopedic trauma? A systematic review. IJOO 45, 197–207 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.80037
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.80037